Lecture 31 - McMaster Physics and Astronomy
advertisement

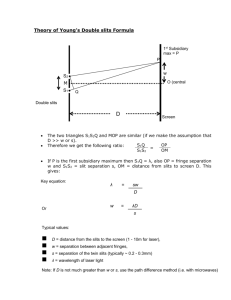
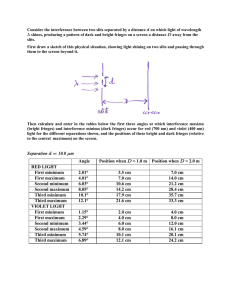
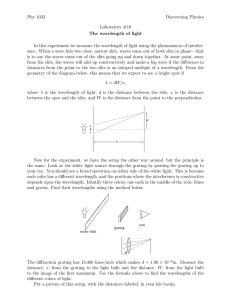
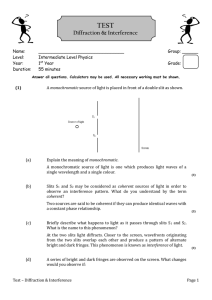
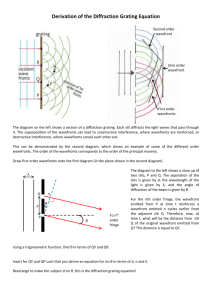
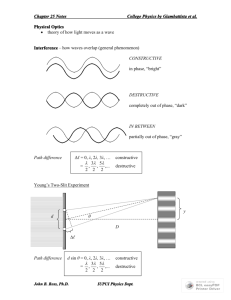
Physical Optics Ch 37 and 38 Physical Optics Light is an electromagnetic wave. Wave properties: Diffraction – wave bends around corners, spreads out from narrow slits Interference – waves from two or more sources interfere Electromagnetic Waves E , B, v all Eo E B v Usually we keep track of the electric field E : E( x, t ) Eo sin( kx t ) amplitude The Electromagnetic Spectrum l (m) 300 3 3 x 10-3 10-6 3x 7 x 10-7 4 x 10-7 3x 10-9 3x 10-12 f (Hz) Radio TV Microwave Infrared Visible Ultraviolet X rays g rays 106 108 1011 1014 5x1014 1017 1020 Infrared Red 780 nm Yellow 600 nm Green 550 nm Blue 450 nm Violet Ultraviolet 380 nm Infrared Red l 780 nm Yellow 600 nm Green 550 nm Blue 450 nm Violet Ultraviolet 380 nm Visible-Light Spectrum The EM Spectrum Coherent sources are sources that have a constant phase difference between them (lasers). In phase sources are sources that have zero phase difference between them. Monochromatic sources have the same wavelength. Plane waves mean the wavefronts are planes Wavefronts are surfaces on which we have only crests, or troughs for example. Double Slit (Thomas Young, 1801) θ incident light,plane waves Two slits, separation d m=2 m=1 m=0 m=-1 m=-2 screen Result: Many bright and dark fringes or lines on the screen: The slits act as sources of light in phase. Due to diffraction, the light spreads out after it passes through each slit. When the two waves arrive together at some point P on the screen, they are out of phase, due to the difference in the length of the paths. This path difference varies from place to place on the screen. P x1 x2 d q x x2 x1 d sin q screen Constructive Interference: (bright fringe) Δx = mλ, or d sin θ = mλ, m = 0, 1, 2, … Destructive Interference: (dark fringe) Δx = (m + ½)λ, or d sin θ = (m + ½) λ, m = 0, 1, 2, … Example 1 2 slits, 0.20 mm apart; red light (l = 667 nm) y 0 3m screen Where are a) the m=0,1 bright fringes? b) m=0,1 dark fringes? (give values of y) Solution Example 2 2 slits, red light (l = 690 nm) y 50 cm 0 screen If the distance between the first and the third minima in the diffraction pattern is 3.0mm, what is the width of the slit? Solution Quiz Which of the following would cause the separation between the fringes on the screen to decrease? (There may be more than one answer.) A) B) C) D) E) F) Increasing the wavelength Decreasing the wavelength Moving the slits closer together Moving the slits farther apart Moving the screen further from the slits Moving the screen closer to the slits Test Discussion