TEST Diffraction & Interference
advertisement

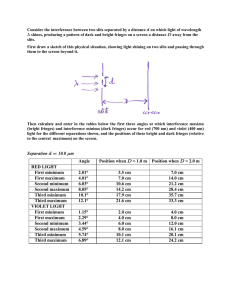
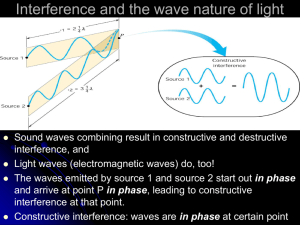
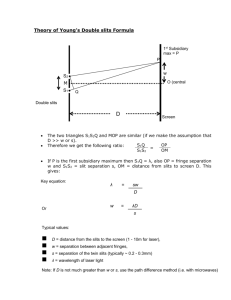
TEST Diffraction & Interference Name: Level: Year: Duration: ________________________________ Intermediate Level Physics 1st Year 55 minutes Group: ______ Grade: Answer all questions. Calculators may be used. All necessary working must be shown. (1) A monochromatic source of light is placed in front of a double slit as shown. (a) Explain the meaning of monochromatic. A monochromatic source of light is one which produces light waves of a single wavelength and a single colour. (b) Slits S1 and S2 may be considered as coherent sources of light in order to observe an interference pattern. What do you understand by the term coherent? Two sources are said to be coherent if they can produce identical waves with a constant phase relationship. (c) (3) Briefly describe what happens to light as it passes through slits S 1 and S2. What is the name to this phenomenon? At the two slits light diffracts. Closer to the screen, wavefronts originating from the two slits overlap each other and produce a pattern of alternate bright and dark fringes. This phenomenon is known as interference of light. (d) (3) (3) A series of bright and dark fringes are observed on the screen. What changes would you observe if: Test – Diffraction & Interference Page 1 (i) S1 and S2 are moved closer together, More fringes with a wider fringe spacing are observed. (ii) (2) the slits are kept the same distance apart, but made wider, The number of observable fringes decreases and fringes appear brighter. (2) (iii) white light replaces the monochromatic source? All colours of the visible spectrum show up on all bright bands except for the central bright fringe. Violet is deviated least so it appears closer to the central bright band. (2) (2) Microwaves pass through two slits as shown. A detector is moved along the line XY and detects a series of maxima and minima. (a) Explain, in terms of phase difference, the condition which must be satisfied in order for the detector to detect: (i) a maximum, For a maximum, constructive interference should take place with waves meeting in phase. This happens if the path difference between the two interfering waves equals an integral multiple of wavelengths. (ii) a minimum along XOY. For a minimum, destructive interference should take place with waves meeting out of phase. This happens if the path difference between the two interfering waves equals half multiple of wavelengths. (b) (3) (3) Assuming that microwaves of wavelength 3cm are incident on a double-slit with slit separation 0.1cm, calculate how far should a screen be placed from the double-slit if two cosecutive bright fringes are to be separated by 2cm. 𝑦= 𝐷 𝑑 3𝐷 2= 0.1 𝐷 = 0.067𝑐𝑚 Test – Diffraction & Interference (4) Page 2