Portfolio Submission Form
advertisement

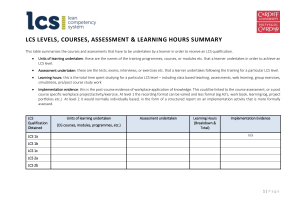
WWW.LEANCOMPETENCY.ORG ACCREDITATION SUBMISSION FORM Standard Accreditation HOW TO COMPLETE: 1 Replace the instructions and guidance text in the grey shaded boxes with your response for each section; attach or embed supporting documents where appropriate. When this form is a working document, you can provide an indication of how complete each section is by selecting one of six items from the drop down box next to section completion status (default value is 0%) State if the information required is not applicable in your circumstances. Note that several tables, forms and templates that need to be completed are embedded in this document and can be opened and used. These are also available on the LCS website. Refer to the GUIDE TO ACCREDITATION for more information on the accreditation process. ORGANISATION DETAILS Section completion status: 0% 1.1 ORGANISATION NAME The organisation entity that will be accredited. This could be the organisation itself or a specific department or entity, such as a training academy or function. 1.2 PORTFOLIO AUTHOR The person responsible for writing the submission and to whom queries and comments can be addressed. 2 BACKGROUND & CONTEXT Section completion status: 0% 2.1 ORGANISATION BACKGROUND INFORMATION A brief description of the organisation, indicating main products/services and activities, size (eg turnover, employees), location(s) and any relevant strategic information. 1|Page LCS ACCREDITATION SUBMISSION FORM 2.2 ORGANISATION’S USE OF THE LCS Statement of how the organisation proposes using the LCS as part of its lean/CI training and/or commercial activities. For example, this could be for staff training or for training clients’ staff. If there is an international dimension to the training, then this should be detailed here 2.3 LEAN TRAINING SYSTEM STRUCTURE & COMPONENTS Explanation of the structure of the training organisation – ie position within overall organisation, department, main roles, training programme responsibilities Description of the main components of the lean training system – ie number of courses, course hierarchy 2.4 INTEGRATION OF LEARNING WITH PRACTICAL APPLICATION Describe the training system’s approach to ensuring that knowledge gained through training is applied by the learner in the organisation to provide a business improvement. For example, this may be achieved through a practical dimension in assessments or through integrating CI activity in personal development planning. 2.5 LCS LEVELS TO WHICH TRAINING SYSTEM ALIGNED List of the LCS levels to which the training system aims to align. Note that there may be a plan to increase the number of levels over time as the training system matures. 2.6 CERTIFICATES ISSUED PER YEAR An estimate of certificates issued per year over the accreditation period 3 COURSE DESCRIPTIONS, AIMS & LEARNING OUTCOMES Section completion status: 0% 3.1 COURSES DETAILS A list course titles, their aims and learning outcomes. The aims are the broad goals or purpose of the course, while the learning outcomes state what the participants should know and/or be able to do at the end of a particular course of training. See the LCS Guide to Developing Learning Outcomes. A timetable of proposed courses to be delivered over the accreditation period could be provided, if available or relevant. 3.2 LIST OF TOPICS COVERED A list of the topics covered in courses. 3.3 LEARNING TIME Detail the overall contact hours, how these are organised or spread over a particular time period (eg 15 hours on 3 separate days spread over 2 months). © Lean Competency System 2|Page LCS ACCREDITATION SUBMISSION FORM Indicative learning hours for each LCS level are indicated below, though these should be used as a guide only. Note that this includes class based face-to-face teaching time, post course activities, assessments, self-study, follow up reading and research, work based learning. 4 LCS 1a: 3 to 6 hours (the latter typically with activities, simulations) LCS 1b: 40 hours LCS 1c: 40 hours LCS 2a: 50 hours LCS 2b: 25 hours ALIGNMENT Section completion status: 0% 4.1 NARRATIVE EXPLAINING ALIGNMENT A description indicating how the organisation’s training programme aligns with the Lean Competency System. This should include details of how courses, modules, learning units relate to the lean competency levels. The organisation will need to reference the LCS Level Detailed Descriptions which specify the precise expectations regarding the knowledge and practical ability for each level. Appendix I contains the LCS framework and summarises the key knowledge components of each LCS level. More details on level descriptions are on the LCS website. 4.2 LCS ALIGNMENT MATRIX An alignment matrix shows how the training links to the levels of lean competency. A copy of the matrix is embedded1 below. Word and Excel versions are available – the latter are for larger or more complex systems. ☐ Check box to indicate an alignment matrix is attached or ☐ Check box to indicate an alignment matrix is embedded below Embed document here -> (blank template attached) 5 Microsoft Excel Microsoft Word 97 97-2003 Worksheet 2003 Document TRAINING MATERIAL Section completion status: 0% 5.1 TRAINING MATERIAL SOURCE & DEVELOPMENT A statement of how the training material has been sourced and developed. 1 To embed a file in this document 1) copy the file icon ; 2) place cursor in destination location; 3) Click paste special; 4) select Microsoft Excel/Word Worksheet Object and check Display as Icon; 5) Click OK © Lean Competency System 3|Page LCS ACCREDITATION SUBMISSION FORM 5.2 TRAINING MATERIAL EXAMPLES Provide representative examples of presentations, workbooks, guides and other handouts used in courses. ☐ Check box to indicate example materials are attached or ☐ Check box to indicate example materials are embedded below Embed documents here -> List the documents attached or embedded in the box below: 5.3 TEACHING STYLE Describe the teaching style employed - eg lectures, workshops, level of interaction, practical exercises, linkage to workplace activities etc. 5.4 PRACTICAL ACTIVITIES Describe any practical activities used in teaching. 6 ASSESSMENT Section completion status: 0% 6.1 OVERALL ASSESSMENT APPROACH An explanation of the assessment approach that will be used by the training system, indicating how knowledge will be assessed and ensuring that learning outcomes have been achieved. The assessment approach should ensure it is consistent with some key underlying principles underpinning the LCS, namely: 6.2 There should be a knowledge test for each LCS level where a certificate is awarded There should be implementation evidence linked to courses and assessment (except 1a) An appropriate course of training should be delivered for each LCS level where a certificate is awarded TYPES OF ASSESSMENTS A list of the type of assessments that are used by the training system – eg multiple choice tests (Inc. on line), exams, interviews, group projects, A3 reports, project implementation reports etc. Where multiple choice tests are being used, these will typically be 50 questions in length for each level (though less for LCS 1a – typically up to 25 questions). See the LCS Guide to Developing Multiple Choice Tests on the LCS Website. 6.3 ASSESSMENT EXAMPLES © Lean Competency System 4|Page LCS ACCREDITATION SUBMISSION FORM Provide examples of assessments – eg multiple choice questions and answers, exam questions, interview guides etc ☐ Check box to indicate example assessments are attached or ☐ Check box to indicate example assessments are embedded below Embed documents here -> 6.4 PASS MARKS & RESITS Detail the policy relating to pass marks and re-sitting tests after test failure. Note that the pass mark for a typical multiple choice test (without negative marking) should be at least 66%. After failing a multiple choice test a learner would usually be allowed one further attempt. If that is failed, then the learner would usually be required to have further training input before a third attempt was permitted. 6.5 QUESTION BANKS The training system should contain a bank of test questions for use in multiple choice tests and exams Questions for tests should be rotated on a regular basis. 6.6 ASSESSMENT ADMINISTRATION Describe how assessments are administered – for example, invigilated timed, tests, or taken on line via a learning system. 6.7 USE OF IT IN ASSESSMENTS How IT is used as in assessments. 6.8 REVIEW & CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT OF ASSESSMENTS A statement of the approach taken to reviewing and continuously improving assessments – eg method, frequency, who involved, etc. 6.9 COURSES ASSESSMENT & LEARNING HOURS SUMMARY Complete the table (embedded below) that summarises the units of learning and assessments that have to be undertaken by a learner in order to receive an LCS qualification, along with the expected learning hours involved. ☐ Check box to indicate that an LCS LEVELS, COURSES, ASSESSMENT & LEARNING HOURS SUMMARY table is attached or ☐ Check box to indicate a LCS LEVELS, COURSES, ASSESSMENT & LEARNING HOURS SUMMARY table are embedded below © Lean Competency System 5|Page LCS ACCREDITATION SUBMISSION FORM Embed document here (blank template attached) Microsoft Word 97 2003 Document 6.10 LINKAGE OF TRAINING WITH WORKPLACE APPLICATION [Applies to LCS level 1] Describe the approach that provides linkage of course work with the application of tools and techniques in the workplace. For example, there may be mechanisms to record post course implementation activities and any linkage with personal development planning. 6.11 FORMAL MECHANISMS TO ASSESS IMPLEMENTATION PROJECTS [Applies to LCS level 2] Describe the approach for the assessment of Level 2 implementation projects (see notes below). 6.12 NOTES ON ASSESSMENT 6.12.1 Knowledge Element Note that learners need to undertake a knowledge test for each LCS level through which they progress. 6.12.2 Practical Element – Level 1 For LCS levels 1b and 1c, an in-house training system should ensure there is evidence of the learner’s practical implementation of lean knowledge in the workplace (following training activity). This could be in a variety of formats, such as A3’s, a dairy, project portfolio, learning log, etc. The candidates should have played a meaningful role in the implementation activity, usually as part of a team or sometimes on an individual basis. The evidence should be endorsed by an appropriate manager/stakeholder to signify it is an accurate account of what happened. Such evidence builds into a cumulative body of practical evidence that could be used, for example, in personal development planning or appraisals. Note that it is not a requirement that this type of practical evidence is formally marked (as with the knowledge test) and no evidence is required for level 1a. 6.12.3 Practical Element – Level 2 For LCS level 2, the evidence of the practical implementation of lean knowledge should be more formalised and the training system should ensure that candidates submits an appropriate project implementation report, clearly documenting how the candidate as implemented a lean initiative, demonstrating appropriate knowledge and expertise. This report should be formally assessed. Further information is contained in the document Project Implementation Report Guide on the LCS Website. To complete the assessment for level 2, both the knowledge and implementation aspects need to be passed. © Lean Competency System 6|Page LCS ACCREDITATION SUBMISSION FORM 7 DELIVERY, TEACHING METHODS & STAFFING Section completion status: 0% 7.1 TEACHING METHODS An account of the teaching methods used should be provided for different audiences (eg lectures, workshops, on-site activities, use of case studies, simulations, exercise etc.) 7.2 DELIVERY CAPABILITY MATRIX A delivery capability matrix should be completed and included in the portfolio. This indicates the relative strength of the delivery resources across the key LCS knowledge levels and can be produced through a staff self-assessment exercise. A template for this is embedded below. ☐ Check box to indicate a Delivery Capability Matrix is attached or ☐ Check box to indicate a Delivery Capability Matrix is embedded below Embed document here (blank template attached) 7.3 Microsoft Word 97 Microsoft Excel 2003 Document 97-2003 Worksheet TRAINERS BIOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION Provide a list of those who will deliver training along with biographical information for each containing relevant information about their lean work experience/teaching credentials. A template for this is embedded below. ☐ Check box to indicate biographical Information is attached or ☐ Check box to indicate biographical Information is embedded below Embed document here (blank template attached) 7.4 Microsoft Word 97 2003 Document CLASS SIZE Describe the approach taken to class sizes, including the expected number in groups. 7.5 EXTERNAL DELIVERY RESOURCES Provide a statement of the policy towards using external delivery resources (if applicable). 8 ADMISSIONS Section completion status: 0% © Lean Competency System 7|Page LCS ACCREDITATION SUBMISSION FORM 8.1 METHODS AND CRITERIA USED TO SELECT COURSE PARTICIPANTS The selection policy for course participants should be described. This should include the selection process, typical level in organisation, job titles, etc. This may not be relevant for consultancies 9 QUALITY ASSURANCE & CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT Section completion status: 0% 9.1 TRAINING EVALUATION Describe the approach for learners to evaluate the training they undertake. 9.2 EXAMPLES OF EVALUATION QUESTIONNAIRES Provide examples of any evaluation questionnaires used. ☐ Check box to indicate evaluation questionnaire is attached or ☐ Check box to indicate evaluation questionnaire is embedded below Embed document here 9.3 OTHER PARTICIPANT FEEDBACK PROCESSES Describe other feedback processes for learners, whether formal or informal. 9.4 COURSES CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT PROCESS Indicate the measures that demonstrate that there is a continuous improvement process in place after course evaluation and review. 9.5 INTERNATIONAL COORDINATION & MANAGEMENT Where a training system is to be used on an international scale, detail the approach taken to ensure consistency in the delivery of the programme and the maintenance of standards. 10 TRAINING SUPPORT & ORGANISATION Section completion status: 0% 10.1 TRAINING FACILITIES Describe the facilities that will be used for training, including a description of other physical, IT support resources available. NB: this may not be applicable for some organisations. 10.2 TRAINING PROGRAMME MANAGEMENT & SUPPORT © Lean Competency System 8|Page LCS ACCREDITATION SUBMISSION FORM Describe how the training will be managed and supported – eg from which department or function, key roles undertaken by dedicated resources (names) or the use of other organisational support resources, such as HRM 10.3 LEARNER RESOURCES Describe any resources that are available to learners to support their training, such as libraries, IT based knowledge resources, mentoring, networks, etc. 10.4 TRAINING RECORDS Indicate how records are stored so that there is a secure history of a learners training history (eg date courses taken, assessments taken, certificate awarded, etc.) 10.5 TRAINING RECORDS EXAMPLES Provide an example of a training record (eg screenshot, spreadsheet, etc.) ☐ Check box to indicate training record example attached or ☐ Check box to indicate training record example is embedded below Embed document here (blank template attached) 10.6 UNIQUE CERTIFICATE NUMBERING SYSTEM Indicate the method used to give each certificate a unique reference number that will allow traceability. Typically, these include components which reference the organisation, date, individual, etc. © Lean Competency System 9|Page LCS ACCREDITATION SUBMISSION FORM 11 APPENDIX I: THE LEAN COMPETENCY SYSTEM FRAMEWORK 11.1.1 Overall Structure 1a—Awareness 1. FUNDAMENTAL 1b—Diagnosis and Analysis 1c—Improvement and Implementation 2. TECHNICAL 2a—Implementation and Design 3. STRATEGIC 3a—Strategic Enterprise 2b—Implementation and Leadership 3b—Strategic Supply Chain 11.1.2 Summary Level Descriptions Descriptions of the overall competence for each level are shown below: 1a—Awareness 1. FUNDAMENTAL 1b—Diagnosis and Analysis 1c—Improvement and Implementation OVERALL COMPETENCE a. Awareness and basic understanding of lean thinking principles and underlying/related concepts. Ability to understand and articulate the fundamental lean ideas. b. Knowledge of lean diagnostic and analytical techniques and the ability to use them in the workplace to understand the current state, solve problems and propose future states. c. Knowledge of lean improvement and implementation techniques and the ability to apply them in the workplace to support sustainable continuous improvement. 2. TECHNICAL 2a—Implementation and Design 2b—Implementation and Leadership OVERALL COMPETENCE a. In depth knowledge and understanding of the lean techniques and associated approaches required to develop a lean implementation programme to achieve business improvement objectives; insight into the business implications of lean thinking to the wider enterprise and supply chain; ability to lead lean programmes and projects with support and guidance; ability to design and communicate strategically integrated lean programmes and projects. © Lean Competency System 10 | P a g e LCS ACCREDITATION SUBMISSION FORM b. In depth knowledge and understanding of the lean techniques and associated approaches required to develop a lean implementation programme to achieve business improvement objectives; insight into the business implications of lean thinking to the wider enterprise and supply chain; ability to lead lean programmes and projects with support and guidance; ability to design and communicate strategically integrated lean programmes and projects. 3. STRATEGIC 3a—Strategic Enterprise 3b—Strategic Supply Chain OVERALL COMPETENCE a. Well-developed knowledge and mature understanding of lean philosophy, techniques and approaches and associated schools of thought; knowledge of the strategic and management dimensions of lean implementation; ability to implement and manage a lean strategy at an enterprise or business unit level; wide implementation experience in several organisational contexts over a period of at least 10 years; well developed and practiced leadership and change management competences. b. High level knowledge and mature understanding of lean philosophy, techniques and approaches and associated schools of thought; knowledge of the strategic and management dimensions of lean implementation; ability to implement and manage a lean strategy at an organisation or extended enterprise level; wide implementation experience in several organisational contexts over a period of at least 15 years; advanced and widely practiced leadership and change management competences. © Lean Competency System 11 | P a g e