Weather - Cloud Formation
advertisement

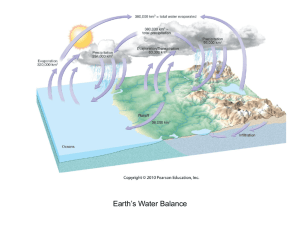
Weather Cloud Formation May 19, 2008 Adiabatic Temperature Changes • When air is allowed to expand, it cools, and when its is compressed, it warms. • Do you know of any examples? Water’s Changes of State Adiabatic Rate • Dry adiabatic rate – only applies to air that is unsaturated – 10°C for every 1000 meters • Wet adiabatic rate – only applies to air that is saturated – 5-9°C for every 1000 meters • Why do you think there is a difference between the wet and dry adiabatic rate? • The latent heat absorbed or released by the water. Processes That Lift Air • • • • Orographic Lifting Frontal Wedging Convergence Localized Convective Lifting Orographic Lifting • Orographic lifting is the lifting that occurs when elevated terrains, such as mountains, act as barriers to air flow. Frontal Wedging • Frontal wedging is what happens when a mass of warm air and a mass of cool air come together. The less dense warm air rises above the more dense cool air. Convergence • Convergence is what happens when there is a collision between contrasting air masses. Localized Convective Lifting • Localized convective lifting is caused by unequal heating of the Earth’s surface. This causes pockets of air to be warmed more than the surrounding air. Summary • What is adiabatic temperature change? • Why is there a difference between the dry adiabatic rate and the wet adiabatic rate? • Describe orographic lifting. • Describe frontal lifting. • Describe convergence. • Describe localized convective lifting.