Chapter 8 Study Guide
advertisement

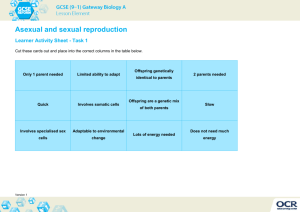
Chapter 8 Study Guide Lesson 1 (pgs. 250-259) Describe the functions of roots, stems and leaves o Roots-anchor the plant, absorb water and nutrients o Stems-carries substances between roots and leaves, provides support o Leaves-capture sun’s energy and carry out photosynthesis Stomata Transpiration Describe the structure of roots, stems and leaves o Roots Taproot & Fibrous root Root Hair Root Cap Vascular Tissue Area of Dividing Cells o Stems Woody & Herbaceous Vascular Tissue Cambium Heartwood o Leaves Stomata Why do they open and close? When are they open? When are they closed? Upper Leaf Cells Lower Leaf Cells Describe the structure and function of seeds o Seed Coat o Cotyledons o Embryo Describe the process of germination and how it begins Describe what happens in seed dispersal and why it happens Know the structures and function of the parts of a flower o Sepal o Petals o Stamens o Pistils Describe what happens in pollination Lesson 2 (pgs. 260-267) Know what happens in the sporophyte and gametophyte stages of a plant’s life cycle Know the difference between annuals, perennials and biennials Know how plants reproduce o Pollination o Fertilization o Zygote Formation o Asexual and Sexual Reproduction Explain the difference between vascular and non-vascular plants Know what a gymnosperm is: o Reproductive structure = cone o Explain reproductive cycle Know what an angiosperm is: o Reproductive structure = flower o Explain reproductive cycle Explain how seeds can be dispersed in gymnosperms and angiosperms Identify differences and similarities in gymnosperm and angiosperm reproduction Lesson 3 (pg. 268-275) Explain how organisms reproduce asexually o Budding o Fragmentation Know how many parents are involved in both asexual and sexual reproduction Explain why sexual reproduction results in offspring with DNA from mom and dad Explain why asexual reproduction results in offspring with DNA from one parent only Identify advantages and disadvantages for asexual and sexual reproduction Explain the life cycle of the jelly fish and how it is both sexual and asexual o Know the terms medusa, polyp and larva Explain internal fertilization Explain external fertilization and where it usually occurs Know what a gestation period is and why it varies Lesson 4 (pgs. 276-287) Know the structures and function of the parts of an amniotic egg o Embryo o Amniotic Fluid o Shell o Yolk o Albumin o Allantois Know what the placenta does in placental mammals Explain what complete metamorphosis is: o 4 stages Egg Larva Pupa Adult Explain what incomplete metamorphosis is: o 3 stages Egg Nymph Adult Explain the process of metamorphosis for: o Insects o Be able to give examples for complete and incomplete metamorphosis Discuss the advantages and disadvantages for parental care or noparental care