Science P5
advertisement
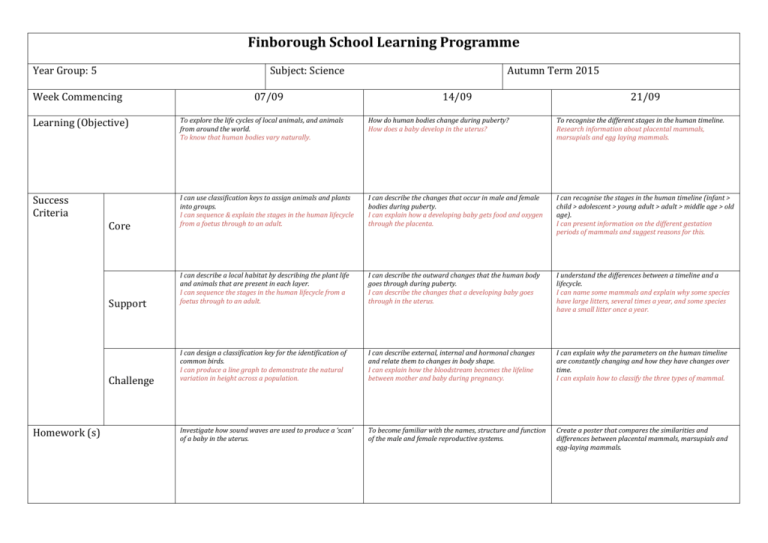
Finborough School Learning Programme Year Group: 5 Subject: Science Week Commencing 07/09 Autumn Term 2015 14/09 21/09 Learning (Objective) To explore the life cycles of local animals, and animals from around the world. To know that human bodies vary naturally. How do human bodies change during puberty? How does a baby develop in the uterus? To recognise the different stages in the human timeline. Research information about placental mammals, marsupials and egg laying mammals. Success Criteria I can use classification keys to assign animals and plants into groups. I can sequence & explain the stages in the human lifecycle from a foetus through to an adult. I can describe the changes that occur in male and female bodies during puberty. I can explain how a developing baby gets food and oxygen through the placenta. I can recognise the stages in the human timeline (infant > child > adolescent > young adult > adult > middle age > old age). I can present information on the different gestation periods of mammals and suggest reasons for this. I can describe a local habitat by describing the plant life and animals that are present in each layer. I can sequence the stages in the human lifecycle from a foetus through to an adult. I can describe the outward changes that the human body goes through during puberty. I can describe the changes that a developing baby goes through in the uterus. I understand the differences between a timeline and a lifecycle. I can name some mammals and explain why some species have large litters, several times a year, and some species have a small litter once a year. I can design a classification key for the identification of common birds. I can produce a line graph to demonstrate the natural variation in height across a population. I can describe external, internal and hormonal changes and relate them to changes in body shape. I can explain how the bloodstream becomes the lifeline between mother and baby during pregnancy. I can explain why the parameters on the human timeline are constantly changing and how they have changes over time. I can explain how to classify the three types of mammal. Investigate how sound waves are used to produce a ‘scan’ of a baby in the uterus. To become familiar with the names, structure and function of the male and female reproductive systems. Create a poster that compares the similarities and differences between placental mammals, marsupials and egg-laying mammals. Core Support Challenge Homework (s) Finborough School Learning Programme Year Group: 5 Subject: Science Week Commencing 28/09 Autumn Term 2015 05/10 12/10 Learning (Objective) What is the life cycle of a bird? To learn about the life cycle of a frog and other amphibians. Comparing the lifecycle of a butterfly with a grasshopper. How do life cycles of rainforest animals compare to other animals? A tree frog study. Research the life cycle of a marine creature. An eel study. To learn about the life cycles of desert animals. Success Criteria I can identify the parts of an egg. I can explain metamorphosis. I can describe the stages of an insect lifecycle using the terms vertebrate, invertebrate, endoskeleton, exoskeleton and moulting. I can explain what a resonator is on a tree frog, and how it allows sound to be heard at a greater distance. I can describe the characteristics of the 5 zones of an ocean (sunlight zone, twilight zone, midnight zone, abyss and trenches). I can describe the difference in life span of a desert tortoise and a desert mammal. I can describe the lifecycle of a bird. I understand that an amphibian starts its life cycle in water and into an adult that survives on land. I can describe the 4 stages of a butterfly lifecycle. I can explain how tree frogs can reproduce without living in a pond. I can describe the changes an eel goes through during its lifecycle. I can describe the changes a desert tortoise goes through during its lifecycle. I can describe the risks to survival during the lifecycle of a bird. I can explain the difference between an external and internal gill. I can name insects that have a caterpillar stage, and that have a nymph stage. I can design an experiment to test a theory. I know the zones of the ocean and can locate and name the oceans of the world. I can describe the lifecycle of an animal in the Sahara, Gobi and Patagonian deserts. What is unusual about the midwife toad? Investigate the lifecycle of one or more rainforest animals (one hatched, one born). What do you know about the lifecycle of dinosaurs? Core Support Challenge Homework (s) Finborough School Learning Programme Year Group: 5 Subject: Science Week Commencing 02/11 Autumn Term 2015 09/11 16/11 Learning (Objective) What do we know about materials? To compare and group together everyday materials on the basis of their properties. Why do certain materials have electrical conductivity? Why do certain materials have thermal conductivity? To understand that the properties of everyday materials are linked with everyday use. What properties do waterproof fabrics possess? Success Criteria I can say why materials have been chosen for certain purposes, based in their properties. I can consider the properties need for a tabletop and can test materials for hardness. I can identify when an electrical circuit will conduct electricity, and when it will not. I can identify materials that will conduct heat faster than others. I know that each material used in an object is linked to its use. I can explain the difference between waterproof and water resistant, and give examples of items that have been used for their waterproofing properties. I can say what the properties of a solid and liquid are. I can test materials for hardness. I understand how electricity flows. I understand that heat travels through materials and is always trying to escape. I know that a number of everyday materials can be used in one object. I understand that waterproof means water is unable to go through something. I can construct a simple series electrical circuit and can name some conductors and insulators. I can devise a fair test to find out the hardness of floor coverings. I can identify different components of electrical goods, explaining why certain parts are made from particular materials. I can think of examples of everyday objects that are used for a purpose because of their thermal conductivity properties. I can say how petrol, gas, wool, sugar and flour are manufactured. I can investigate the downside of using a membrane like polythene (high levels of perspiration). What is wurzite boron nitrade and lonsdaleite? What are they used for and why? Insulating a home. What features do houses have to stop heat escaping? How can sports clothing be breathable and waterproof? Core Support Challenge Homework (s) Finborough School Learning Programme Year Group: 5 Subject: Science Week Commencing 23/11 Autumn Term 2015 30/11 07/12 Learning (Objective) To compare how materials absorb water. To understand how water moves through some materials. Separating solids, liquids and gases, through filtering, sieving and evaporating. To know that some materials will dissolve in liquid to form a solution. Describe how to recover a substance from a solution. Success Criteria I can consider when I want a material to be the opposite of waterproof (absorbent). I understand how water moves through some materials and call this ‘capillary action’. I know how to separate dry materials and how layers of sediment are formed when materials are in water. I can identify substances that are soluble and insoluble in water and that evaporation is the reverse of dissolving. I understand how evaporation can be used as a means of recovering a dissolved solid. I can name some everyday items which have good absorption. I understand that water droplets are held together by a force called ‘surface tension’. I can explain how to use sieves to separate materials by size. I know that when some mixtures mix with water some of their components may dissolve. Evaporation can be used to recover a dissolved solid. I can define solution, evaporation and vapour. I can devise a fair test to show the differences in bricks and unfired clay for absorption. I can explain how cohesive and surface tension forces, act against gravity to allow water to climb into small spaces. I can use time-interval photography to explain how soil components can be separated in water. Investigate why crystals form in different shapes during evaporation. I can use diagrams and images to explain evaporation, a solute, a solution and a solvent. What is porosity? Investigate what it is and how it is useful for geologists to understand porosity. How is sedimentation used in industry? A paper-making case-study. Prepare a manual of information, explanations and tips, on how to separate substances and reverse changes in materials. Core Support Challenge Homework (s)