Physics Quiz: Rotational Motion & Gravitation - High School

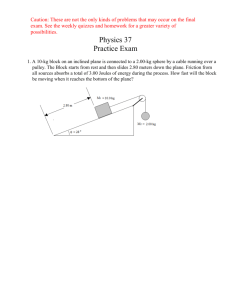
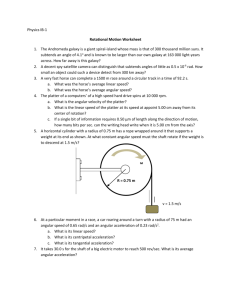
Quiz (#)
Grade
Cluster
11
ES AK
Subject
Date
Duration
I-Choose the best answer: (6 marks. 1 each)
1. An object, originally at rest, begins spinning under uniform angular acceleration. In 5 s, it completes an angular displacement of 30 rad. What is its angular acceleration?
A. 0.3 rad/s 2
B. 0.6 rad/s 2
C. 1.2 rad/s2
D. 2.4 rad/s2
E. 3.6 rad/s 2
2. The rotor on a helicopter turns at an angular speed of 3.2 × 102 revolutions per minute. What is the rotor’s angular speed in radians per second?
A. 0.03 rad/s
B. 3.14 rad/s
C. 6.28 rad/s
D. 33.5 rad/s
E. 320 rad/s
Page 1 of 5
3. Rashid and Ahmed are riding on a merry-go-round. Rashid rides on a horse at the outer rim of the circular platform, triple as far from the center of the circular platform as Ahmed, who rides on an inner horse. When the merry-go-round is rotating at a constant angular speed, Rashid’s angular speed is _______________________.
A. twice Ahmad’s
B. the same as Ahmad’s
C. half of Ahmad’s
D. one quarter of Ahmad’s
E. impossible to determine
4. A space probe is directly between two moons of a planet. If it is twice as far from moon A as it is from moon B, but the net force on the probe is zero. What can be said about the relative masses of the moons?
A. Moon A is twice as massive as moon B.
B. Moon A has the same mass as moon B.
C. Moon A is four times as massive as moon B.
D. Moon A is half as massive as moon B.
E. Moon A three times as massive moon B.
Explanation
The equation for gravitational force is . So, if one distance, r, is twice the other distance, then the for\ce for equal masses, is one-fourth as large. Therefore, the mass has to be four times larger to compensate.
5. Centripetal force on an object in circular motion is
Page 2 of 5
A. in the same direction as the tangential speed.
B. in the direction opposite the tangential speed.
C. in the same direction as the centripetal acceleration.
D. in the direction opposite the centripetal acceleration
E. in the same direction of both centripetal acceleration and tangential
velocity.
6. When calculating the gravitational force between two extended bodies, you should measure the distance
A. from the closest points on each body.
B. from the most distant points on each body.
C. from the center of each body.
D. from the center of one body to the closest point on the other body.
E. from the center of one body to the distant point on the other body.
II- Solve the following problems [12 marks]
7. A compact disc of radius 3.2 cm rotates from rest up to an angular speed of 28.2 rad/s in a time of 0.65 s. A microbe is held at the rim of the disk.
(a) Through what angle does the disc turn while coming up to speed?
( 6marks )
Page 3 of 5
(b) Find the tangential speed of a microbe riding on the rim of the disc when t = 0.65 s. (2 marks)
(c) What is the magnitude of the tangential acceleration of the microbe at the given time? (2 marks)
8. From a telecommunications point of view, it’s advantageous for satellites to remain at the same location relative to a location on Earth. This can occur only if the satellite’s orbital period is the same as the Earth’s period of rotation, 24.0 h. At what distance from the center of the Earth can this geosynchronous orbit be found? (2 marks)
Given: G = 6.67 × 10 −11 kg. m 3 /s 2 , and the mass of the Earth, M
E
= 5.98 ×
10 24 kg.
II- Answer the following question(s): (2 marks)
Page 4 of 5
9. Why is a vehicle with wheels that have a large diameter more likely to roll over than a vehicle with wheels that have small diameter?
Large diameter wheels will make the car higher, and thus shifting the center of gravity higher. In this manner the vehicle will be less stable.
10. Newton’s law of universal gravitational states objects attract other objects with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses, and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Page 5 of 5