CCOT Essay Guide: History Continuity and Change Over Time
advertisement

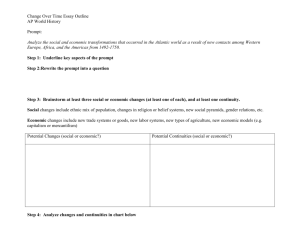
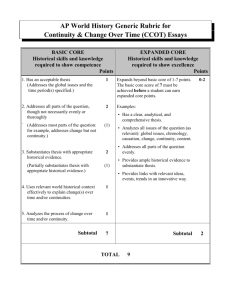
The Continuity and Change Over Time (CCOT) Essay About the CCOT • Primary purpose of CCOT is to test students’ mastery of their historical thinking skills (argumentation, causation, contextualization, synthesis). • The student must show what has changed and what has remained continuous from the beginning to the end of the time period given. • The continuities must be substantial, not obvious (Germans remained Germans), nor can change be continuous. • The important element is WHY things did or did not change. • Time allotted for this essay is 40 minutes (5-10 of which should be spent planning/outlining). • If possible, pick the nonwestern regions. CCOT Prompts 2002-2013 Find the Phrase 2002 CCOT • Choose TWO of the areas listed below and analyze how each area’s relationship to global trade patterns changed from 1750 to the present. Be sure to describe each area’s involvement in global patterns around 1750 as your starting point. • • • • • • • Latin America East Asia Eastern Europe North America South/South East Asia Sub-Saharan Africa Middle East 2003 CCOT • Describe and analyze the cultural, economic, and political impact of Islam on ONE of the following regions between 1000 CE and 1750 CE. Be sure to discuss continuities as well as changes. • West Africa • South Asia • Europe 2004 CCOT • Analyze the changes and continuities in labor systems between 1750 and 1914 in ONE of the following areas. In your analysis, be sure to discuss the causes of the changes and the reasons for the continuities. • Latin America and the Caribbean • Russia • Sub-Saharan Africa 2005 CCOT • Analyze the social and economic transformations that occurred in the Atlantic world as a result of new contacts among Western Europe, Africa, and the Americas from 1492 to 1750. 2006 CCOT • Analyze the cultural and political changes and continuities in ONE of the following civilizations during the last centuries of the classical era. • Chinese (100-600 CE) • Roman (100-600 CE) • Indian (300-600 CE) 2007 CCOT • Analyze major changes and continuities in the formation of national identities in ONE of the regions listed below from 1914 to the present. Be sure to include evidence from specific countries in the region selected. • Middle East • Southeast Asia • Sub-Saharan Africa 2008 CCOT • Analyze the changes and continuities in commerce in the Indian Ocean region from 650 CE – 1750 CE. 2009 CCOT • Analyze the continuities and changes in patterns of interactions along the Silk Roads from 200 BCE to 1450 CE. 2010 CCOT • Describe and explain continuities and changes in religious beliefs and practices in ONE of the following regions from 1450 to the present. • Sub-Saharan Africa • Latin America/Caribbean 2011 CCOT • Analyze changes and continuities in longdistance migrations in the period from 1700 to 1900. Be sure to include specific examples from at least TWO different world regions. 2012 CCOT • Analyze continuities and changes in trade networks between Africa and Eurasia from circa 300 CE to 1450 CE. 2013 CCOT • Analyze how political transformations contributed to continuities and changes in the cultures of the Mediterranean region during the period circa 200 CE to 1000 CE. AP Rubric & Class Expectations Thesis • Acceptable thesis statements need to address both change and continuity, stating as least one of each. • Thesis statements need to be explicit, not restatements of the question or vague statements, such as “there were more changes than continuities.” • Thesis Musts • Address Prompt • Place/Time • 3 Categories/Groups • 1:2 Ratio (1 Continuity and 2 Changes / 2 Continuities and 1 Change) How to Construct the Thesis • “From (this date) to (that date), (X) showed changes in (A), yet showed consistency in (B) and (C).” • “From (this date) to (that date), (X) showed consistency in (A), but showed changes in (B) and (C).” • “Even though (A) showed changes in (this place) at (this time), (B) and (C) continued to happen.” • “Even though (A) remained the same in (this place) at (this time), (B) and (C) changed.” Sample Thesis 2012: Analyze continuities and changes in trade networks between Africa and Eurasia from circa 300 CE to 1450 CE. “From (this date) to (that date), (X) showed consistency in (A), but showed changes in (B) and (C).” From 300 CE to 1450 CE, trade relations between Africa and Eurasia showed consistency in the basic types of exports and imports as well as the importance of coastal cities, but also showed changes in the arrival of Islam, the extent and degree of trade, and the rise of new and powerful empires in Eurasia. The Order • Introduction – Thesis Sentence • Paragraph 1 – Group 1 (how it changed/continued from beginning to end) • Paragraph 2 – Group 2 (how it changed/continued from beginning to end) • Paragraph 3 – Group 3 (how it changed/continued from beginning to end) • Conclusion if time What Order? Continuity Change Continuity Change Continuity Continuity Continuity Continuity Change Change Change Continuity Continuity Change Change In case time is not to your advantage, always organize your essay according to the top row. What Good Responses Should Include • Moves beyond a mechanistic “beginning, middle, end” format • Provides solid chronological knowledge across the entire time period • Include dates to demonstrate the ability to describe with some precision when continuity and change happen World Historical Context World Historical Context • Must provide the surrounding historical events and climate so that the reader understands what is occurring while these changes and continuities are happening • Essay relates or describes extra-regional connections or global process to explain a continuity OR change in response to the prompt World Historical Context • Example: “During the time from 200 BCE to roughly 400 CE, major empires such as the Romans in Europe, Gupta in India, Han in China, and stability in Persians allowed the Silk Roads to prosper, until disease and nomadic invasions disrupted this peace and the Silk Roads fell into disease.” • “Over a period of time, Silk Roads were responsible for bringing different cultures into contact“ is NOT acceptable because of the lack of specificity. Analyzing Process of Change or Continuity Analyzing Process of Change or Continuity • Must analyze at least one reason for a continuity or change • Why does this particular thing change? What causes that change, and why does that change occur right then and not at some other time? • Why does this particular thing stay the same? Is something prevented change, or is consistency with this thing desired? Analyzing Process of Change or Continuity • Example: “Buddhism’s popularity declined in India during the Classical period as a direct result of many factors. First, the Guptas promoted Hinduism in a period directly after Buddhist Kushan rule where Buddhism had come to be associated with foreignness. Secondly, Buddhism rejects the idea of the caste system, a social structure which was deeply engrained into Indian society as a result of Aryan and Hindu influence.” 2006 CCOT Marking it up Write an essay that: • Has a relevant thesis and supports that thesis with appropriate historical evidence. • Addresses all parts of the question. • Uses world historical context to show change over time and/or continuities. • Analyzes the process of change over time and/or continuity. 2006 CCOT Marking it up Write an essay that: • Has a relevant thesis (1) and supports that thesis with appropriate historical evidence (2). • Addresses all parts (2) of the question. • Uses world historical context (1) to show change over time and/or continuities. • Analyzes (1) the process of change over time and/or continuity. 2006 CCOT “Analyze the cultural and political changes and continuities in ONE of the following civilizations during the last centuries of the classical era. Chinese, 100 CE – 600 CE Roman, 100 CE – 600 CE Indian, 300 CE – 600 CE 2006 CCOT Brainstorm: India, 300 CE - 600 CE • Gupta Empire, 320-550 CE, ruling family using regional divisions, stable and prosperous initially • Fell with invasions of White Huns, 5th-6th centuries • Golden Age: Gupta emperors supported Hinduism, math and science • Gradual decline of Buddhism in India, spread beyond India into Southeast Asia • Because of Buddhism and trade, India’s influence extends to SE Asia • • • • Continued patriarchy Continued strength of Hinduism Continued trade by land and sea Continued caste system 2006 CCOT Brainstorm: China, 100 CE – 600 CE • • • • Han Empire, 206 BCE-220 CE- centralization, bureaucracy Fell due to internal problems (disagreements at court, corruption) Fell due to external problems (conflicts with Hun invasions) 220-589: 3 Kingdoms Period, regional kingdoms, warlords, disorder • 589-618-Sui dynasty • 618-907 Tang dynasty who reunified China • Buddhism slowly becomes more popular, coming in on Silk Road • • • • • Continued Daoism Confucianism continued Continued patriarchy, filial piety, veneration of ancestors Continued examination system Continued expansion of Great wall Tuesday, September 3rd – 2006 CCOT due Type the essay at home, double-space it, and annotate the following parts: 1) 2) 3) 4) Thesis – bold Categories/Groups – underline Evidence - italicize World History Context – different font 5) Analysis – larger size