American Indians
advertisement

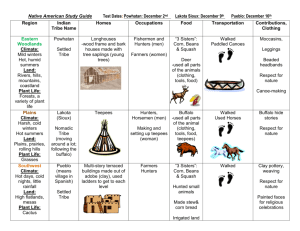
American Indians Inuit Kwakiutl Pueblo Lakota Iroquois First Americans Arrive on the Continent Many archaeologists believed that the first Americans came from Asia over a strip of land called Beringia that once connected Asia and North America. Cactus Hill Archaeologists have recently found artifacts at Cactus Hill, a site which is about 45 miles south of Richmond, Virginia. These artifacts are 18,000 years old. Now some scientists believe that the first people who reached North America came by boat from Europe, perhaps following a route from Iceland to Greenland to Canada. Many Native American Nations Many Native American cultures grew, developed and even disappeared in the 12,000 years from the last Ice Age until the present. By the year 1400 AD more than 300 different nations were living in North America. They spoke different languages, lived in different types of homes and had different cultures. This year we will study 5 groups of Native Americans. Inuit Inhabited present-day Alaska and northern Canada They lived in Arctic areas where the temperature is below freezing most of the time Inuit Food Fish Seal Whale Polar Bear Caribou Walrus Musk Ox Small Game (Arctic Hare) Inuit Clothing Seal, polar bear, caribou skin and fur Inner and outer clothing Jackets, mittens, trousers, boots Inuit Shelter (Housing) Igloo Skin Tents Sod Houses with underground rooms Inuit Transportation Sled dogs Kayak Umiak Foot Traditional Umiaks were paddle craft. The open umiak is significantly larger than the enclosed kayak which was built to carry one or two men while hunting. A large umiak is 6 to 10 meters long and can hold more than 20 people. About seven skins are needed for the cover on a boat of 30 foot (9.1 meter). It has traditionally been used in summer to move people and possessions to seasonal hunting grounds and for hunting whales and walrus. Men race in a umiak in Nome, Alaska. Role of Man and Woman Men hunted, fished, made tools, and houses Women cooked, prepared food, and raised children Art and Music Carved Ivory, Soapstone and Bone Scrimshaw Kwakiutl Homeland includes the Pacific Northwest coast in Washington (USA) and British Columbia (Canada) Rainy, mild climate Kwakiutl Food Salmon Elk Deer Bear Nuts Berries Roots Trade Kwakiutl Clothing Woven Cedar Bark Animal Skins Kwakiutl Shelter (Housing) Plank Houses made of cedar Totem Poles were often in front of homes Kwakiutl Transportation Dugout Canoes made of Cedar Kwakiutl Role of Man and Woman Men hunted, fished, traded, built houses and canoes Women gathered food, wove cedar, and raised children Kwakiutl Art Masks Totem Poles Carvings Pueblo Pueblo tribes inhabited the Southwest in present-day New Mexico, Utah and Arizona Lived in desert areas and areas bordering cliffs and mountains Pueblo Food Grew corn, beans, squash Irrigated crops during drought Hunted rabbit and made stew Hunted antelope Pueblo Clothing Grew cotton for cloth Men wove cotton Used some animal skins (rabbit) Pueblo Shelter Pueblo made of stone and adobe (mud/clay bricks) Many levels Cliff Dwellers Pueblo Transportation Foot (walk and run) Homes in Pueblos were all near one another . Pueblo Art and Music Pottery Baskets Kachinas Pueblo Role of Man and Woman Men farmed, made tools, gathered cotton and wove it into clothing. Men also built the pueblos, hunted and were warriors when neeeded Women ground corn, prepared food and taught children. Women wove baskets and made pottery. Pueblo is a Spanish word that means “village” The Pueblo nation includes the Tewa, Hopi and Zuni tribes. They are the descendents of the Anasazi – the Ancient Ones – who built the great adobe cities in the Southwest. Around 750 a huge city was built by the Anasazi in what is now New Mexico. What happened to that city? It was abandoned. Perhaps climate changes in the 1300’s and long periods without rain forced the people to move away. Some Pueblo people still live traditional lives in the American Southwest. Many of them still farm, weave baskets , make beautiful rugs, silver jewelry and fine pottery. Some of their homes, like the Taos Pueblo in New Mexico, were built about 1,000 years ago. The Pueblo live along side the Navajo in Arizona, Utah and New Mexico. The Navajo and the Pueblo are alike in many ways. Lakota Lakota people inhabited the Great Plains, an area with limited rain, grasslands and rolling hills. It was the perfect environment for the buffalo. What is the difference between the Lakota, the Dakota and the Sioux? There is no real difference. "Lakota" and "Dakota" are different pronunciations of the same tribal name, which means "the allies.“ "Sioux," on the other hand, is not a Lakota name. It comes from the Ojibway name for the tribe, which means "little snakes." Many Lakotas use the word Sioux to refer to themselves when they're speaking English, however. Most prefer the name Lakota. Lakota Food Hunted and ate bison, which are buffalo Also hunted elk, antelope and other animals. Lakota Clothing Buffalo hides, very decorated and sewn with sinew (animal tendon) Lakota Shelter Tepees of buffalo hides Tepees can be taken down quickly and move with the tribe. This was important to the Lakota, who were nomads following buffalo herds. Lakota Transportation Horses (after 1730’s) Dogs and horses pulled a travois (type of sled) The Lakota Indians of the northern plains have been called a “horse nation” because they have strong ties, culturally and historically, with horses. The Lakota originally lived by the Great Lakes. When European-American settlers came it forced many tribes to move westward, often into neighboring tribal land. The Lakota migrated west from the Great Lakes region to the Great Plains. They were introduced to horse culture by the Cheyenne about 1730. After their adoption of the horse their society centered on the buffalo hunt with the horse. Lakota Role of Man and Woman Women made tepees and butchered buffalo Women cooked and cared for children Men hunted and protected the tribe Lakota Art and Music Very decorated clothing and headdresses Drums and pipes The Lakota weren’t the only people living in the Great Plains. There were Cheyenne, Arapaho, Blackfeet, Comanche and Pawnee. All had many things in common, but one of the biggest was the importance of the buffalo. The Plains Indians depended on the bison for almost everything. These huge shaggy beasts provided meat, leather, sinew for bows, grease, dried dung for fires, and even the hooves could be boiled for glue. When times were bad, bison were consumed down to the last bit of marrow. Iroquois Their homeland is in northeast North America, the Eastern Woodland. This region is heavily forested and gets plenty of rain and snow. The Iroquois nation was in the area that is now New York. Iroquios The Iroquois Indians originally lived near Lake Ontario and along the Mohawk River in New York State. Five tribes, the Mohawks, the Oneidas, the Onondagas, the Cayugas, and the Senecas, banded together to form a confederacy, the Iroquios Nation. Later a sixth tribe, the Tuscarora, joined. This confederacy created the Great Law of Peace which explained how to settle diputes. It brought peace and prosperity to the Iroquois for hundreds of years. That peace was shattered when settlers came from Europe. Iroquois Food Grew corn, squash, beans Fish Deer Bear Small Game (rabbits, squirrels, turkeys) Pumpkins Nuts, berries . Iroquois Clothing Deerskin clothing Long fringed skirts, breech cloths, moccasins, leggings Iroquois Shelter Longhouses made of wood, bark, animal skins Up to 100 feet long—4 or 5 families shared one longhouse Hole in ceiling for cooking Iroquois Transportation Canoes made of elm or birch bark Role of Man and Woman Women were the head of the family and owned land. Women held a powerful position in the Iroquois tribe. They owned longhouses, controlled the land, and chose the chief and the ruling group. Children belonged to their mother's clan. When a man married, he lived with his wife's clan. Men were hunters and fishers and built the longhouses. They also made canoes and tools. Iroquois Art and Music Baskets Pottery