Primary & Secondary Growth in Plants
advertisement

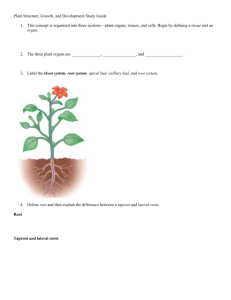
Plant Structure, Growth & Function Dermal Tissue Outer Covering Protection Vascular Tissue “Vessels” in Plant Transports Materials Ground Tissue “Body” of Plant Photosynthesis, Storage, Support Meristems can generate new dermal, vascular and ground tissue in plants Primary Growth accounts for a plant’s lengthwise growth from root and shoot tips Secondary growth accounts for increases in width (girth) among woody dicots only Shoot apical meristem Apical meristems produce the new cells that enable a plant to grow in length, both above and below ground, as well as to branch Developing vascular strand Axillary bud meristems The shoots of some monocots have intercalary meristems at the base of each internode, causing continual elongation The root cap is a cone of cells that protects the delicate, actively dividing cells of the apical meristem It replaces the cells of the root cap that are scraped away by the soil and it produces the cells for primary growth Runs continuous throughout the plant and transports materials between roots and shoot Xylem tissue transports water and dissolved minerals upwards from roots into the shoots Phloem tissue transports food from the leaves to the roots and to non-photosynthetic parts of the shoot system Phloem Sclerenchyma (fiber cells) Xylem Pith Epidermis Ground tissue Ground tissue connecting pith to cortex Vascular bundle Cortex 1 mm (a) Cross section of stem with vascular bundles forming a ring (typical of dicots) Epidermis Key to labels Dermal Ground Vascular Vascular bundles (b) Cross section of stem with scattered vascular bundles (typical of monocots) 1 mm Primary growth in stems Epidermis Cortex Shoot tip (shoot apical meristem and young leaves) Primary phloem Primary xylem Pith Lateral meristems: Axillary bud meristem Vascular cambium Cork cambium Secondary growth in stems Periderm Cork cambium Cortex Root apical meristems Primary phloem Pith Primary xylem Secondary xylem Secondary phloem Vascular cambium Vascular Cambium is a cylinder of actively dividing cells located between the xylem and phloem. It adds cells on both sides Secondary Xylem towards the inside of the stem Secondary Phloem towards the outside of the stem Cork Cambium is another lateral meristem which produces cork (part of bark) Together, the secondary vascular tissues (formed by vascular cambium) and periderm (formed by cork cambium) makes up the secondary plant body Bark is made of phloem, cork cambium and cork. Older phloem is pushed outward Annual Growth Rings are xylem tissue formed by the vascular cambium during one growing season (1 year) Environmental conditions during the growing season affect xylem Springwood – large and thin-walled cells (cooler, wet climate) Summerwood – narrow and thick-walled cells (hotter, dry climate)