Distillation
advertisement

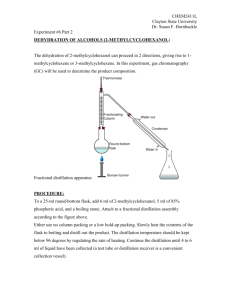
Read the following passageson how distillation worksDistillation, the separation of one substance from another by evaporation and condensation. The product obtained by distillation is called the distillate. This process is used for purifying liquids having undesired substances in them, for separating different kinds of liquids from each other, and for producing chemical changes in solid substances. There are three main types of distillation: simple, fractional, and destructive. Simple Distillation Simple distillation is used to eliminate solid impurities from a liquid. Water can be freed of salt or other minerals through this process. Water is boiled in a closed container called a boiler. Vapor evaporating from the surface of the boiling water passes through a pipe leading from the boiler to a vessel called a condenser. The condenser, in turn, opens into a third vessel. The entire apparatus is called a still. In its simplest form, the condenser is a tube surrounded by a larger tube filled with cold water. The water vapor from the boiler never touches the cold water, which cools the vapor as it passes through the inner tube. As the vapor loses its heat, it becomes liquid and flows into the collecting vessel. The process continues until all the water in the boiler has evaporated. Solid impurities that had been in the water remain on the bottom of the boiler. In vacuum distillation, the atmospheric pressure inside the boiler is reduced, allowing the liquid to boil at a lower temperature. In steam distillation, steam is fed into the boiler and turns the substance to be distilled into vapor. The setup for a simple distillation is shown in Figure 1. A simple distillation apparatus consists of a boiling flask (round-bottom flask) attached to an adapter holding a thermometer (to determine the boiling temperature of the liquid). The adapter connects to a condenser into which cold water is constantly passed through. The condenser leads into a collection flask for the purified liquid. Figure 1. Simple distillation. Distillation - How does it work? Distillation is a water purification process that uses a heat source to vaporize water and separate it from contaminants and other undesirable elements commonly found in ground and surface water. Distillation heats raw (untreated) water until the water reaches its boiling point and begins to vaporize. The heat is then kept at a constant temperature to maintain water vaporization while prohibiting other undesirable elements from vaporizing. Water has a lower boiling point than salt and other mineral sediments. This process also separates the water molecules from microscopic, disease-causing organisms. Once all of the water has vaporized, the vapor is led into a condenser, where, upon cooling, the water reverts to the liquid form and runs into a receiving container. The remaining elements, whose boiling point was too high to permit vaporization, remain in the original container and constitute the sediment (Holland, Siqueiros, Santoyo, Heard, & Santoyo, 1999). Because the distillation process can never ensure a complete separation between water and other materials, it is often repeated one or more times with the treated water. Throughout history, people have experiment with the use of solar power in distillation (Holland et al, 1999). Because of the cost of a heating source to initiate the distillation process, solar power seems an efficient and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional power. Though solar power can be effective for distillation purposes, it works only with relatively small amounts of liquid. Also, the time required for multiple distillations is much greater when relying on solar power than when using traditional power sources. Purpose: Write a procedure for constructing a simple distillation flask. Test the effectiveness of the distillation flask at purifying water. A Picture of the completed flask is shown below. Materials: Mason Jar, Glass Funnel, Beaker, Wooden Block, Ziploc Bag, Ice, 50mL beaker, Contaminated Water, Pipet, Hot Plate, Tongs Apparatus: Procedure: Write a detailed two part procedure for the construction and operation of the distillation flask. Visually inspect the distilled water and check for conductivity. Data: and Observation: Describe in detail what is happening inside the flask. Draw a cartoon model showing the flow of water in the flask. Report the results of your distillation. Conclusion: Did the flask purify the water? Why or why not. Explain in detail the function of each component in the distillation flask. Why is it necessary? What would happen if it were removed?