Indian Removal
advertisement

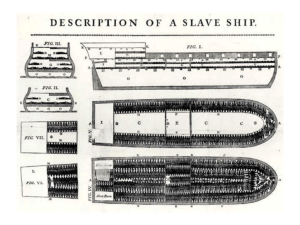
3.6.2014 Students will understand the concept of “paternalism” and will apply it to Indian Removal Please get out your notes Westward Expansion & Division between the North and the South McGuire Honors US History Enduring Understandings 1. Differences between the North and the South caused severe tension in the new United States. 2. Most White Americans, though, agreed on the “savagery” of Native Americans and treated them as children. Paternalism: A policy or practice of treating or governing people in a fatherly manner, especially by providing for their needs without giving them rights or responsibilities. ● It assumes you are less than fully rational. ● Treating someone as if they are a child, when in fact you are equals. Examples of Paternalism • Requiring the wearing of seatbelts • Banning drugs that are accepted to be harmful • Doctors not telling patients (or patients’ family) certain information because they would be “better off” not knowing • “All of these rules, policies, and actions may be done for various reasons; may be justified by various considerations. When they are justified solely on the grounds that the person affected would be better off, or would be less harmed, as a result of the rule, policy, etc., and the person in question would prefer not to be treated this way, we have an instance of paternalism” Paternalism with Natives • Saving them from their savage ways • Showing them the way “civilized” people go about things Context for Native American policy choices: • Under George Washington (1789-1797): Acculturation--The U.S. sent people to train Cherokee Natives in how to build log cabins, use Southern style plantations, setup American-ized schools, and teach the Natives Christianity. • Under Thomas Jefferson (1801-1809): Acculturation continued. If Natives were successful in showing that they were becoming like real “Americans” they could stay east of the Mississippi. • Under Andrew Jackson (1829-1837): Indian Removal--almost completely regardless of their culture or feelings, Jackson wanted to set up a plan of complete Indian Removal Act: May 28, 1830 Indian Removal Primary Source Activity • Answer questions 1 and 2 on your own. • Answer #4 with your partner (no quotes needed). • When you use a quote from a primary source put the reading # in parenthesis. – For example, “Here is my quote” and here is my commentary (Reading 1). If you have the Document with 5 readings, read 1, 2, and 5. Tomorrow OPVL either the author of Reading 1 (Andrew Jackson) or Reading 2 (The Council of the Cherokee Nation) 3.7.2014 Students will develop an argument on upholding Native treaties and support it in a silent discussion. Please get out your assignment from yesterday! On the back of your assignment… • Please respond to this prompt: – To what extent do you agree with Aaron Huey that the Black Hills should be given back to the Sioux/Lakota? – Please be culturally sensitive in your answers. Respectfully address both sides as nations. – 6 minutes Silent Discussion • You are now going to receive someone else’s answer and read it • Respond to what your classmate has written – Don’t just write your own opinion, thoughtfully address what they have said specifically and provide reasons why you agree or disagree with them – 6 minutes One more time… • Read the two responses • Write a response to both of them, addressing the points that you found interesting and elaborating on them • Agree or disagree with either/both of them? • 6 min Class Discussion 1.What points does Aaron Huey bring up that are valid? 2.Do you find anything unconvincing about his argument? 3.Did you see any evidence of paternalism in the history that Huey shared? MANIFEST DESTINY American Progress by John Gast, 1872 Manifest Destiny Arguments for Expansion • New Land – New Resources – New markets/goods • Western Ports – Access to Asia • Pop. increase – Natural & immigration – Conflicts over employment – Living space • Ethnocentrism and Entitlement – Divine Will Arguments Against Expansion Not all believed U.S. should continue to spread west • Many N accused the S of wanting to spread W so US could gain slave states, proslavery S more votes in Congress • Some Am felt it wrong for US to push peoples off lands that the US had no legal claim to • Some also wished for the US to maintain its longstanding policy of isolationism Another Argument: Westward Movement will lead to conflict And for better or worse, it kind of did… – The Texas Revolution 1836 – Mexican War 1846-1848 – Dispute with British - 1846 – Indian Wars 1840-1890 3-22: Manifest Destiny Please get out your journal H.I. H.I. H.I. H.I. H.I. Mexican American War • Texas was a part of Mexico • American settlers started flooding into the region because the land was desirable to them→this led to independence from Mexico • Annexed into U.S. → led to Mex Am War Significance of Mexican War • U.S. territory increased by 1/3 (including Texas) -Bigger than Louisiana Purchase • Sentiment for Manifest Destiny increased • Ugly turning point in relations with Lat. Am. Two Column Notes Idea/Question Hardships of westward expansion How did westward expansion impact natives? Details about that idea or question Idea/Question Details about that idea or question What was Lewis and • Sacajawea aided them and saved journals Clark Journey like? What did they discover? What were the impacts of westward • More resources like beaver furs expansion? March 26 Please get out your journal Sectionalism Washington's "Farewell Address" makes this economic tradeoff the main practical argument for a continued union of the sections: “The North, in an unrestrained interaction with the South, protected by the equal Laws of a common government, finds in the productions of the latter, great additional resources of Maratime [sic] and commercial enterprise and precious materials of manufacturing industry. The South in the same interaction, benefitting by the Agency of the North, sees its agriculture grow and its commerce expand.” Infrastructure • Steam locomotive made in 1825 • Turnpikes • National Road began in 1811 • By 1838 it stretched from Maryland to Illinois Infrastructure--Erie Canal • By 1825 linked Hudson River to Lake Erie = Great Lakes to the Atlantic • 12 years of a toll paid off project • NYC became dominant port • By 1837 other states built 3,000 miles of canals to make profit Economy—the North • Textiles and manufactured goods • Congress was able to pass tariffs to protect northern economy The North Industrializes • Samuel Slater "Father of the Factory System" -1791, built first efficient cotton-spinning machine in America. • Lowell, Mass. Manufacturing center • North began industrializing rapidly Slaves Using the Cotton Gin “Hauling the Whole Week’s Pickings”William Henry Brown, 1842 Slaves Picking Cotton on a Mississippi Plantation “Cotton is King” Cotton gin • Prior to 1793, the Southern economy was weak and an unprofitable slave system. • Some leaders, such as Jefferson (who freed 10% of his slaves), spoke of freeing their slaves and of slavery gradually dying; Cotton Gin •It was difficult to make a profit from cotton because cottonseeds were removed by hand. • It took one person an entire day to clean one pound of cotton. Cotton Ball, picked 1915 Georgia • Therefore, Eli Whitney invented the cotton gin in 1793. Eli Whitney’s cotton gin. Changes in Cotton Production 1820 1860 Southern Agriculture Monday, April 1st • Please get out your journals • Think about this: What could you do on your HI tonight? Slave Accoutrements Slave Master Brands Slave muzzle Slave leg irons Slave shoes Slave tag, SC Slave Auction Notice, 1823 Southern Society (1850) 6,000,000 “Slavocracy”[pla ntation owners] The “Plain Folk”[white yeoman farmers] Black Freemen 250,000 Black Slaves 3,200,000 Total US Population --> 23,000,000[9,250,000 in the South = 40%] Slave-Owning Population (1850) Slave-Owning Families (1850) A Real Georgia Plantation Slaves posing in front of their cabin on a Southern plantation. A Slave Family A Real Mammie & Her Charge Missouri Compromise, 1820 • Country was equally divided between slave and free states with eleven each. • Northern states wanted Maine admitted as a free state. April 15th • Please get out your journals • Tomorrow, please bring your textbook *Please no H.I. questions this week* Hope you had a great break, I’m happy to see you :) Territories become states 1. Territory pop. Reached 60,000 2. People of territory could petition admission to Union 3. draft a state Const. 4. elect rep. 5. Congress approval to be state US Laws Regarding Slavery 1. 3/5 Compromise 2. Fugitive Slave Acts 3. Slave Codes Slave Codes • Virginia, 1650 – “Act XI. All persons except Negroes are to be provided with arms and ammunitions or be fined at the pleasure of the governor and council.” • Virginia, 1662 – “Whereas some doubts have arisen whether children got by any Englishmen upon a Negro shall be slave or Free, Be it therefore enacted and declared by this present Grand assembly, that all children born in this country shall be held bond or free only according to the condition of the mother." • Maryland, 1664 – “That whatsoever free-born [English] woman shall intermarry with any slave [...] shall serve the master of such slave during the life of her husband; and that all the issue of such free-born women, so married shall be slaves as their fathers were.” Slave Codes • Alabama, 1833, section 31 - "Any person or persons who attempt to teach any free person of color, or slave, to spell, read, or write, shall, upon conviction thereof by indictment, be fined in a sum not less than two hundred and fifty dollars, nor more than five hundred dollars." • Alabama, 1833, section 32 - "Any free person of color who shall write for any slave a pass or free paper, on conviction thereof, shall receive for every such offense, thirty-nine lashes on the bare back, and leave the state of Alabama within thirty days thereafter..." • Alabama, 1833, section 33 - "Any slave who shall write for any other slave, any pass or free-paper, upon conviction, shall receive, on his or her back, one hundred lashes for the first offence, and seven hundred lashes for every offence thereafter..." Early Emancipation in the North Southern Slavery--> Behind the times? ➢ 1780s: 1st antislavery society created in Phila. ➢ By 1804: slavery eliminated from last northern state. ➢ 1808: US abolishes the slave trade ➢ 1820s: newly indep. Republics of Central & So. America declared their slaves free. ➢ 1833: slavery abolished throughout the British Empire. ➢ 1844: slavery abolished in the Fr. colonies. ➢ 1861: the serfs of Russia were emancipated. 4 Main problems people saw with slavery 1. 2. 3. 4. Lack of freedoms Violence Separation of Families Psychological Damages The Scourged Back • Slave named Gordon, escaped his master in Mississippi • His back scarred with the traces of a whipping administered on Christmas Day • Took refuge with the Union Army at Baton Rouge and, in 1863 • Three engraved portraits of him were printed in Harper’s Weekly • Used as propaganda by Northern abolitionists Southern Population (1860) JERMAIN LOGUEN (circa 1813-1872) • “No day dawns for the slave, nor is it looked for. It is all night—night forever” • Son of his Tennessee master and a slave woman. Underground agent and ordained minister, he helped 1,500 escapees and started black schools in New York State. Slave Resistance 1. Escape via the Underground Railroad. 2. Refusal to work hard. 3. Isolated acts of sabotage. Theft. Runaway Slave Ads Run away • Estimated 1810-1850 75,000100,000 slaves were freed via Underground RR • Harriet Tubman made 19 journeys bringing slaves north • Escorted 300+ slaves • "There was one of two things I had a right to, liberty or death; if I could not have one, I would have the other; for no man should take me alive...." Underground Railroad“concea ling their actions”Conducto rs— those who guided slaves to freedomPassenge rs— slaves seeking freedomStations —homes or businesses where fugitive slaves would hide Underground Railroad John Rankin’s house - Ohio • It was here that Harriet Beecher Stowe heard the escaping slave's story which became the basis for part of her famous work, Uncle Tom's Cabin. (sells 300,000 copies in its first year of publication) • "At times attacked on all sides by masters seeking their slaves, [John Rankin and his sons] • A lighted candle stood as a beacon which could be seen from across the river, and like the north star was the guide to the fleeing slave." Escape on the Underground Railroad • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yXjaFF 1OImk April 16th “When I was a boy and I would see scary things in the news, my mother would say to me, ‘Look for the helpers. You will always find people who are helping.” --Fred Rogers Please get out your journal and textbook 1854—Kansas-Nebraska Act • Setting aside the Missouri Compromise of 1820, Congress allows these two new territories to choose whether to allow slavery. • Abolitionists were outraged because both of these regions would have been free states under the M.C. of 1820. • Violent clashes erupt….Why would that be? Chapter 10 Reading • Read Chapter 10 and take notes in your journal – Focus on bolded words/names – Those names will be possible players in your group project you will get tomorrow – The chapter needs to be read by Thursday Oregon Trail by Albert Bierstadt 1869