Geology
advertisement

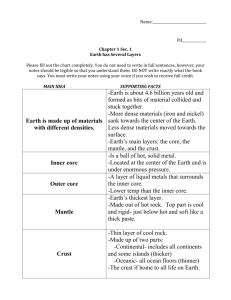
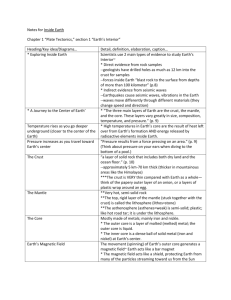
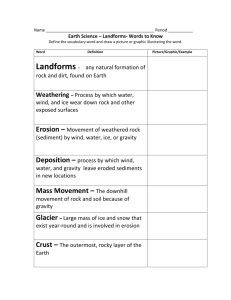
Unit Essential Question: How does the Earth Change? In your Science journal record the UEQ How does the Earth Change? Activating Strategy: Your lab group will have the opportunity to use your observation skills and inferring skills to predict the contents of three film canisters. Lesson Essential Question: What is the content of the three film canisters? Write numbers 1-3 in your journal under today’s date. LEQ: What is the content of the three film canisters? Date 1. 2. 3. You may: tap, roll, shake, or weigh your canister. What differences do you notice between the canisters? Apart from the canisters all being the same in appearance, are the canisters similar in any way? How did you obtain this evidence? Survey page 17. Titles: The Science of Geology & Studying Surface Changes Bold print: geologists, rock, geology, constructive forces, destructive forces & continents. The study of planet Earth There are two groups of forces that change the surface of our Earth – constructive forces and destructive forces. 1. Geologist – a _scientist_ who studies the _forces_ that _make_ and _shape_ planet _Earth_ . 1. geologist – a _scientist_ who studies the _forces_ that _make_ and _shape_ planet _Earth_ . 2. rock – the _material_ that _forms_ Earth’s _hard surface_ . 1. geologist – a _scientist_ who studies the _forces_ that _make_ and _shape_ planet _Earth_ . 2. rock – the _material_ that _forms_ Earth’s _hard surface_ . 3. geology – the _study_ of _planet Earth_ . 4.constructive force – a _force_ that _builds up mountains_ and landmasses on Earth’s _surface_ . 5. destructive force – a _force_ that slowly _wears away mountains_ and other features on the surface of _Earth_ . 6. continent – a great _landmass_ surrounded by __oceans_ . How do Scientist answer the question – What’s inside Earth? The deepest mine in the world, a gold mine in South Africa, reaches a depth of 3.8 kilometers. You would have to travel more than ________ times that distance ---- over _________ kilometers ---- to reach the Earth’s center. You would have to travel more than _1,600_ times that distance ---- over _6,000_ kilometers ---- to reach the Earth’s center. 7. seismic wave – a _vibration_ that travels through _Earth_ carrying the _energy_ released during an _earthquake_ . What would you have to consider to travel to the center of the Earth? What would you have to consider to travel to the center of the Earth? 1. Temperature At first the rock around you is cool. At about 20 meters down your instruments report that the rock is getting warmer. For every 40 meters that you descend (go down) from that point, the temperature rises 1°C. 2. Pressure 8. pressure – the _force_ pushing on a _surface_ or _area_ . Crust Mantle Core 9. crust - _layer_ of _rock_ that forms Earth’s _outer_ skin . The crust consists mostly of dense rocks such as basalt (buh SAWLT) and granite. 10. basalt – dark, _dense _, _igneous_ rock with a fine _texture_, found in _oceanic_ crust . 11. granite – a usually _light_- colored _rock_ that is found in _continental_ crust . 12. mantle – the _layer_ of _hot_, _solid_ material _between_ Earth’s _crust_ and _core_ . What are the two parts of the mantle? 13. lithosphere – a _rigid_ layer made up of the uppermost part of the _mantle_ and _the crust_ . 14. asthenosphere – the _soft_ layer of the _mantle_ on which the_lithosphere_ floats . 15. outer core – a _layer_ of molten (_melted_) _iron_ and _nickel_ the surrounds the _inner_ core of Earth . 16. inner core – a _dense_ sphere (ball) of _solid_ iron and nickel in the _center_ of Earth .