An Overview of IDEA & ESE
advertisement

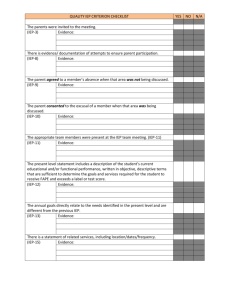
ESE Exceptional Student Education Dana Brock & Frances Celis IDEA • Prior to 1997, IDEA did not specifically address general curriculum involvement of disabled students. The 1997 Amendments shifted the focus of the IDEA to one of improving teaching and learning, with a specific focus on the Individualized Education Program (IEP) as the primary tool for enhancing the child’s involvement and progress in the general curriculum. • The Individuals with Disabilities Education Improvement Act 2004 (IDEA) aligns IDEA closely to the No Child Left Behind Act (NCLB), helping to ensure equity, accountability and excellence in education for children with disabilities. ABC’s of ESE You Try!!! ABC’s of ESE • • • • • • • • • • ESE – Exceptional Student Education IEP – Individual Education Plan FBA/BIP – Functional Behavior Assessment/Behavior Intervention Plan PLF – Present Level of Functioning LRE – Least Restrictive Environment SLD – Specific Learning Disability EH – Emotionally Handicapped SED – Severely Emotionally Disturbed EMH – Educable Mentally Handicapped TMH – Trainable Mentally Handicapped • • • • • • • • • • • • • PMH – Profoundly Mentally Handicapped GIF - Gifted DD – Developmentally Delayed SI – Speech Impaired LI – Language Impaired HI – Hearing Impaired VI – Vision Impaired OI – Orthopedically Impaired OHI – Other Health Impaired TBI – Traumatic Brain Injury AUT – Autism OT – Occupational Therapy PT – Physical Therapy Percentage of FL Students in ESE Programs SLD - Specific Learning Disability 35.10% • Specific learning disabilities refers to a group of psychological processing disorders evidenced by significant difficulties in the acquisition and use of language, reading, writing, or mathematics. • Examples: Dysnomia, Auditory Processing, Visual Motor Integration, Dyslexia, Sensory Processing, Visual Integration Processing, etc. SLD Qualifications • Documented evidence which indicates that general education interventions have been attempted and found to be ineffective. • Evidence of a disorder in one or more of the basic psychological processes required for learning. • Evidence of academic achievement which is significantly below the student’s level of intellectual functioning. GIF – Gifted 22.53% • One who has superior intellectual development and is capable of high performance. • Qualifications: – Superior intellectual development as measured by an intelligence quotient of two standard deviations or more above the mean on an individually administered standardized test of intelligence. – Full Scale IQ = 130 +/- SI – Speech Impaired 11.43% • An impairment in articulation is substitutions, distortions, or omissions of speech sounds which are not age appropriate. • An impairment in fluency is abnormal flow of speech which impairs rate and rhythm and may be accompanied by struggle behavior. • An impairment in voice is absence or abnormal production of voice quality, pitch, loudness, resonance, or duration. LI – Language Impaired 7.08% • An impairment in the language system is an abnormal processing or production of: – a. Form including phonology, syntax, and morphology – b. Content including semantics – c. Function including pragmatics EH – Emotionally Handicapped 6.30% • An emotional handicap is defined as a condition resulting in persistent maladaptive behavior, which exists to a marked degree, which interferes with the student’s learning process, and which may include but is not limited to any of the following characteristics: – An inability to achieve adequate academic progress which cannot be explained by intellectual, sensory, or health factors. – An inability to build or maintain satisfactory interpersonal relationships with peers and teachers. – Inappropriate types of behavior or feelings under normal circumstances. – A general pervasive mood of unhappiness or depression. – A tendency to develop physical symptoms or fears associated with personal or school problems. EH Qualifications A student is eligible for a special program for emotionally handicapped if there is evidence that: • The student, after receiving supportive educational assistance and counseling services, still exhibits an emotional handicap. • An emotional handicap exists over an extended period of time, and in more than one situation. • The emotional handicap interferes with the student’s own learning, reading, arithmetic or writing skills, social-personal development, language development, or behavioral progress and control. EMH – Educable Mentally Handicapped 6.09% • An educable mentally handicapped student is a student who is mildly impaired in intellectual and adaptive behavior and whose development reflects a reduced rate of learning. The measured intelligence of an educable mentally handicapped student generally falls between two and three standard deviations below the mean, and the assessed adaptive behavior falls below that of other students of the same age and sociocultural group. IEP at a Glance Important Sections: • Primary exceptionality • ESE services – frequency and location • Modifications, accommodations, & supports • Standardized assessment • Present level of functioning (PLF) • Goals and Objectives Last Thoughts • Students are eligible for services from their third birthday until they graduate with a standard diploma or G.E.D., or until age 22. • All students who have been placed in an ESE program must have an active IEP. • At age 14, a transition IEP must address post secondary education goals. • ESE students must be served in their Least Restrictive Environment. • All ESE procedures and referrals are done with parent permission. References • Clay County Special Programs and Procedures Manual • Clay County Admissions and Placement Manual • Florida Department of Education website