Unit 5, Part 1 Study Guide
advertisement

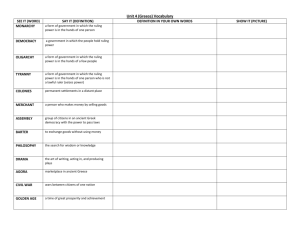
Unit 5, Part 1 Study Guide Mr. Davis Warrior Social Studies January 2015 Vocabulary (p. 1 of Interactive Notebook) • • • • • • • • • • Polis = a city-state Classical = a period marked by great achievements Acropolis = a high hill, usually with a fortress on top Democracy = a type of government where people rule themselves Aristocrats = wealthy landowners Oligarchy = a type of government where a small council of aristocrats rule Citizens = people that have the right to participate in government Tyrant = a leader who gets and keeps power through force Mythology = a body of stories to explain how the world works Fables = stories that teach the reader a lesson Geography of Ancient Greece • Greece is a mountainous peninsula with many natural harbors • A rugged, jagged coastline • Surrounded by islands, but the Greek mainland is a PENINSULA. Effects of Geography • Because travel by land was so difficult, the Greeks had to turn to the seas for travel and trade. • They became expert shipbuilders Minoans • The Minoans created an ancient civilization on the island of Crete. • Historians don’t consider the Minoans to be Greek because they did not speak Greek. The Mycenaeans did speak Greek and lived on the Greek mainland. • The Minoans were destroyed by a volcanic eruption and its effects: the ash buried crops and a giant wave flooded the island of Crete The Dark Ages • After invading armies destroyed Mycenaean civilization, Greece had a period of warfare and disorder known as the Dark Ages. The agora • The agora served as a market place for farmers to bring in goods • A meeting place for political and religious assemblies • Shops were located there Democracy in Ancient Greece • Athens was a democracy for about 170 years and reached its height under Pericles. • Pericles encouraged people to take pride in their city and participate in government—he paid people to serve in offices or on juries. • Athenian democracy is DIRECT DEMOCRACY— where every citizen votes and debates on every law to be passed. • Only males who owned property were considered to be citizens—people who could participate in government. Democracy in the U.S. • The U.S. has a REPRESENTATIVE DEMOCRACY. A direct democracy wouldn’t work in the U.S. because our population is too large—it is not practical for all citizens to debate and vote on every single law to be passed. • Citizens elect representatives to debate and vote on issues for them. • Some officials create laws (legislative), enforce laws (executive), and others are judges (judicial) • Men and women (over the age of 18) have the right to vote Juries in Athens • Juries in Athens often had an odd number of people serving on them to prevent ties. Outside Meetings in Greece • Since Athenians wanted to be sure all citizens could attend, and because it took 6,000 people to create an assembly, meetings would be held outside. • Every citizen had the right to speak and debate on issues as they wanted. Greek Myths • The Greeks created a body of mythology to help explain how the world worked. • For example, the Greeks believe there are different seasons because Demeter is separated from her daughter, Persephone for six months. When Persephone is with Hades, it is fall and winter, when she is reunited with her mother Demeter, it is spring and summer. Greek Myths in Our Culture • Colleges and pro sports teams are named for characters in Greek mythology (USC Trojans, MSU Spartans, Tennessee Titans) • The Olympics, originally held to honor Zeus, are still held every 4 years. • Phrases such as “Achilles Heel” and “Titanic” are still part of the English language. Homer • Homer wrote The Iliad and The Odyssey. • His epic poetry was the basis for much of the Greek education system. Lyrical Poetry • Lyrical poetry is poetry set to music. • Named for the LYRE—a common Ancient Greek instrument • Sappho was a famous lyric poet in Ancient Greece Aesop • Aesop was a Greek writer known for his fables • Fables are stories that teach lessons to the reader. • Animals are typically the main characters (personification) Obvious Influence of Greek Culture • Our language—many of the root words in our language come from the Greeks. • “Democracy,” = Remember “dem people” Greek Gods and Goddesses (p. 20 in your Interactive Notebook) • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Zeus = king of the gods Hera = queen of the gods Poseidon = sea Hades = Underworld Demeter = agriculture Hestia = hearth Athena = wisdom Apollo = sun Artemis = moon Ares = war Aphrodite = love Hephaestus = metalworking Dionysus = celebration & wine Hermes = messenger Three Key Greek Heroes • Theseus = killed the minotaur in the labyrinth • Jason = sailed the Argo with his sailors, the Argonauts. Basis of Homer’s Odyssey • Hercules = Most famous—killed the Hydra as well as performed many other “impossible feats.”