Bacteria - wsscience
advertisement

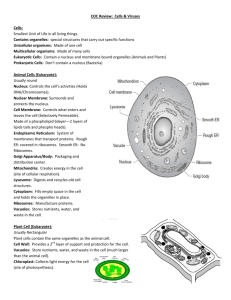
Bacteria Prokaryote – single celled with no nucleus • Eubacteria – peptidoglycan (a carbohydrate) cell wall • Archaebacteria – cell wall of lipids, no peptidoglycan in the cell wall Identifying Prokaryotes • Shape a. bacilli – rod shaped b. cocci – spherical shaped c. spirilla – corkscrew shape http://biology.clc.uc.edu/graphics/bio106/bacteria.jpg Identifying Prokaryotes • Cell Wall – use gram stain i. gram positive has peptidoglycan wall ii. gram negative has no peptidoglycan wall • Movement – may or may not move >flagella >lash, snake, or spiral forward >glide on slime like secreted layer Metabolic Diversity • Heterotrophs: chemotrophs & photoheterotrophs • Autotrophs >photoautotrophs – ex. Cyanobacteria http://steel.ced.berkeley.edu/cris/ hiddenecologies/HE/wp-content/uploads/ 2006 Metabolic Diversity • >chemoautotrophs – energy from chemical reactions is used to make food (from ammonia, hydrogen sulfide (H2S), nitrites, sulfur, or iron) Growth & Reproduction • Binary fission http://www.biology-resources.com/drawing-amoeba-reproduction.html Growth & Reproduction • Conjugation http://americanscientist.org/Libraries/images/thumbnail/20033711443_307.gif Growth & Reproduction • Spore Formation: structures of DNA & some cytoplasm (formed when conditions were unfavorable for growth) remain dormant for months or years until the right conditions exist http://ppdl.purdue.edu/PPDL/images/ daylily_rust_spores400x.jpeg Importance of Bacteria • Decomposers – recycle nutrients & maintain equilibrium • Nitrogen fixers – change nitrogen gas into useable compound plants can use www.windows.ucar.edu/earth/climate/images/ nitrogencycle.jpg Importance of Bacteria • Human use – make food & beverages, clean up oil spills, remove waste products from ground, synthesize drugs & chemicals, make vitamins our bodies need (E.coli in large intestine) www.javno.com/slike/slike_3/r1/g2007/ www.fotosearch.com/LIF145/pdb07006/ http://library.thinkquest.org/J002755/graphics/vitamins.gif Viruses • Virus: particles of nucleic acid, protein, & sometimes lipids (typically DNA or RNA core with a protein coat) >only reproduce by infecting living cells >use living cells to make more viruses Image by Karsten Schneider/Science Photo Library Viruses • Capsid: protein coat of a virus >capsids bind to cell host & “trick” the cell to let the virus inside the healthy cell • Bacteriophages: viruses that only infect bacteria Viral Infection • Lytic – virus enters a cell, makes copies of itself, & causes the cell to burst • Lysogenic - virus combines its DNA with the host cell and the viral DNA replicates with the host’s DNA Viral Infection Retroviruses • Viruses that contain RNA • Named retro because they copy genetic information from RNA to DNA (usually genetic information is copied from DNA to RNA Retroviruses HIV VIRUS • www.chm.bris.ac.uk/.../levasseur/images/hiv.GIF The “take-home” message • STAY HEALTHY • WASH YOUR HANDS, ETC.