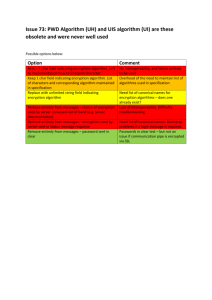
Presentation Outline
advertisement
Chapter 3 Electronic Commerce I’m not sure I want anything to do with the world-wide web. Presentation Outline I. Electronic Commerce II. Security for Electronic Commerce III. Security Issues for Public Key Encryption Systems IV. Encryption Technology in Electronic Commerce V. Assurance and Privacy in E-Commerce Transactions I. Electronic Commerce A. Three Categories of Networks B. The Internet C. Intranets D. Client Server Technology A. Three Categories of Networks Local Area Networks (LANs) – Network spanning a single site. Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs) – Networks spanning a single city or metropolitan area. Wide Area Networks (WANs) – Networks that span at least two metropolitan areas. B. The Internet Electronic highway with no central command or control structure. TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) IP (Internet Protocol) TCP is a protocol for dividing electronic messages into packets of information and then reassembling these packets at the receiving end. IP addresses specify the location of a computer on the internet. Alias names are often used in place of IP addresses. www.bodhop.ais vs. 131.91.120.68 C. Intranets In-house networks that use internet type protocols. Firewalls limit access from outsiders by filtering incoming information to be sure it is from an authorized source (often certain IP addresses). Proxy servers are typically used on the inside of a firewall to serve as filters for all outgoing requests for information. For example, blocking employee access to a game site. D. Client-Server Technology A server is a robot-type program that constantly runs on some computer and exchanges information with users (clients) who request it. Examples include: FTP servers for exchanging files Web servers for browsing the World Wide Web Mail servers Commerce servers for secure business transactions II. Security for Electronic Transactions Encryption involves using a password or digital key to scramble a readable message into an unreadable message. Types of encryption systems include: A. Secret Key Encryption B. Public Key Encryption C. Hybrid Systems or Digital Envelopes D. Digital Signatures E. Digital Time Stamps A. Secret Key Encryption Message Sender Recipient Secret key is used for both encrypting and decrypting message. Problem is that the secret key may be intercepted while it is being transmitted to the recipient. B. Public Key Encryption Message Sender encrypts message with recipients public key. Recipient decrypts message with their own private key. A message is encrypted using the recipient’s public key. Only the recipients private key can decrypt it. Removes problem of having to send a secret key along with the message. C. Digital Envelopes (A Hybrid System) After encoding the message, the secret key is encoded with recipient’s public key. Message Sender Recipient Secret key is used for both encrypting and decrypting message. The recipients public key is used to encrypt the secret key. No one can use the secret key to open the message unless they have a copy of the recipient’s private key to decode the secret key. D. Digital Signatures A digital signature occurs when someone encrypts a message with their own private key. Anyone can use that person’s public key to determine that they sent the message. May also make use of a message digest (see page 79) E. Digital Time Stamps The message to be digitally time stamped is digested, and the digest is sent to a digital time-stamping service (DTS). The DTS attaches a time-stamp to the digest and then adds its digital signature to the two. Anyone can verify the date by decrypting the digital signature of the DTS using its public key. With this approach, the DTS timestamps the message without learning its contents. III. Security Issues For Public Key Encryption Systems A. Cryptanalysis B. Key Management C. Ways in Which Company Privacy May Be Violated. A. Cryptanalysis Cryptanalysis involves the analyzing of encrypted messages in an attempt to decode them without legitimate access to the keys. B. Key Management Each user should create their own public and private keys. Certifying authorities should issue digital certificates attesting that a particular public key belongs to a certain person or organization. All keys should have an expiration date so hackers will not have time to figure out how to break the key’s coding. Certificate revocation lists provide lists of public keys that have expired before their expiration date. A certificate signing unit is a tamperproof box for storing private keys. Contents are destroyed if box is tampered with. C. Ways In Which Company’s Can Be Violated Encrypted messages can be decoded by guessing the plaintext code. Attacker checks guess by using the intended recipient’s public key to encode the guess to see if it matches the encoded message. Factoring attacks breaking prime number codes. Computers that contain sensitive key information can be broken in to. Former employees may use keys that have been discontinued. IV. Encryption Technology in Electronic Commerce A. Digital Cash B. Blinded Digital Cash C. Virtual Cash on the PC D. Virtual Cash in Electronic Cards E. Virtual Private Networks A. Digital Cash Digital cash is created when a bank attaches its digital signature to a note promising to pay the bearer some amount of money. The digital signature may include: Bank’s name and address Dollar value of note Unique serial number Date of note creation Expiration date of note B. Blinded Digital Cash Blinding permits a bank to issue digital cash so that it is unable to link the payer and payee. Blinded Note 1. Alice creates a note that includes a blinding factor S.N. 22222 2. Bank Signs Note Alice 3. Bank returns note to Alice after attaching a digital signature. S.N. 22222 4. Alice removes the blinding factor before spending the note. Bank’s Digital Signature S.N. 11111 Bank’s Digital Signature C. Virtual Cash on the PC User acquires digital cash (from a financial institution), which is then stored in the electronic wallet. Money is received or spent out of the wallet. D. Virtual Cash in Electronic Cards Memory cards – cash balance is stored and and updated using the card. Shared-key cards – a card using secret-key encryption for all communications. Signature transporting cards – a form of shared-key card in which digital cash notes are transferred to the register upon payment. Signature-creating cards – cards allowing the generation of digital signatures for the purpose of writing electronic checks. E. Virtual Private Network Private Network Decryption Encrypted messages over the Internet Remote Users Plaintext Messages Encryption A virtual private network (VPN) combines encryption technology with Internet communications to allow remote users belonging to a private network to communicate securely over a public network such as the Internet. Remote users first pass through a type of hardware or software gateway that automatically encrypts and decrypts data. Sending or receiving data over a VPN is known as tunneling. V. Assurance and Privacy in E-Commerce Transactions A. Procedures for Transaction Processing B. E-Commerce and Privacy A. Procedures for Transaction Processing CPA’s and CA’s may undergo specialized training to evaluate websites for WebTrust. The WebTrust symbol on a website provides assurance regarding: 1. Information protection – merchant follows its policies and procedures for protecting private customer information. 2. Business practice disclosure – merchant adequately discloses its business practices. 3. Transaction integrity – merchant follows procedures to ensure proper user identification, validation, data accuracy, completeness, and timeliness. There is also proper disclosure of all billing and shipping terms.. B. E-Commerce and Privacy Merchants can place cookies (merchant site information) on your computer when you visit their web site. Merchants can also examine cookies on a person’s computer to discover other web sites that a person has visited. I can tell you the web sites this computer has visited. Summary Network categories, internet, intranet, client servers Encryption and cryptanalysis The Use of Encryption in E-Commerce (digital cash, virtual cash, virtual private networks) WebTrust Cookies