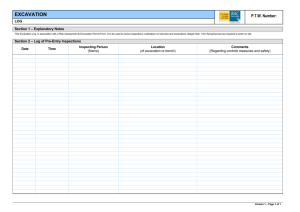
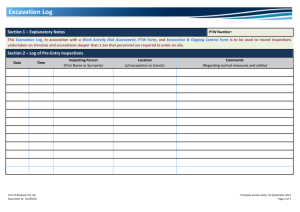
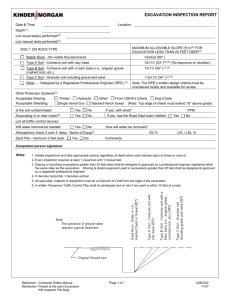
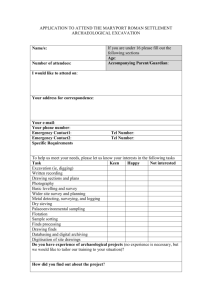
Excavation & Shoring Course
advertisement

Unit Unit Unit Unit Unit Unit Unit Unit Unit Unit 1: 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: 7: 8: 9: 10: Introduction The Need for Excavation Training Controlling Excavation Risks Overview of Excavation Personal Protective Equipment and its’ Use Considerations for choosing a Method of Excavation Site Inspection Work Plans Backfilling Summary Headings: Welcome House Keeping Overview Course To provide personnel with the knowledge and skills to be regarded as the Competent Person as described in the Bechtel SWPP 4MP-T81-03202 Explain the need for excavation training Identify the WH&S Act and Regulation Describe the process for controlling excavation risks Describe the purpose of a “Work Plan” IAW SWPP 4MP-T8103202 Identify the major steps of an excavation Describe the process for dealing with staff who refuse to use appropriate PPE Describe the requirement for the conduct of site inspections Identify factors that affect the stability of an excavation Describe the backfilling process in accordance with SWPP 4MPT81-03202 An Excavation is any man-made cut, cavity, trench, or depression in the earth’s surface formed by earth removal. A trench is a narrow underground excavation that is deeper than it is wide, and no wider than 15 feet (4.5 meters) A man has been rescued from a trench that collapsed in Melbourne's south-east earlier this morning. The 35-year-old construction worker spent almost two hours buried waist-deep in soil on a new estate in Pakenham. Fire crews were called to the scene just before 9am and used special equipment to dig out the man and stabilise the surrounding soil. (The Age – August 11, 2012) When one looks at the cross section of a grave and an unsafe trench of similar dimensions, it can be seen that there is very little or no difference Considering that a cubic metre of earth weighs approximately one tonne, it would certainly make it difficult for the work-person in the trench to breathe with that load resting on him Soil type Water content in soil Weather conditions Pressures – from near by loads Vibration – from passing heavy vehicles Time Rock/clay seam No shoring system used Timber not strong enough Timber badly placed CP218 Excavation and Trenching WH&S Act 2011 WH&S Regulation 2011 SWPP 4MP-T81-03202 Site Excavation and Backfill Act (2011) o Imposes obligations on people at work places to ensure freedom from disease and injury to persons created by work places or activities. Regulation (2011) o You must do what it says CP218 States that it is a requirement at all projects to implement a procedure that provides effective safety measures and methods to protect personnel who are required to work in and around excavations and trenches SWPP - 4MP-T81-03202 Site Excavation and Backfill Defines the standard work process for earthwork related activities at the construction site. It also defines a “Competent Person” The Queensland Workplace Health and Safety Regulation defines a confined space confined space as an enclosed or partially enclosed space that: (a) is not designed or intended primarily to be occupied by a person; and (b) is, or is designed or intended to be, at normal atmospheric pressure while any person is in the space; and (c) is or is likely to be a risk to health and safety from: ◦ (i) an atmosphere that does not have a safe oxygen level; or ◦ (ii) contaminants, including airborne gases, vapours and dusts, that may injury from fire or explosion; or ◦ (iii) harmful concentrations of any airborne contaminants; or ◦ (iv) engulfment cause NB# - All of the above three (3) elements must be met to be considered a Confined Space DOES NOT INCLUDE A MINE SHAFT OR THE WORKINGS OF A MINE. A competent person is a person who has acquired through training, qualification or experience the knowledge and skills to carry out the task. This person should be knowledgeable on: the type of excavation being undertaken, appropriate control systems, and where possible should have experience relating to local soil and rock conditions The CP is the individual on the construction team who is capable of identifying existing and predictable hazards in the surroundings, or working conditions that are unsanitary, hazardous or dangerous to employees and who has the authorisation to take prompt corrective measure to eliminate them. The Competent person is responsible for: • Hazards in the surroundings, or working conditions that are unsanitary, hazardous or dangerous to employees and who has authorization to take prompt corrective measures to eliminate them • identifying hazards, • conducting daily inspections, • monitoring water removal operations and conducting inspections during and/or following rainstorms. • The CP is designated as being responsible for completing the Daily Trench Report, as outlined in BESH Core Process CP-218, Excavation and Trenching. • daily trench safety report form.doc Systematic review Communication tool PFE determines criteria for work operations requiring permit Client Excavation Permit may also be required (reviewed by all parties) Approved prior to commencement of work Permit Register Sequential Permit Number site excavation permit.doc START Site inspection and preparation Is the excavation 1.2m or greater? Y No person is to enter excavation Responsible Field Engineer to organise shoring, battering or benching N Is the ground unstable or prone to collapse? Method of stabilisation complete Y N Are there other circumstances posing threat of collapse. E.g.., structure, vibration etc. N BECHTEL SWPP 4MP-T81-0302 to be followed Competent person to routinely inspect excavated site Y Personnel can enter excavation Complete work in excavation Backfill END Minimise access of persons to an excavation Inspections Shore, batter or bench excavations where the soil or rock is unstable or prone to collapse, where these could cause injury to a person or deeper than 1.2m Access/Egress Management Control of risk by supervision and control of work Barricades The zone of influence: The volume of soil around the excavation affected by any external load (for example, vehicles, plant, excavated material). It is the zone in which there may be an influence on the excavation, including possible ground collapse – Site requirement for spoil material is 1m from edge of trench Determined by the supplier of the shoring or a Geo Technical engineer Depends on the ground conditions The zone in which there may be an influence on excavation Includes possible ground collapse Considerations in Planning: The nature & type of Rock/ Soil Duration the Excavation will be open Proximity of Buildings Likely presence of Water-Seepage/ flooding Underground Water Table Size and profile of excavation Likely existence of filled land Method of excavation Proximity of underground services Previously dug trenches Surcharge on side of excavation (eg. plant ) Excavation across slopes Potential site conditions (eg. bedding planes, fissures) Vibration from vehicles Proximity of excavated material Rain The Responsible Field Engineer will check this prior to permit approval Typically a drawing showing utilities near excavations is provided Additional controls as required to put in place i.e., digging by hand It is important that excavation methods include an initial examination of the area to be excavated, for example sampling the area by exposing a short section of underground services usually using water pressure and a vacuum system to excavate or ‘pothole’ the area Underground essential services exposed by ‘potholing’ Complete as much work from outside the trench as possible Minimise the time the trench is open Barricade and sign - Especially unattended excavations Material on high side could fall into trench Dangerous Situation Shear Plane Failure Worker trapped and crushed Worker smothered When the trench is greater than 1.2m in depth , shoring, battering or benching is mandatory If less than1.2m, shoring, battering or benching required if the trench walls unstable Person Conducting Business or Undertaking (PCBU) with management or control of a workplace where excavation work is to be carried out must: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Obtain current underground essential services information (if applicable) Have regard to the information Provide the information to other duty holder involved in the work Manage risks to health and safety associated with excavation work Comply with specified controls for trenches at least 1.2 metres deep Complete Excavation Permit Conduct daily inspections Proprietary systems (IAW AS 4744.1 – 2000) ◦ Shorco boxes installed, used, maintained and dismantled in accordance with manufacturer’s specifications Non-Proprietary Systems ◦ designed by an engineer ◦ Meets all safety requirements ◦ installed by trained personnel No gaps between edge of trench & shoring Benching ◦ The creation of a series of steps in the vertical wall of an excavation ◦ Steps no greater than 1.2m in Bechtel ◦ overall angle 45 degrees or less Batter ◦ The wall of an excavation is sloped back to a predetermined angle ◦ The wall beside the work area should not exceed 1.2m in Bechtel ◦ Overall angle 45 degrees or less Batter Combination of Bench and Batter • The angle at which a sloping bank of soil or rock will stand without lateral support • The angle of repose should not exceed 45 degrees unless certified by an engineer in writing Types of Soils ◦ Granular Soils ◦ Cohesive Soils ◦ Silts Soil faults ◦ Fissures ◦ Greasy Backs Decide which side of the excavation to place the excavated material if ground is sloping Things to consider: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Access Underground services Earth moving machinery of vehicles Service installation and backfilling Manual work Upper and lower side of excavation If soil is quite dense (hard to shovel) then type A If soil is loose (easy to shovel) then type B Wet / moist sand is considered type C Loose sand subject to any vibration is considered type C General Notes: If layered soils, then classify by weakest layer If two or more layers of distinctly different soil or rock types or clay seams in rock which dip towards the trench with a slope of 4 Hor. To 1 vert. then consider type C Fractured rock is considered type B when dry or type C when wet All rock is considered fractured unless tests and inspections prove otherwise Gravel, sand, or silt, (coarse grained soil) with little or no clay content. Granular soil has no cohesive strength. includes sands and gravels particles are visible feel gritty contains little or no fines Sticky soil such as clay or clayey silt whose strength depends on the surface tension of capillary water If fissures are detected or suspected then a type A soil becomes type B Contains clay either wholly or in part (70% clay content) Includes clay, silty clay, organic clay, gravelly clay, sandy clay, clayey silt, etc. Contains sufficient clay to mould a moist lump without it disintegrating Clays when moist to wet feel sticky and often greasy If dry clay can be broken by hand but not powdered Contains clay either wholly or in part (70% clay content) Includes clay, silty clay, organic clay, gravelly clay, sandy clay, clayey silt, etc. Contains sufficient clay to mould a moist lump without it disintegrating Clays when moist to wet feel sticky and often greasy If dry clay can be broken by hand but not powdered Silt is created by a variety of physical processes capable of splitting the generally sand-sized quartz crystals of primary rocks by exploiting deficiencies in their lattice When in dry, powdered form- it feels fine and flour like (possibly a bit gritty) and often stains the hand When wet the soil does not feel sticky Dry lumps can be easily powered between fingers Visual examination prior to excavation Visual inspection when trench first dug and appearance after excavation observing chunks of soil spall Visual observation for fissures parallel to the direction of the trench Ladders or a means of egress shall be provided every 7.6m (25 feet) Stay within controlled area Do not walk on shoring components Wear PPE Barricades and signs Excavation depth greater than 6 meters designed by a registered professional engineer. Control of Access ◦ Control of people around excavation site Signage and barricading Unattended excavations ◦ Ensure staff within protected area Routine Inspections ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ carried out by a competent person for excavations deeper than 1.2 meters before work in the excavation and during work in a trench if deficiencies detected: cease work immediately & staff should not enter trench until rectification has been carried out Shoring becoming unstable Shoring components not secure Premature removal of shoring Cracks appearing near or parallel to the edge of an excavation Excavated material being placed close to the edge of the trench Machinery operating close to the edge of the excavation Surface falling into the trench Water seeping into excavation from side walls or base Surface water entering the excavation or accumulating on the surfaces near the excavation Inclined bedding planes “dipping” into the excavation Heaving or swelling of the ground at the bottom of the trench Subsidence along side the excavations After a rain event Hazard Identification Risk Assessment ◦ Probability ◦ Severity Risk Control ◦ Eliminate the Hazard ◦ Minimise the Risk Provide “back-up” controls ◦ Administrative controls, safe work practices & PPE Monitor & Review Control Measures ◦ Audits ◦ A written record should be kept (the work plan) Employer Prevent the risk of injury to all personnel Monitoring of work activities Training as required Develop Work Procedures Worker Prevent the risk of injury to yourself from collapsing excavations Comply with instruction given by your employer Ensure your activities do not place other persons at risk Visitor A person not directly engaged in excavation work Must carry out a health or safety direction given by an employer or self employed person The process of excavating An overview of Site Excavation and backfill SWPP 4MP-T81-03202 Obtain a signed excavation permit Personal Protective Equipment Site Inspection and Preparation ◦ Site Inspection Locate services ◦ Barricade and sign the site ◦ ◦ Hand/ Machine Shoring Excavate Bedding / Backfilling Restoration SWPP 4MP-T81-03202 on Bechtel Website Workers' responsibility under the act. PPE required for an excavation Safety Absolute ◦ Hard Hat, Safety Boots, Safety Glasses and Gloves Dealing with Workers who refuse to use PPE Request compliance Stop work Request worker to leave work site Log the event in diary Report incident to ES&H Representative for further action Hand Excavation Machine Excavation Shallow trenches Locations where a machine can not be used Pot holing Cleaning of trenches Excavator: Larger trenching systems; larger pipes; rock breakers; Shorco Boxes; Greater Reach of Machine; Largest Cost Beware Blind Spots Backhoe: Smaller trenches; Better Access; Variety of Trenches; Multi-purpose Mini excavator: Smaller/ shallow trenches; Good Access; Lowest Cost; Less Restoration What is a Site Inspection? How to Conduct a Site inspection for an Excavation Provides on-going safety monitoring Helps identify non-compliance and potential safety risks Assists in the implementation of hazard control strategies Conduct Site Inspection ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Assess Site Conditions Work and Storage Space Locate Other Services Night Work First Aid and Emergency Why is a Work Plan Needed? ◦ To ensure that all labour, equipment, materials, and methods are identified and coordinated to maximum efficiency while meeting construction schedule requirements The RFE shall inspect, test as required, and accepted Upon acceptance, the RFE shall release the area for backfill The excavation shall be cleaned The RFE shall inspect and accept the sub-grade for backfill The RS shall inspect stockpile areas Restoration of site Headings: What has been covered ◦ The Need for Excavation Training ◦ Controlling Excavation Risks ◦ Overview of Excavation ◦ Personal Protective Equipment and its’ Use ◦ Considerations for choosing a Method of Excavation ◦ Site Inspection ◦ Work Plans ◦ Backfilling Using the learning's on site Do you have any questions?