English 11
advertisement

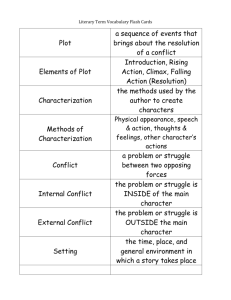
English 11 Literary Terms: Short Stories #32. Setting Setting is the TIME and PLACE of the story Setting is key to establishing MOOD or EMOTION in a story #46. Plot Plot is what happens in a story See your plot chart notes for details of how a plot works 26. Point of View The point of view of a story refers to who is telling the story. First Person: Narrator uses “I” Second Person: Narrator uses “you” Third Person/Limited Omniscient: A god-like narrator who follows the thoughts and feelings of one character. Uses “he” or “she” Omniscient: God-like narrator who knows the thoughts and feelings of all characters Dramatic/Objective: The story is told through the actions and dialogue of the characters 12. Irony Irony is when what happens is the opposite of what is expected. There are a few kinds of irony. Dramatic Irony: The audience knows something that the character does not. Verbal Irony: When the opposite of what is meant is said (basic form: sarcasm) Situational Irony: when the opposite of what was expected happens. Dramatic Irony: You know what the farmer does not Situational Irony: You’d expect cheetahs to run, not speed-walk. Which kind of irony is this? 16. Narrator The teller of the story An unreliable narrator is a story teller whose story may be biased and whose views cannot be trusted by the reader 5. Conflict Conflict is the problem of the story Two types: External and Internal External: Person vs. Person Person vs. Nature Person vs. Society Internal: Person vs. Self 39. Theme Theme is the overarching idea or message meant to be communicated to the reader When written about in formal writing, theme should always be communicated as a statement. Eg. One must open one’s heart to love 38. Symbol A symbol is a person, object, or thing in a piece of writing that represents an idea, concept or emotion. Eg. Lion for courage Symbols may take on different meaning depending upon the context in which they appear 11. Imagery Imagery is the language in a piece of writing that appeals to the five senses. Sight, sound, touch, taste, smell 3. Character A character is the player of the story. Round: Many traits are described Dynamic: The character grows and changes in the course of the story Flat: Few traits are described Static: The character does not grow or change in the course of the story. 37. Style Style can be described as the way that an author writes and the way that they express their ideas Includes the author’s use of figurative language, their sentence length and variation, their diction etc.