AP Biology Name___________________ Transpiration Lab
advertisement

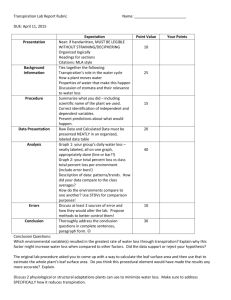
AP Biology Name___________________ Transpiration Lab Objectives: In this laboratory, students will: -Understand how water moves from roots to leaves in terms of the physical and chemical properties of water and the forces provided by differences in water potential. -Understand the role of transpiration in the transport of water within a plant. -Understand the structures used by plants to transport water and regulate water movement. -Test the effects of environmental variables on rates of transpiration using a controlled experiment. Introduction: The amount of water needed daily by plants for growth and maintenance of tissues is small in comparison to the amount that is lost through the process of transpiration. Transpiration is the evaporation of water from plant surfaces. If the water that is lost from aerial plant parts is not replaced by water transported up from the plant roots, the plant will wilt and eventually die. Water is transported up from plant roots in the xylem. Other structures involved in this process are the stomata of leaves, each of which is surrounded by two guard cells. The stomata of a leaf open into the air spaces that surround the mesophyll (middle) cells of the leaf. Water evaporates from the leaf surface, a process called transpiration. As water leaves the leaf, it pulls additional water molecules to the surface due to hydrogen bonding between the molecules. Since the opening of stomata, which allows transpiration to occur, is also required for the entry of CO2 used in photosynthesis, a balance must be maintained between the two processes by regulating the opening and closing of stomata on the leaf surface. Many environmental conditions, including those conditions that influence the opening and closing of stomata, will affect the rate of transpiration. Increases in temperature, light intensity, and the presence of dry air currents can increase the transpiration rates. A humid environment usually slows the rate of transpiration. In this exercise, you will measure the rate of transpiration over time with potted plants. Procedure: 1. Moisten the root ball of the plants you are given completely. Let the excess water drain out. 2. Wrap the entire root ball in a plastic bag, snug it up to the stem with string, and mark with your group name. 3. Weigh the mass of each plant with an electronic balance and record on data table. 4. Place one plant in each of the various conditions: Classroom, Lighted Environment, Dark Environment, Near a Fan Blowing Air, Misted Aquarium. 5. Weigh each successive day for one week. 6. Note: If your plant blooms, be sure any leaves or blooms that fall off are put back in the center of the plant to be weighed each day. Otherwise, their mass will be represented in your data as water loss. 7. Hint: Write the mass of the plant and bag on the plastic bag each day so data will not get “lost” during the week. 8. Calculate the amount of surface area for each plant by calculating it for one leaf in cm 2 for one leaf and extrapolating to the entire plant by counting the number of leaves. 9. To determine % water loss each day, subtract the mass from the Day 1 mass. Then, divide this by the total mass from Day 1 X 100. Hypothesis:_________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Data Table: Mass of Plants, grams Name of Plant Used in Experiment: _____________________________________ Environmental Day 1 Condition: Classroom Dark Light Blowing Air Humidity % Water loss/day: Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Day 5 Day 6 Day 7 Data Table 2: Surface Area of Plants Environmental Condition Classroom Surface Area of 1 Leaf: cm2 Total Number of Leaves in Plant Total Surface Area Dark Light Blowing Air Humidity Data Table 3: Cumulative Water Loss in cm2 Environmental Condition Classroom Total Water Loss in 7 Days Water Loss in g/cm2 Dark Light Blowing Air Humidity Analysis Questions: 1. Which treatment best serves as a control for this experiment? Why? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Explain how each of the experimental conditions causes an increase or decrease in transpiration compared to the control. Treatment: _________________ Effects: ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Treatment:__________________ Effects: ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Treatment: ___________________ Effects: ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Treatment: ____________________ Effects: ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3. What are disadvantages to a plant keeping its stomates closed? Explain ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 4. What are some adaptations that enable plants to reduce water loss from their leaves? Include both structural and physiological adaptations. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________