Yohimbe influence on a mammalian stem cell line
advertisement

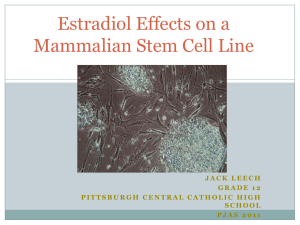
Yohimbine Influence on a Mammalian Stem Cell Line Patrick Leech Pittsburgh Central Catholic High school Grade 11 PJAS 2011 What is Tissue Engineering • An interdisciplinary field that applies the principles of engineering and life sciences toward the development of biological substitutes that restore, maintain, or improve tissue function or a whole organ. Principles of Tissue Engineering Stem Cell Overview • unspecialized cells capable of renewing themselves through cell division • under certain physiologic or experimental conditions, they can be induced to become tissue- or organ-specific cells with special functions • stem cells offer new potentials for treating diseases such as diabetes and heart disease C2C12 Stem Cell Line • Subclone of the mus musculus (mouse) myoblast cell line. • Mouse stem cell line is frequently used as a model in tissue engineering experiments. 1. Differentiates rapidly, forming contractile myotubes and produces characteristic muscle proteins. 2. Useful model to study the differentiation of nonmuscle cells (stem cells) to skeletal muscle cells. Variable Yohimbine • Corynanthe yohimbine- a psychoactive plant which contains the tryptamine alkaloid yohimbine • main active chemical present in yohimbe bark is yohimbine HCl (indole alkaloid), found in the bark of the Pausinystalia yohimbe tree. • Strong stimulant, effects both norepinephrine and epinephrine pathways and modulates feedback loops. • Several uses such as a weight loss supplement, blood pressure boosting agent, and most importantly a muscle supplement. • Purpose • To examine the effects of Yohimbine on the proliferation, differentiation, and survivorship of normal C2C12 cells. Hypothesis • Null Hypothesis: The addition of Yohimbine WILL NOT significantly affect the proliferation, differentiation, and survivorship of C2C12 stem cells. • Alternative Hypothesis: The addition of Yohimbine WILL significantly affect the proliferation, differentiation, and survivorship of C2C12 stem cells. Materials • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Cryotank 75mm2 tissue culture treated flasks Twenty 25 mm2 tissue culture treated flasks Fetal bovine serum (FBS) C2C12 Myoblastic Stem Cell Line Trypsin-EDTA Pen/strep Macropipette + sterile macropipette tips (1 mL, 5 mL, 10, mL, 20 mL) Micropipettes + sterile tips DMEM Serum - 1% and Complete Media (4 mM L-glutamine, 4500 mg/L glucose, 1 mM sodium pyruvate, and 1500 mg/L sodium bicarbonate + [ 10% fetal bovine serum for complete]) 75 mL culture flask Incubator Nikon Inverted Compound Optical Scope Aspirating Vacuum Line Laminar Flow Hood Laminar Flow Hood UV Sterilizing Lamp Labeling Tape Yohimbine Hemocytometer Sterile PBS Ethanol (70% and 100%) Distilled water Procedure Stem Cell Preparation • • • A 1 mL aliquot of C2C12 cells from a Cryotank was used to inoculate 30 mL of 10% serum DMEM media in a 75mm2 culture flask yielding a cell density of approximately 106 to 2x106 cells. The media was replaced with 15 mL of fresh media to remove cryo-freezing fluid and incubated (37° C, 5% CO2) for 2 days until a cell density of approximately 4x106 to 5x106 cells/mL was reached. The culture was passed into 3 flasks in preparation for experiment and incubated for 2 days at 37° C, 5% CO2. Procedure Day 0 After trypsinization, cells from all of the flasks were pooled into 1 common 75mm2 flask (cell density of approximately 1 million cells/mL). 0.1 mL of the cell suspension was added to 20 25 mm2 tissue culture treated flasks containing 5 mL of DMEM (com) media, creating a cell density of approximately 105 cells per flask. The 1 M stock solution of Yohimbine was created using 1 mL of sterile dilution fluid (PBS) and 0.28842 grams of Yohimbine. The 10-6 M, and 10-8 M concentrations were created from the stock, where 10-8 M is the suggested working concentration of the drug. The 2 experimental groups and the control group were created by adding: 20 µl of the 10-6 M solution to 1 flask 20 µl of the 10-8 M solution to 1 flask 20 µl of PBS to 1 flask (Control) The cells were incubated at 37°C, 5% CO2 for the remainder of the study. Two flasks from each group were used in the Proliferation Experiment and two flasks from each group were used in the Differentiation Experiment. Procedure Proliferation • Day 1 and Day 3 • Using one flask from each group, cell densities were determined as follows: • The cells were trypsinized and collected into cell suspension. • 25 µl aliquots were transferred to a Hemocytometer for quantification (4 counts per flask). • Day 1 and Day 3 • Using the Nikon Inverted Microscope, images of eight representative areas of each flask were taken. Day 1 and Day 6 Using the Nikon Inverted Microscope, images of eight representative areas of each of the flasks were taken. Day 2 The original media was removed and replaced with 1% DMEM media (serum starvation) to induce myotube differentiation. Result of Proliferation Assay P-value 5.81E-12 2500000 Cell Count (Cells/flask) 2000000 1500000 Day 1 Day 3 1000000 500000 0 Control - 10^6 conc Concentrations - 10^8 conc Statistical Analysis • ANOVA • Compares the variation within groups to variation between groups • If p-value is <0.05 reject the null hypothesis • P-value 5.81E-12 therefore the null hypothesis is rejected • Dunnett’s Test • Compares each individual experimental group back to the control • T-critical in this experiment is 3.03 Dunnett’s Test Concentration T- Critical Variation 10^-8 19>3.03 Significant 10^-6 179>3.03 Significant Control (Differentiation) • Day 1 Day 6 10^-8 Differentiation • Day 1 Day 6 10^-6 Differentiation • Day 1 Day 6 Conclusion • Proliferation From the ANOVA and the subsequent Dunnett’s test, the addition of Yohimbine induced a statistically significant increase in proliferation in the C2C12 cells in both concentrations. Differentiation From the qualitative analysis of the images gathered from the flasks, it appears that the addition of Yohimbine induced myotubule formation. Limitations and Extensions • Limitations • Differentiation • purely qualitative • Solution- quantitative differentiation assay (anti-body assay) ◦ CyQUANT™ Cell Proliferation Assay ◦ More quantitative than counting from a hemocytometer ◦ Extensions ◦ Use higher quantities of Yohimbine and use different kinds of muscle stimulants similar to it ◦ Trypan blue assay to determine if the cells are alive ◦ Anti-body assay Sources • Becker AJ, McCulloch EA, Till JE (1963). "Cytological demonstration of the clonal nature of spleen colonies derived from transplanted mouse marrow cells". Nature 197: 452–4. doi:10.1038/197452a0. PMID 13970094. • Ulloa-Montoya F, Verfaillie CM, Hu WS (Jul 2005). "Culture systems for pluripotent stem cells". J Biosci Bioeng • Adewumi O, Aflatoonian B, Ahrlund-Richter L, et al. (2007). "Characterization of human embryonic stem cell lines by the International Stem Cell Initiative” • Rosengren, A. H.; Jokubka, R.; Tojjar, D.; Granhall, C.; Hansson, O.; Li, D.-Q.; Nagaraj, V.; Reinbothe, T. M. et al. (2009). "Overexpression of Alpha2A-Adrenergic Receptors Contributes to Type 2 Diabetes". Science 327 (5962): 217–20 • Yonezawa A, Yoshizumii M, Ebiko M, Amano T, Kimura Y, Sakurada S (October 2005). "Longlasting effects of yohimbine on the ejaculatory function in male dogs". Biomedical Research 26 (5): 201–6. • Millan MJ, Newman-Tancredi A, Audinot V, et al. (February 2000). "Agonist and antagonist actions of yohimbine as compared to fluparoxan at alpha(2)-adrenergic receptors (AR)s, serotonin (5-HT)(1A), 5-HT(1B), 5-HT(1D) and dopamine D(2) and D(3) receptors. Significance for the modulation of frontocortical monoaminergic transmission and depressive states". Synapse 35 • Kaumann AJ (June 1983). "Yohimbine and rauwolscine inhibit 5-hydroxytryptamine-induced contraction of large coronary arteries of calf through blockade of 5 HT2 receptors". NaunynSchmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology 323