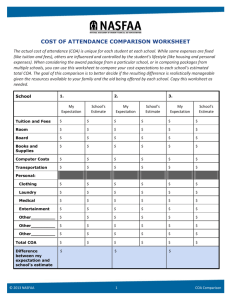
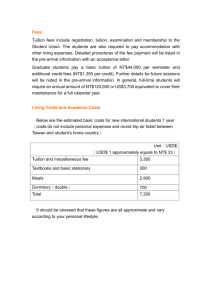
Cost of Attendance (COA)
advertisement

NCASFAA 2015 Fall Pre-Conference New Aid Officers Training Workshop Overview of Cost of Attendance Budget Creation, and Making/Documenting COA Adjustments Objectives • Identify eight allowable Title IV Cost of Attendance Components • Present overview of budgets based on enrollment and living arrangements, and allowable components for each • Discuss principles of budget construction and the process of creating student budgets 3 Cost of Attendance (COA) “The cost of attendance is the cornerstone of establishing a student’s financial need, as it sets a limit on the total aid that a student may receive for purposes of the TEACH Grant, Campus-Based Programs and Stafford/PLUS loans, and is one of the basic components of the Pell Grant calculation.” 4 Definition Cost of Attendance is an estimate of student’s educational expenses for the period of enrollment. COA (Cost of Attendance) – EFC (Expected Family Contribution) NEED (Financial Need) 5 COA Components Determined by law (Higher Education Act, Sec. 472) and are not subject to regulations by the Department – apply to all Title IV Aid Allowable Costs: • Tuition and fees • Books, supplies, transportation, and misc. personal expenses • Room and board • Dependent care expenses • Study abroad expenses • Disability expenses • Employment expenses for co-op study • Loan fees 6 Tuition and Fees • Actual or average tuition costs can be used • If overall average used for all students at the school, it must be weighted – Accounts for the number of students subject to each of the school’s different tuition charges • Tuition costs may differ for various categories of students 7 Books, Supplies, Transportation and Misc. Expenses An allowance for books, supplies, transportation, and miscellaneous personal expenses • May establish different categories for different circumstances • Allowances and exceptions should be documented • Reasonable allowance for documented rental or purchase of personal computer may be included for students attending at least half-time • Cost of rental or purchase of equipment, materials, or supplies if these are mandatory for all students in same course of study • Option to include one-time cost of obtaining a first professional license or certificate 8 Room and Board • Allowance (as determined by the institution) for room and board incurred by the student – Without dependents residing at home with parents – Without dependents residing in institutionally owned or operated housing – Living in housing located on a military base or for which a basic allowance is provided, only expenses for board may be included • Exception: include allowance for room for dependent students who are not living with parents, either on base or off base and receiving military housing allowance – All other students 9 Dependent Care • Dependent care allowance covers care during periods that include, but are not limited to class time, study time, field work, internships, and commuting time • Should be based on number and age of dependents • Should not exceed reasonable cost in community 10 Study-Abroad Expenses Include reasonable costs for study-abroad for student: • • Enrolled at least half-time In program approved for academic credit by home institution and concurrent enrollment at the home school Special costs may include: • • • • • Transportation Passport fee Immunization costs Administrative fees charged by institution or coordinating agency Additional cost for tuition and fees, room and board, and other relevant charges that exceed those costs assessed by home institution 11 Disability-Related Expenses Expenses include: • • • • Special services Personal assistance Transportation Equipment and supplies Expenses NOT included: • Special services provided by another agency • Services available and provided free of charge to student 12 Employment Expenses for Cooperative Education • Student must be enrolled at least half-time in co-op program • Employment expenses might include: – Uniforms – Tools – Special equipment – Commuting or transportation costs – Meals away from home – Any other costs incurred as a result of the work experience 13 Student Loan Fees • May use actual or average cost of loan fees • Student must be enrolled at least half-time • Non-federal student loan fees may be included • PLUS loan fees must also be included • If a loan is declined, loan fees must be deducted from COA to avoid over award 14 Cost of Attendance Allowances Telecommunications Programs Offered in whole or in part via Telecommunications • No distinction is made with respect to the mode of instruction • Based on the HERA, student enrolled in certificate and degree programs offered wholly or in part by telecommunications are eligible for Title IV aid – Includes short-term certificate programs of less than one year • Costs determined using standard COA components • For Pell Grant Program only, full-time full-year costs are used – Need to prorate upward costs for program of less than one academic year 15 Exceptions: Less Than Half-Time Students Cost of Attendance Allowances • COA components for less-than half-time students – Tuition and fees – Allowance for books and supplies – Transportation (not miscellaneous & personal expenses) – Allowance for dependent care expenses – Limited allowance for room and board for up to three semesters (or the equivalent) with no more than two of those semesters (or the equivalent) being consecutive 2014-2015 FSA Handbook (Vol. 3 Ch. 2) 16 Exceptions: Correspondence Study Cost of Attendance Allowances • COA components for correspondence study (must be part of associate, bachelor’s, or graduate-degree program) – Tuition and fees (may include books and supplies) • If cost of books and supplies are separate, they may also be counted – Travel, room, and board may ONLY be included if incurred in required residential program 17 Exceptions: Incarcerated Students Cost of Attendance Allowances • COA components for incarcerated students limited to – tuition and fees and – required books and supplies • Not eligible for FSA loans • Not eligible for Pell grants if incarcerated in a federal or state penal institution 18 Exceptions: Professional Judgment Cost of Attendance Allowances • Financial aid officer has authority to use professional judgment (PJ) on a case-bycase basis to adjust COA or the data used to calculate EFC – Adjustment reason must be fully documented in student’s file – Adjustment submitted to CPS via FAA Access or third-party software – Adjustment only valid at the school making it – Common reasons to adjust include: • • • • • Rent or actual housing charges Equipment, supplies, or other program-related expenses Technology expenses Dependent care Education-related travel 19 Period of Enrollment Pell Grant Program • COA is always based on nine-month period of enrollment for a full-time student, regardless of student’s actual period of enrollment and enrollment status – Costs must be prorated for any enrollment longer or shorter than nine months • Less than half-time – Only include COA components allowable – Components based on amount for full-time, full-year • Actual or average cost for group of similar students in same category may be used 20 COA Decision Factors Budget Components Budget Decisions Student Categories Tuition and fees depends on education level, enrollment status, state/county residence, program of study, course requirement for a computer, whether there is a cost for a 1st professional degree Books, supplies, transportation, personal expenses depends on education level, enrollment status, program of study, school or home residence Room and board depends on length of enrollment, school residence, enrollment status Dependent care include if student must pay dependent care to attend Study abroad include if student is enrolled at least half time in a program earning credit at the home school Disability related include if student needs specific disability assistance not already covered by an agency to attend Cooperative education include if student is enrolled at least half time in a co-op program Loan fees include if student’s financial aid package contains a Direct Loan (including PLUS Loans) Other COA Factors • Tuition and fees not paid by the student – If tuition and fees are charged to the student o Charges are included in COA o Charges paid by someone other than the student are counted as estimated financial assistance – If tuition and fees are not charged to the student o Charges are not included in COA 22 COA Information Consumer Information Requirements Released to current and prospective students and their families Minimum financial aid requirements include: • • • • Must provide the cost of attending the school and any additional costs How students apply for aid and how eligibility is determined The rights and responsibilities of students receiving aid How and when financial aid will be disbursed Civil penalty for non-compliance • In addition to limiting, suspending, or terminating the participation of any school that fails to comply with the consumer information requirements, ED may impose civil fines of up to $27,500 for each violation 2014-2015 FSA Handbook (Vol. 2 Ch. 6) 23 Budget Construction • Student budgets should be – – – – – Realistic Comprehensive Adequate Moderate Documented Budget construction is NOT intended as enrollment management tool – Inappropriate to use inflated or deflated costs 24 Separate Budgets for Different Categories of Students • Use at the institution’s discretion • Appropriate application of the purposes of budget construction • May establish distinct standard budgets for categories of students such as: • • • • • Undergraduates Graduates State residents Nonresidents Online students 25 Budget Creation - Collecting data to set Cost of Attendance component amounts 26 Primary Sources of Data Primary sources of data come directly from the student. They include but are not limited to student surveys such as: Personal interviews; Budget questionnaires; and Expenditure diaries The best approach is to use a combination of collection tools Sample should be drawn from school’s entire student body 27 Secondary Sources of Data Use data from secondary sources to validate student data and increase confidence in amounts established. Secondary data sources are any source other than students deemed reliable. Secondary data can be obtained from: Published institutional resources; Institutional faculty and staff; The local community; and Local, state, regional, and national indices 28 College Board Living Expense Budgets Information is available on the College Board website at: http://sitesearch.collegeboard.org/?q=Expense%20Budgets – Living Expense – Nine-Month Academic Year 29 Bureau of Labor Statistics Resources, including data tools are located at: http://www.bls.gov 30 Consumer Price Index • Measures day-to-day consumer inflation • May be used to adjust cost of attendance cost components • Collaborate with institutional research office or another office to determine the correct index to use • To access the tutorial, go to: http://www.bls.gov/tutorial/one_screen/ 31 Summary • Student budgets must be designed to meet statutory cost of attendance requirements as well as realistically reflect educational expenses • The process used to establish and update cost of attendance components and the school’s budget construction process should be well documented • Information on the cost of attending the school must be made available to all current and prospective students • The school’s cost of attendance policies should be described in the financial aid policies and procedures manual 32 Your Questions, Please! 33