Cardiac Drugs Part II
advertisement

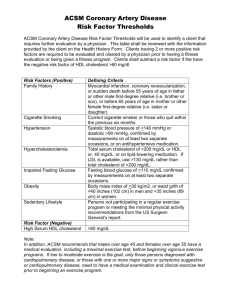
Cardiac Drugs Part II Diuretic Drugs Coagulation Modifier Drugs Antilipemic Drugs The Kidney Nephron The microscopic filtration unit of the kidney, consisting the glomerulus, proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, distal convoluted tubule, collecting duct, which empties urine into the ureters. Glomerular Filtration Rate GFR Is a laboratory value the serves as a gauge of how well the kidneys are functioning as filters. 180 liters of blood filtered through kidneys per day. Diuretic Drugs All major classifications developed between 1950 and 1970 and are the most commonly prescribed drugs in the world. Diuretic Drugs Classified according to site of action Classifications of Diuretics 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Carbonic Anhydrase (Diamox): acts on the nephrons Loop diuretics (Lasix): acts on the loop of Henle Osmotic diuretics (Mannitol): works in the kidney on the glomerular filtration Potassium sparing (Spiraldactone): works in the distal tubules Thiazides (Diuril): works in distal tubules 1. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Action: inhibit the action of the enzyme carbonic anhydrase. Site of action: nephrons Indications: glaucoma, edema, epilepsy, and high altitude sickness. Carbonic Anhyrase Inhibitors Contraindications: Drug allergy Severe renal or hepatic dysfunction Adrenal gland insufficiency Adverse effects Drowsiness Anorexia Paresthesias Hematuria (blood in urine) Melena (blood in stool) Interactions Increase in digoxin toxicity in clients taking digoxin. Corticosteroids may cause hypokalemia. Use with hypoglycemic drugs in diabetic type 2 Acetazolamine Trade name: Diamox Classification: carbonic anhyrase inhibitor Caution: check with patient regarding drug allergy to sulfonamides or significant liver or renal dysfunction. Dosing Oral dosage for adults is 250 to 375 mg / day. Oral dosing for pediatric patient is 5 mg / kg /day. 2. Loop Diuretics Potent diuretics The drugs act primarily along the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle, blocking chloride and sodium resorption. Also activate renal prostaglandins which results in dilation of blood vessels in kidneys and lungs and rest of body. Loop Diuretics Used when rapid diuresis is needed. Onset of action is1 hour and duration is 1-2 hours. Usually given in a single daily dose Major Side Effect Electrolyte imbalance Especially sodium and potassium Nurse alert: always check serum potassium and sodium levels before administering. Good Effects of Loop Diuretics Reduces blood pressure Reduces pulmonary vascular resistance Reduces systemic vascular resistance Reduces central venous pressure Reduces left ventricular end-diastolic pressure. Contraindications Drug allergy Allergy to sulfonamides Furosemide Trade name: Lasix Therapeutic classification: diuretic Pharmacologic classification: loop diuretic Primary use: pulmonary edema and edema associated with heart failure, liver disease and nephrotic syndrome. Used in treatment of hypertension caused by heart failure. Lasix Dosing Adult: IV 0.5 to 1 mg / kg / dose (maximum 200 mg / day. Drug calculation problem Client weighs 170 pounds Convert pounds to kilograms _________ Safe range of drug _______ to _______ Physician order: 56 mg of Lasix IV STAT Drug calculation problem Lasix is provided as 10 mg / mL How much would you need to draw up to give the 56 mg? 3. Osmotic Diuretics Action: increases the osmotic pressure of the glomerular filtrate inhibiting the reabsorption of water and electrolytes. When Used? Oliguric phase of acute renal failure. Increased intracranial or intraocular pressure. mannitol Trade name: Osmitrol, Resectisol Therapeutic classification: diuretic Pharmacologic classification: osmotic diuretic mannitol adverse effects CNS: confusion and headaches EENT: blurred vision Cardiovascular: transient fluid expansion, chest pain, CHF, pulmonary edema, tachycardia GI: Nausea, vomiting and thirst GU: urinary retention Dosing Adult dosing: 500 mg / kg (Given in intravenous solution) Onset 30 to 60 minutes Peak 1 hour Duration 6-8 hours Nursing Assessment Monitor vital signs Urine output Signs and symptoms of dehydration Decreased skin turgor Fever Dry skin and mucous membranes Low urine output 4. Potassium Sparing Diuretics Also called aldosterone-inhibiting diuretics because they block the aldosterone receptors. This causes sodium and water to be excreted and potassium to be retained. Potassium Sparing Diuretics Action: drugs work in the collecting ducts and distal convoluted tubules, where they interfere with sodium-potassium exchange. Indications Used with other agents to treat edema or hypertension Contraindications and Precautions Use with caution in geriatric or debilitated patients or patients with diabetes mellitus (increased risk of hyperkalemia). Renal insufficiency (BUN >30 History of gout or kidney stones Adverse Reactions / Side Effects CNS: dizziness, clumsiness, headache Gastrointestinal: cramps, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea Other: urinary frequency, weakness, hyperkalemia. spironolactone Trade name: Aldactone Therapeutic classification: diuretic Pharmacological classification: potassiumsparing diuretic Aldactone Onset: unknown Peak: 2-3 days Duration: 2-3 days Dosing PO Adults 25-400 mg per day as a single dose or 2-4 divided doses. PO Children 1-3 mg / kg / day. Daily or 2-4 divided doses. 5. Thiazides and Thiazide-Like Diuretics Action: increases excretion of sodium and water by inhibiting sodium reabsorption in the distal tubule. Therapeutic effects: Lowering of blood pressure in hypertensive patients and diuresis with mobilization of edema. Often the first drug used to lower blood pressure. Contraindications Allergy to sulfonamides Used cautiously in clients with renal or severe hepatic impairment. Adverse Reactions and Side Effects CNS: dizziness, drowsiness, lethargy and weakness CV: hypotension GI: anorexia, cramps, hepatitis, Dermatology: photosensitivity, rashes Fluid / electrolytes: Hypokalemia, dehydration, hyponatremia MS: muscle cramps hydrochlorothiazide Trade name: Esidrix, HydroDIURIL Therapeutic classification: antihypertensive, diuretic Indication: management of mild to moderate hypertension Treatment of edema associated with CHF, renal dysfunction, cirrhosis, corticosteroid therapy, hormonal therapy Dosing PO adults: 250 mg – 1 gram / day as a single dose or in divided doses PO children > 6 months: 10-20 mg/kg/day as a single dose or in divided doses. HydroDIURIL Onset 2 hours Peak 3-6 hours Duration 6-12 hours Laboratory Considerations Electrolytes especially potassium Blood glucose BUN Serum Creatinine Uric acid Coagulation Modifier Drugs Chapter 27 Anticoagulant A substances that prevents or delays coagulations of the blood. Antiplatelet Drugs A substance that prevents platelet plugs from forming, which may be beneficial in defending the body against heart attacks and strokes. Anticoagulants Prevent the formation of a clot by inhibiting certain clotting factors called anticoagulants. Only given prophylactically because they have no direct effect on a clot that has already formed. Clots / Embolus Clot: Insoluble solid elements of blood that have chemically separated from the liquid of plasma component of the blood. Embolus: a blood clot that has been dislodged from the wall of a blood vessel and is traveling throughout the bloodstream. Anticoagulants Also called antithrombotic drugs because they all work to prevent the formation of clots or thrombus. Embolus Stoke or cerebral vascular accident occurs when a blood clot travels to the brain. Pulmonary embolism occurs when a blood clot travels to the lungs. Deep vein thrombosis or DVT: clot in the veins of the legs. Anticoagulants All anticoagulants work in the clotting cascade, but do so at different points. Heparin Therapeutic classification: anticoagulants Pharmacologic classification: Antithrobotic Action of heparin is to turn off the coagulation pathway and prevent clots from forming. Indications Prophylaxis and treatment of various thromboembolic disorders including: Venous thromboembolism Pulmonary embolism Atrial fibrillation with embolization Acute and chronic coagulopahties Used in low doses to maintain patency of IV catheters (heparin flush) Contraindications Uncontrolled bleeding Severe thrombocytopenia Open wounds Use with caution: Severe liver or kidney disease Untreated hypertension Ulcer disease Spinal cord or brain injury Heparin Use with extreme caution: Severe uncontrolled hypertension Bacterial endocarditis Bleeding disorders Hemorrhagic stroke GI bleeding / ulcers Recent CNS or ophthalmologic surgery Drugs that interact with heparin Aspirin (salycilates) NSAIDs Dosing IV adults: Intermittent bolus: 10,000 units followed by 5000 – 10,000 units q 4-6 hours Continuous drip: 5000 units (35-70 units / kg) SubQ: 800 to 10,000 units q 8 hours or 15,000 to 20,000 units every 12 hours IV children: Intermittent bolus: 50 units / kg followed by 100 units / kg q 4 hours. warfarin Trade name: Coumadin Therapeutic classification: antigoagulants Pharmacologic classification: coumarins Action: Interferes with hepatic synthesis of vitamin K – dependent clotting factors (II, VII, IX and X) Used to prevent thromboembolic events Adverse Reactions and Side Effects GI: cramps and nausea Derm: dermal necrosis Hemat: Bleeding Dosing PO adults: 2.5 – 10 mg / day for 2-4 days and then dose adjusted by results of prothrombin time (PT) or international normalized ration (INR). Use lower doses in the geriatric population. Laboratory Values Prothrombin time (PT): measures how long it takes a clot to form in a sample of blood. PT 1.3 to 1.5 International normalization rate (INR): a standardized measure of coagulation achieved by drug therapy. INR of 2.0 to 3.0 Nursing Responsibilities Take exactly as directed If a dose is missed take as soon possible Do not double up on doses Review food high in vitamin K Vitamin K is antidote for warfarin overdose Instruct on brushing teeth with soft brush. Report any unusual bleeding or bruising Foods high in Vitamin K Green leafy vegetables Prunes Noodles: spinach Pie crusts enoxaparin Trade name: Lovenox Therapeutic classification: anticoagulant Pharmacologic classification: antithrombotic A prototype of heparin – replacing the use of heparin since laboratory values do not need to be monitored so tightly. Lovenox Action: Potentiates the inhibitory effect of antithrombin on factor Xa and thrombin. Used to control formation of emboli production post surgery. Dosing DVT prophylaxis before knee / hip surgery 30 mg SC twice a day starting within 24 hours post-op and continuing for 7 – 10 days or until ambulating. Deep Vein Thrombosis Nursing Assessment Assess for signs of bleeding and hemorrhage Bleeding gums Nose bleed Unusual bleeding Black tarry stools Hematuria Fall in hematocrit Bleeding from surgical site Antiplatelet Drugs Generic name: salicylates Trade name: Aspirin and aspirin combinations Indication: prophylaxis of transient ischemic attacks and myocardial infarct. Action: decreased platelet aggregation. Antilipemic Drugs Chapter 28 Cholesterol A fat-soluble crystalline steroid alcohol found in animal fats and oils and egg yoke and widely distributed in the body especially in the bile, blood, brain tissue, liver kidneys, adrenal glands and myelin sheaths of nerve fibers. Cholesterol Levels LDL: low density cholesterol HDL: high density cholesterol (good cholesterol) Why is high LDL a problem? Atherosclerotic plaque formation High correlation between Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) and high LDL and low HDL. Treatment Guidelines Current guidelines recommendations: LDL levels exceeding 190 LDL levels of 160 to 190 with CAD Other risk factors Waist circumference greater than 40 inches Serum triglycerides of 150 or greater HDL cholesterol less than 40 Blood pressure of 130/85 or higher Fasting serum glucose greater than 110 LDL / HDL Ratio The HDL should ideally be 1/4 to 1/3 of the total cholesterol level. If the total cholesterol level is 130 If the total cholesterol level is 220 LDL is 100 HDL is 30 LDL is 150 HDL is 70 If the total cholesterol level is 150 LDL is100 HDL is 50 Statins A class of cholesterol-lowering drugs that are more formally known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. First classification developed in 1987. Action: lower the blood cholesterol by decreasing the rate of cholesterol production. Liver requires HMG-CoA reductase to produce cholesterol. Contraindications Drug allergy Pregnancy Liver disease or elevation of liver enzymes. Adverse Effects Mild transient GI disturbances, rash and headache. CNS: headache, dizziness, blurred vision, fatigue, nightmares, insomnia. Severe side effect: muscle pain (myopathy) Elevation of liver enzymes: need to be monitored about 6-8 weeks after therapy started and yearly thereafter. Antilimpemic Drugs HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors Lipitor Zocor Crestor Lescol Mavacor Pravachol atorvastatis Lipitor Most commonly used drug to lower LDL and raise HDL Client needs to have liver enzymes drawn and cholesterol levels drawn 6-8 weeks after they start the drug therapy. Call physician if muscle weakness is noted. Niacin Niacin or nicotinc acid is another lipid lowering drug. Higher doses are needed than available in OTC vitamins or niacin pills. Adverse effects: flushing, pruritus (itching) and gastrointestinal disturbances. Life Changes Diet: limit intake of high fat foods and animal proteins Increase intake of omega oil contained in fish Exercise Weight control