File
advertisement

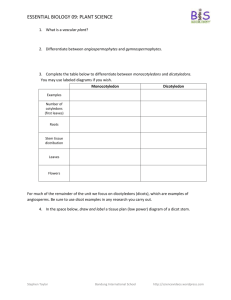
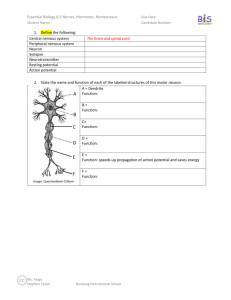
Essential Biology 06.5: Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis Resources: http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com/bis-ib-diploma-programme-biology/06-human-healthphysiology/nerves-hormones-homeostasis/ 1. Extend the organizational chart below to briefly describe the components of the central and peripheral nervous systems. Neurons are cells which can carry rapid electrical impulses. 2. Draw a simple diagram of a motor neuron (nerve cell), including: Cell body, nucleus, dendrites, axon, terminal branches, motor end plates, myelin sheaths, Nodes of Ranvier and the direction of the nerve impulse. 3. The diagram below shows a typical reflex arc. Name the labeled structures and state the processes taking place at 1, 2 and 3. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 06.5: Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis 4. Define resting potential. 5. Define action potential. 6. Complete the diagram below to show why the resting potential of a neuron is negative. 7. Define depolarization. 8. Define repolarisation. 9. Complete the table below to compare action potentials and resting potentials: Also known as… Resting potential Action potential ____-polarisation ___- polarisation Internal potential is… (positive/ negative) Sodium ions are… Potassium ions are… Membrane proteins used (voltage-gated sodium channels or sodium potassium pump?) Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 06.5: Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis 10. Annotate the graph below to explain what is happening in each stage of an action potential (AP). Include the movement of ions into and out of the cell and how this occurs. 11. What is the importance of the refractory period in propagation of an action potential? 12. What is the importance of these membrane proteins in nerve impulses? Sodium-potassium pump Sodium channel Potassium channel 13. In a nerve impulse, what happens at the site following the highest point of the action potential? A. Voltage-gated sodium ion channels open and Na+ is pumped in. B. Voltage-gated sodium ion channels open and Na+ diffuses out. C. Voltage-gated potassium ion channels open and K+ is pumped out. D. Voltage-gated potassium ion channels open and K+ diffuses out. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 06.5: Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis 14. Define synapse. When an AP reaches the terminal end of a neuron, it is converted from an electrical signal to a chemical message for synaptic transmission. 15. What form does this ‘chemical message’ take? 16. Complete the summary of synaptic transmission below: 17. Neurotrasmitters are specific to their receptors. What does this mean? 18. Some drugs act as competitive inhibitors to neurotransmitters. What would be the effect of this? Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 06.5: Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis 19. What are the roles of the following components of the endocrine system? Glands Hormones Target tissues 20. The endocrine system is responsible for hormone-mediated communication within the body. Which endocrine glands are mostly responsible for: Control of blood sugar Control of body temperature Control of water levels in blood Initiation of puberty Production of sex cells 21. Draw a simple flow chart to show how the endocrine system functions based on stimulus, hormone secretion and negative feedback control. 22. Define homeostasis. 23. List five factors that are maintained through homeostasis. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 06.5: Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis 24. Complete the flow chart below to show how the hypothalamus controls body temperature through hormones. What are the body’s responses? 25. The sense of taste is normally caused by the stimulation of chemoreceptors in the taste buds of the tongue. There are four main 'tastes': sweet, salty, bitter and sour. The tongue also has receptors for temperature. It is known that the taste of food can vary according to whether it is cold, warm or hot. Scientists discovered that just warming or cooling parts of the tongue, even when no food was present, also caused a sensation of taste. Scientists experimented with a group of people. They gradually cooled the tips of their tongues and measured the intensity of the taste felt by each member of the group. The experiment was repeated, this time warming the tip of the tongue. The graphs show the average values for the group. Cooling the tongue tip Warming the tongue tip Taste intensity felt / arbitrary units moderate weak just detectable 35 25 35 20 35 15 35 10 35 5 20 25 Decrease in temperature from 35 ºC Key: Salty Bitter 20 30 20 35 20 40 Increase in temperature from 20 ºC Sweet Sour [Source: modified from Cruz and Green, Nature (2003) 403, page 889] Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 06.5: Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis (a) Identify which taste was felt most strongly when the tip of the tongue was (i) cooled............................................................................................................ (ii) warmed.......................................................................................................... (1) (b) Compare the effects on the taste of sweetness, of warming and cooling the tip of the tongue. ......................................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) It is important that such experiments use a population sample that is representative. Suggest two biological criteria the scientists would have used to select the people to be tested. ......................................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................................... (1) (d) Explain whether cooling or warming the tip of the tongue has the greater effect on the sensation of taste. ......................................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................................... (2) Continued… Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 06.5: Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis The scientists discovered that there were two types of chemoreceptor in the tongue tip. They called these A and B. They tested these chemoreceptors using solutions of sucrose to find out the type of taste and the intensity felt. The results are shown in the bar chart. moderate weak Taste intensity felt / arbitrary units just detectable sweet detected Key: (e) sour detected A B Compare the effects of sucrose on the A and B chemoreceptors by giving two similarities and two differences. Similarities........................................................................................................................ ......................................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................................... Differences....................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 10 marks) Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 06.5: Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis 26. Blood glucose levels are maintained by hormones produced in the pancreas. Complete the table to show glucoregulation. The pancreas contains… High Blood Sugar Low Blood Sugar ___________________ cells… ___________________ cells… …which secrete… … carried in blood to…. & … causing conversion of.. … to … Overall effect: Glucose removed from blood Glucose released into blood 27. Diabetes mellitus is a disease in which regulation of blood glucose is difficult. There are two types of diabetes (Type I and Type II) Distinguish between them in terms of action, age of onset and risk factors. Type I: Type II: 28. How can we tell from this table that the patient has diabetes? Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 06.5: Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis 29. Distinguish between nerves and hormones. Nerves Route Direct from coordinator to effector Hormones Through: From: To: Signal type Chemical Time to take action longer Duration of effects 30. In which part of the brain are nerve impulses converted to hormonal signals? 31. Complete the steps below to show how the nervous and endocrine systems work together to regulate body temperature. Stimulus: Sensory neurons: Relay: Effector: Hormone 1: Gland: Target cells: Effect: release of thyroid hormone Target cells: Effect: Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com