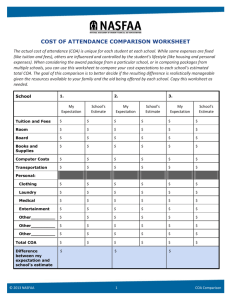
cost of attendance
advertisement
COST OF ATTENDANCE ALSO KNOWN AS THE BUDGET Presented by Vicki Mattocks, FA Director, Missouri State University AGENDA IDENTIFY AND REVIEW CORE COMPONENTS REVIEW ADDITIONAL ALLOWED COMPONENTS COA RESTRICTIONS DETERMINE WHEN RECALCULATION IS REQUIRED PRINCIPLES FOR BUDGET CONSTRUCTION HOW PROFESSIONAL JUDGEMENT APPLIES A CONCLUSION 2 What is the Cost of Attendance? The total, average amount of money it will reasonably cost a student to attend a particular institution during an academic year. 3 BACK TO BASICS Why is it important? The COA is the foundation of financial aid awards; COA combined with EFC determine the parameters of financial need. *COA – EFC = NEED* General principle for awarding financial aid: Need based aid and other resources cannot exceed the difference between COA and EFC 4 GENERAL BUDGET CONCEPTS The Dept. of Ed may not regulate the COA Within each component, FA administrators determine the amount of the allowance. Once established, the costs must be applied consistently. If exceptions permitted, documentation required. COA includes only the student’s costs. 5 GENERAL BUDGET CONCEPTS Pell Grant COA – always based on full time enrollment. Other Title IV Aid – typically based on full time enrollment, but are adjusted appropriately. 6 BASIC COA COMPONENTS Apply to all Title IV programs Three basic components √ Tuition and fees √ Books, supplies, transportation, and miscellaneous personal expenses, including a reasonable allowance for the rental or purchase of personal computer √ Room and board 7 Tuition May use actual or average tuition charges May establish separate averages for separate categories If one overall average tuition charge is used, it must be a weighted average Exception: Tuition not assessed, not included in COA. 8 Example: Weighted Average Tuition Charge Tuition: in-state = $2,000; out-of-state = $4,000 9,000 in-state students; 1,000 out-of state students Weighted average: + $2,000 $4,000 x x 9,000 = 1,000 = $18,000,000 4,000,000 $22,000,000 $22,000,000 ÷ 10,000 = $2,200 Weighted average tuition charge for COA = $2,200 9 Fees Include in COA if: Necessary for student’s program of study; or Required of all students or a broad category of students Do not include in COA if: Paid to third parties 10 Equipment, Materials, and Supply Charges The tuition and fees component may include the cost for rental or purchase of equipment, materials, and supplies if: The item is required for all students in the same program of study Mandatory expenses are associated with academic program 11 Books, Supplies, Transportation, Miscellaneous Personal Expenses May establish single allowance for books and supplies or allowances for different categories Transportation allowance must be reasonable Miscellaneous personal allowance should enable a reasonable standard of living 12 Personal Computer Cost Reasonable costs for rental or purchase of computer equipment allowed if student is enrolled at least half time √ Computer need not be required by student’s program √ May be purchased in the summer for use in the following fall enrollment period √ School determines conditions and documentation for adding costs to budget 13 Room and Board Three categories √ Students without dependents living at home with parent(s) √ Students without dependents living in campus housing √ All other students Only the student’s expenses can be included (i.e., cannot include expenses of other household members) If room and board is supplied at no charge, that component of the COA would be zero If room and board is charged and the charge is then waived, the value of the room and board is included in the COA 14 Additional Allowances Additional allowances for: √ Dependent care expenses √ Disability-related expenses √ Cooperative education program expenses √ Study abroad expenses √ First professional credential cost, at the option of the school √ Educational loan fees 15 Dependent Care Allowance Dependent may be student’s child or other person May be actual amount determined on a case-by-case basis or an average amount May not exceed reasonable cost in community for the kind of care provided Includes, but is not limited to, class time, study time, field work, internships, and commuting time 16 DISABILITY RELATED EXPENSES Student’s disability-related expenses that are reasonably incurred and not provided by another agency or program Must be determined and documented on an individual basis 17 Cooperative education program expenses Cooperative education program: A credit bearing academic program that combines professional work experience in a student’s field of study with academic research and course work. COA may include an allowance for reasonable costs associated with such employment. Expenses include: transportation, meals away from home, and any other costs incurred as a result of the coop program. 18 STUDY ABROAD ALLOWANCE COA may include reasonable costs for a student enrolled in a Study Abroad program • Program must be approved for credit by the home institution. • Costs are determined by the institution at which a student is enrolled. • Home institution must accept coursework for credit 19 COST OF PROFESSIONAL CREDENTIAL Effective July 1, 2006, the COA may include the one-time cost of obtaining the first professional credentials for a student in a field requiring professional licensure or certification (HERA) 20 EDUCATIONAL LOAN FEES Must be included in COA if student borrows a FFEL or Direct Loan May be included for all other types of educational loans May use actual or average fee amount for FFEL or Direct Loan based on: Type of loan for different student categories Type of loan borrowed On a case-by-case basis If loan declined or lower amount requested, must ensure an over award is not masked 21 COST OF ATTENDANCE RESTRICTIONS Costs are more restrictive for students who are: Enrolled in correspondence programs Enrolled less than half time Incarcerated 22 COA RESTRICTIONS: LESS THAN HALF TIME ENROLLMENT COA components limited to: Tuition and fees Books, supplies, & transportation costs Dependent care expenses A/O July 1, 2006, a room and board allowance for not more than three semesters or the equivalent, of which not more than two semesters may be consecutive 23 COA RESTRICTIONS: CORRESPONDENCE STUDY A correspondence course is one for which a school provides instructional materials and exams for students who don’t physically attend classes at the school. COA components limited to: Tuition and fees Books and supplies Transportation and room and board if incurred specifically for required residential training 24 COA RESTRICTIONS: INCARCERATED STUDENTS COA components limited to: Tuition and fees Books and supplies, if required 25 RECALCULATION OF THE COA A. FEDERAL PELL GRANT PROGRAM Recalculation of Federal Pell Grant COA is not required for cost changes unless school’s policy is to recalculate for a change in costs When recalculation of Federal Pell Grant award is required, any changes to Federal Pell Grant COA must be taken into account 26 RECALCULATION OF THE COA B. CAMPUS-BASED PROGRAMS COA may be recalculated as part of over award resolution 27 RECALCULATION OF THE COA C. FFEL/DIRECT LOAN PROGRAMS If the student temporarily ceases at least half-time enrollment before loan proceeds delivered or disbursed, recalculation is required to determine whether the student continues to qualify for the entire loan 28 PRINCIPLES FOR BUDGET CONSTRUCTION Realistic Adequate Moderate Documented Non-manipulative Made available to students 29 Setting Costs Fixed Institutional Costs Costs Tuition Fees Institutional room and board Non-institutional . Books & Supplies . Transportation . Personal Expenses . Off Camp. Housing . Utilities . Food . Dependent Care . Medical 30 COLLECTING DATA TO SET COSTS Student budget questionnaires Student expenditure questionnaires Institutional Publications Community Sources Local, state, and federal Indexes 31 STUDENT BUDGET SOURCES Publishers Weekly http://www.publishersweekly.com/ U.S. Department of Labor Bureau of Labor Statistics http://stats.bls.gov The College Board’s “Trends in College Pricing 2005” http://www.collegeboard.com/trends 32 Professional Judgment and the COA The law states that “nothing…shall be interpreted as limiting the authority of the financial aid administrator, on the basis of adequate documentation, to make adjustments on a case-by-case basis to the cost of attendance…to allow for treatment of an individual eligible applicant with special circumstances.” 33 Professional Judgment: Allows for flexibility and exceptions to normal COA rules Must be documented on a case-by-case basis Examples: √ use of actual costs vs. standard or average √ exceptional medical/health care expenses √ unusual child care expenses 34 Professional Judgment Restrictions Post enrollment costs cannot be added, except for cost of first professional credential, as discussed. New categories of cost components may not be created. Except for child care, additional expense must be incurred by student him/herself during enrollment period. Disability related expenses can be added to less-than-half-time budget. 35 COST OF ATTENDANCE In conclusion, student budgets must be designed to: √ Meet statutory COA requirements √ Realistically reflect a student’s educational expenses √ Be documented and maintained by the institution √ Be included in a schools policies and procedures manual. 36