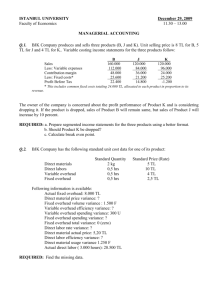
Flexible Budgets and Standard Costs

Chapter 22
Prepare a flexible budget for the income statement
Static Budget
Prepared for only one level of sales volume
Flexible Budget
Prepared for several different volume levels within a relevant range
Separates fixed and variable costs
Variance = difference between actual and budget
Favorable – actual amount increases income
Unfavorable – actual amount decreases income
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
3
Prepare an income statement performance report
Actual
Results
Flexible Budget based on actual number of outputs
Static Budget based on expected number of outputs
Flexible Budget Variance Sales Volume Variance
Static Budget Variance
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
5
Sales Volume Variance
Master Budget
(for the expected number of units to be sold)
Flexible Budget
(for the number of units actually sold)
Flexible Budget Variance
Flexible Budget
(for the number of units actually sold)
Actual results
(for the actual number of units to be sold)
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
6
Output units
Sales revenue
Variable costs
Fixed costs
Total costs
Operating income
Actual
Results at
Actual Prices
41,000
White Pro Company
Income Statement Performance
Year Ended July 31, 2011
Flexible
Budget
Variance
-
Flexible Budget for Actual # of
Output Units
41,000
Sales
Volume
Variance
7,000
$ 215,000
85,000
107,000
192,000
$ 23,000
$
$
-
6,000
6,000
12,000
12,000
U
U
U
U
$ 215,000
$
79,000
101,000
180,000
35,000
$
$
19,000
9,000
-
9,000
10,000
Static
Budget
34,000 F
F $ 196,000
U 70,000
101,000
U 171,000
F $ 25,000
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
7
Identify the benefits of standard costs and learn how to set standards
Budget for a single unit
Each unit has standards for:
Quantity Price
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
9
Direct materials
• Consider early-pay discounts, freight-in, and receiving costs
• Managers look for ways to cut costs
Direct labor
• Consider pay rates, payroll taxes, and fringe benefits
• Accountants work with human resource managers
Manufacturing overhead
• Accountants work with production managers
• Appropriate allocation base chosen
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
10
Direct materials
• Consider product specifications, spoilage
Direct labor
• Consider time requirements
• Use of time-and-motion studies and benchmarking
Manufacturing overhead
• Based on overhead application rate
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
11
Price Standard Quantity Standard
Direct Materials Responsibility: Production managers
Factors: Purchase price, discounts, delivery, credit policy
Responsibility: Production managers & engineers
Factors: Product specifications, spoilage, production scheduling
Direct Labor Responsibility: Human resource managers
Responsibility: Production managers & engineers
Factors: Wage rate, payroll taxes, fringe benefits
Factors: Time requirements
Manufacturing
Overhead
Responsibility: Production managers
Factors: Nature and amount of resources needed for support activities
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
12
Helps managers:
In budget preparation
Target levels of performance
Identify performance standards
Set sales prices
Decrease accounting costs
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
13
Actual Price
X
Actual Quantity
Standard Price
X
Actual Quantity
Standard Price
X
Standard Quantity
Price Variance Efficiency Variance
Total Cost Variance
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
14
Measures how well the business keeps unit costs within standards
(Actual Price x
Actual Quantity)
OR
(Actual Price
– Standard Price)
(Standard Price x
Actual Quantity)
Actual
Quantity
(AP – SP)
x AQ
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
15
Measures how well the business keeps unit costs within standards
( Standard Price x
Actual Quantity)
OR
(Actual Quantity
– Standard Quantity)
(Standard Price x
Standard Quantity)
Standard
Price
(AQ – SQ)
x SP
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
16
Actual
Results
Flexible Budget based on actual number of outputs
Static Budget based on expected number of outputs
Price
Variance
Efficiency
Variance
Flexible Budget Variance Sales Volume Variance
Static Budget Variance
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
17
Compute standard cost variances for direct materials and direct labor
Gather necessary data:
◦
Identify fixed and variable costs
◦
Compare actual results with flexible budget
◦
Prepare flexible budget based on standard costs
◦
Compute actual quantities and prices of materials and labor
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
19
Direct materials price variance
(Actual Price – Standard Price)
($1.15 – $1.10)
Actual
Quantity
2900 yards
$145 U
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
20
Direct materials efficiency variance
(Actual Quantity – Standard Quantity) Standard
Price
2900 yards – (1000 units x
3 yards)
$1.10
$110 F
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
21
Actual price x
Actual quantity
Standard price x
Actual quantity
Standard price x
Standard quantity
$1.15 x 2900 = $3,335 $1.10 x 2900 = $3,190 $1.10 x 3000 = $3,300
Price variance
$145 U
Efficiency variance
$110 F
Total materials variance
$35 U
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
22
Direct labor price variance
(Actual Price – Standard Price)
($9.50 – $10.00)
$325 F
Actual
Hours
650 hours
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
23
Direct labor efficiency variance
(Actual Hours – Standard Hours) Standard
Price
650 hours –
(1,000 units x 1 hour/unit)
$10.00
$3,500 F
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
24
Actual price x
Actual hours
Standard price
Actual hours x Standard price x
Standard hours
$9.50 x 650 = $6,175 $10.00 x 650 = $6,500 $10.00 x 1,000 = $10,000
Price variance
$325 F
Efficiency variance
$3,500 F
Total labor variance
$3,825 F
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
25
Analyze manufacturing overhead in a standard cost system
Actual overhead cost minus
Standard overhead allocated to production
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
27
Overhead allocated to production
Standard
(predetermined) overhead rate
Standard quantity of the allocation base allowed for actual output
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
28
Shows how well managers controlled overhead costs
Actual overhead costs
Flexible budget overhead for actual output
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
29
Occurs when actual production differs from expected production
Flexible budget overhead for actual output
Standard overhead allocated to actual production
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
30
Record transactions at standard cost and prepare a standard cost income statement
Materials inventory and Manufacturing wages are recorded at standard prices
Unfavorable variances are recorded as debits; favorable variances are recorded as credits
Work in process inventory is recorded at standard quantities and standard prices
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
32
DATE
GENERAL JOURNAL
DESCRIPTION
Materials inventory
REF DEBIT
(@ standard price)
CREDIT
Direct materials price variance (if U-debit, if F-credit)
Accounts payable (@ actual price)
To record purchase of direct materials
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
33
DATE
GENERAL JOURNAL
DESCRIPTION
Work in process inventory
REF DEBIT CREDIT
(@ standard price & quantity)
Direct materials efficiency variance (If U-debit, if F-credit)
Materials inventory
(@ standard price & actual quantity)
To record use of direct materials
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
34
DATE
GENERAL JOURNAL
DESCRIPTION
Manufacturing wages
REF DEBIT
(@ standard rate)
CREDIT
Direct labor price(rate) variance
(If U-debit, if F-credit)
Wages payable (@ actual rate)
To record labor costs
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
35
DATE
GENERAL JOURNAL
DESCRIPTION
Work in process inventory
REF DEBIT CREDIT
(@ standard rate & hours)
Direct labor efficiency variance (If U-debit, if F-credit
Manufacturing wages
(@ standard rate & actual hours)
To allocate direct labor to production
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
36
DATE
GENERAL JOURNAL
DESCRIPTION
Manufacturing overhead
REF DEBIT
(actual costs incurred)
CREDIT
Various accounts
To record actual overhead costs incurred
Work in process inventory
Manufacturing overhead
(standard OH rate x standard allocation base )
To allocate overhead costs to production
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
37
DATE
GENERAL JOURNAL
DESCRIPTION REF
Finished goods inventory
DEBIT
Work in process inventory
To record completion of goods at standard cost
CREDIT
Cost of goods sold
Finished goods inventory
To record the cost of goods sold at standard cost
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
38
DATE
GENERAL JOURNAL
DESCRIPTION
Overhead flexible budget variance
Overhead production volume variance
Manufacturing overhead
REF
To record overhead variances and close out the
Manufacturing overhead account
DEBIT CREDIT
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
39
Any Company
Standard Cost Income Statement
Year Ended July 31, 2011
Sales revenue at standard
Sales revenue variance
Sales revenue at actual
Cost of goods sold at standard cost $$,$$$
Manufacturing cost variances
Direct materials price variance
Direct materials efficiency variance
Direct labor price(rate) variance
Direct labor efficiency variance
Overhead flexible budget variance
Overhead production volume variance
Cost of goods sold at actual cost
Gross profit
Marketing and administrative expenses
Operating income
$,$$$
($,$$$)
$,$$$
$,$$$
($,$$$)
$,$$$ $,$$$
$$$,$$$
$,$$$
$$$,$$$
$$,$$$
$$,$$$
$$,$$$
$,$$$
Copyright (c) 2009 Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
40