DNA-Mediated Transformation
advertisement

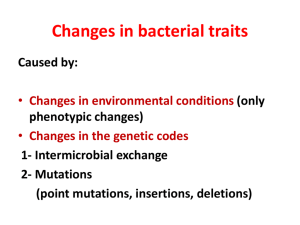
Changes in bacterial traits Caused by: Changes in environmental conditions (only phenotypic changes) Changes in the genetic codes 1- Intermicrobial exchange 2- Mutations (point mutations, insertions, deletions) Intermicrobial exchange Transformation (Capturing DNA from solution) Transduction (Phage-mediated) Conjugation (Bacterial Sex) Original Transformation Exp. F. Griffith (1928) using pneumococci DNA-Mediated Transformation DNA-Mediated Transformation Intermicrobial exchanges by vectors Characteristics of genetic vectors must be capable of carrying a significant piece of donor DNA must be readily accepted by the host plasmids – small, well characterized, easy to manipulate & can be transferred into appropriate host cells through transformation bacteriophages – have the natural ability to inject their DNA into bacterial hosts through transduction 8 Transduction (madiated by phage) Lytic versus Lysogenic Generalized Transduction Generalized Transduction Transduction Types of transduction Generalized - Transduction in which potentially any dornor bacterial gene can be transferred. Specialized (Restricted): Transduction in which only certain donor genes can be transferred. Restricted Transduction (Lysogenic Phage) bio gal gal gal bio gal bio bio bio Transduction Definition Types of transduction Significance Common in Gram+ bacteria Lysogenic (phage) conversion • e.g. Corynebacterium diptheriae toxin • Toxin derived from lysogenic phage Conjugation Conjugation Definition: Gene transfer from a donor to a recipient by direct physical contact between cells Mating types in bacteria Donor • F factor (Fertility factor) F (sex) pilus Donor Recipient • Lacks an F factor Recipient Conjugation Significance Gram - bacteria • Antibiotic resistance Gram + bacteria • Production of adhesive material by donor cells Conjugation Conjugation: Sex or F Pilus Plasmids Plasmids Definition: Extrachromosomal genetic elements that are capable of autonomous replication (replicon) Plasmid Types: Congugative & Non-congugative Episome - a plasmid that can integrate into the chromosome Casmid – An integration of a plasmid and a bacteriophage Phenotypic effects Fertility (F factor) Bacteriocinogenic (or encoding some other toxins) Resistance (R factors) Structure of R Factors RTF RTF Conjugative plasmid Transfer genes R determinant Resistance genes R determinant Self-Transmissible R Plasmid Conjugation: F Plasmid Transfer F+ and HFr cells F+ Hfr Integrated (Hfr) (High Frequency of Recombination) Hfr and F’ cells Hfr F’ Mechanism of Hfr x F- Crosses Hfr Hfr F- F- Hfr Hfr F- F- Mechanism of F’ x F- Crosses F’ F’ F- F’ F’ F- F’ F’ Transposable Genetic Elements Definition: Segments of DNA that are able to move from one location to another (across the genome or from one genome to another) Properties “Random” movement • Transposase Transposition may be accompanied by duplication Types of Transposable Genetic Elements Transposons (Tn)/ Insertion elements (IS) Definition: Elements that carry other genes in addition to those involved in transposition Nomenclature - Tn10, IS6110 Structure • Composite Tns Importance IS Resistance Gene(s) IS IS Resistance Gene(s) IS • Antibiotic resistance •Epidemiology and evolutionary studies