Int plasmids and Homogenotization
advertisement
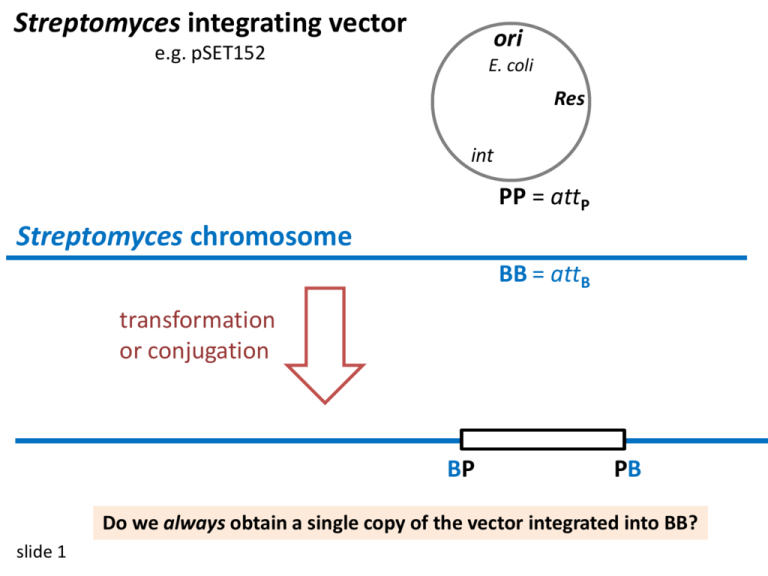
Streptomyces integrating vector ori e.g. pSET152 E. coli Res int PP = attP Streptomyces chromosome BB = attB transformation or conjugation BP PB Do we always obtain a single copy of the vector integrated into BB? slide 1 E. coli plasmids from rec- strains are mostly dimers. 1 BP 2 PP PB ori E. coli Res int PP How can we find out? slide 2 Some streptomycetes have several inefficient bb bb bP bb Pb bP How can we find out? slide 3 Pb Sequence the unknown flanking regions bP Restriction digest R R R R R bP slide 4 Pb Pb R R R R bP Pb ori E. coli LM-PCR Res Ligation-mediated PCR int PP b slide 5 R b Summary 1. Integrating vectors often for tandem inserts 2. Some streptomycetes lack a perfect BB, and insertion occurs into multiple, secondary bbs This can be important if experiments need to be reproducible. slide 6 Complementation: testing whether a mutation of a particular gene causes the observed phenotype. E.g. does a gene knockout have a polar effect on downstream genes in an operon? mRNA slide 7 Mutant phenotype Wild-type phenotype ? integrated or on plasmid Can we be sure that the downstream gene is not involved ? slide 8 homogenotization homo-geno-tization up to 5% !! and How can we prove that complementation was correct? slide 9 homogenotization homo-geno-tization up to 5% !! and 1. 2. slide 10 How can we prove that complementation was correct? Is there another possible gene arrangement? 1. Integrating plasmids, dimers and bbs 2. Homogenotization slide 11 Kleinia a species of Mangrove slide 12 slide 13 slide 14