Geometry
advertisement

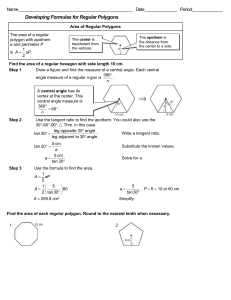
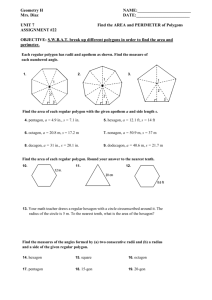
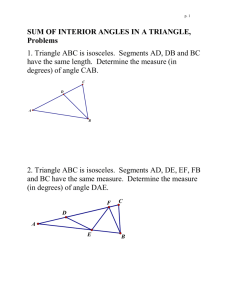
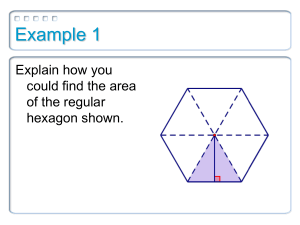
11.2 Areas of Regular Polygons Geometry Find the area of the triangle below What if the sides were variables? THEOREM 11.3 AREA OF AN EQUILATERAL TRIANGLE The area of an equilateral triangle is one fourth the square of the length of the side times square root of 3. Find the area of the equilateral triangle Parts of a Polygon • The center of the polygon is the center of its circumscribed circle • The radius of the polygon is the radius of the circumscribed circle • The apothem of the polygon is the distance from the center to any side of the polygon. – The apothem is the height of a triangle in the polygon Finding the Area of a Regular Polygon THEOREM 11.4 AREA OF A REGULAR POLYGON The area of a regular n-gon with side length s is half the product of the apothem a and the perimeter P: A = (1/2)aP A = (1/2)a · ns Find the area of the regular polygons Examples 1. Find the area of an equilateral triangle with 10 cm sides. 2. Find the area of a regular nonagon with each side being 8 and the apothem equal to 4.77 Central Angle of a Regular Polygon A central angle of a regular polygon is an angle whose vertex is the center. You can divide 360 by the number of sides to find the measure of each central angle of the polygon. Find the Central Angle Find the Central Angle When would we need to know the central angle? • Finding the side length of the regular polygon • Finding the apothem of the regular polygon REGULAR QUADRILATERAL SQUARE REGULAR HEXAGON Examples Examples 1. Find the area of a regular hexagon with each side 5. 2. Find the area of a regular hexagon with a radius of 8. Let’s take a look at a couple of regular polygons POLYGON QUADRILATERAL PENTAGON HEXAGON HEPTAGON # OF SIDES CENTRAL ANGLE BASE ANGLES What about other regular polygons? Other Regular Polygons We will have to use trig to find the missing sides of other regular polygons. 1. Find the central angle 2. Draw in the apothem to make a right triangle 3. Divide the central angle by 2 to get the angle in the right triangle 4. Set up a trig function to find the missing sides. Find the area of the Regular Pentagon Find the area of the regular octagon Find the Area of a Regular Dodecagon The enclosure on the floor underneath the Foucault Pendulum at Houston Museum of Natural Sciences in Houston, Texas, is a regular dodecagon with a side length of about 4.3 feet and a radius of about 8.3 feet. What is the floor area of the enclosure? Example The bottom of a glass is a regular 12-gon with a side length of about 1.2 cm and a radius of 2.3 cm. What is the area of the bottom of the glass?