Vocab.
advertisement

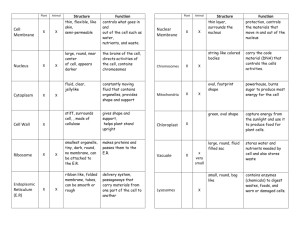
CHAPTER 3 By: Bailey WHAT IS CELL THEORY? CELL THEORY o Cells are building blocks for plants and animals o Cells are produced by division for preexisting cells o Cells are the smallest object that perform physiological functions o Each cell maintains homeostasis at cellular level o Homeostasis at the tissue, organ, system, and individual levels reflects the combined and coordinated actions of many cells o *Homeostasis- the maintenance of a relatively constant internal environment COMPARE FLUID CONTENTS OF CELL WITH THE EXTRACELLULAR FLUID FLUID CONTENT Cytosol High concentration of potassium Relatively high concentrations of dissolved proteins (enzymes that regulate metabolic operations) Contains dissolved nutrients, ions, soluble and insoluble proteins and waste products Contains small quantities of carbohydrate and large reserves of amino acids and lipids Extracellular High concentration of sodium All body fluid not within the cell Plasma and interstitial fluid are included in this CELL MEMBRANE CELL MEMBRANE Str ucture Composed of I. Phospholipids II. Proteins III. Glycolipids IV. Cholesterol * Cytosol is what mostly makes up the cell. Surrounding that is the Phospholipid bilayer, and within that layer are the proteins and channels Impor tance I. Separates the inside of the cell from the surrounding extracellular fluid II. Controls the entry of ions and nutrients, and eliminates waste and the release of secretory products III. Let’s the cell respond and recognize to molecules in its environmental IV. Gives tissues a stable structure CELL AND THEIR ENVIRONMENT INTERACTION WITH ENVIRONMENT A cell needs to maintain homeostasis It does this through the cell membrane Taking in nutrients and obtaining water balance and giving off waste These all are from the environment that need to be taken in or let into the environment from the cell STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION ORGANELLES Cell Membraneisolation, protection, sensitive, organization Cytosoldistributes materials by diffusion ORGANELLES Nonmembranous Organelles Membranous Organelles • Cytoskeleton • Microtubules • Microfilaments • Microvilli • Cilia • Centrioles • Ribosomes • Nucleus • Endoplasmic reticulum • Rough ER • Smooth ER • Golgi Apparatus • Lysosomes • Peroxisomes NONMEMBRANOUS • Cytoskeleton- strength, movement of cellular structures and material • Microtubules- gives strength to the cell • Microfiliments-slender protein strand • Microvilli-absorption of extracellular fluid • Cilia- movement of materials over surface • Centrioles- movement of chromosomes during cell division • Ribosomes- protein synthesis MEMBRANOUS • Mitochondria- protein synthesis • Nucleus- control of metabolism; stores and processes genetic info. • Nucleolus- site of RNA synthesis • Endoplasmic Reticulumsynthesis of secretory products; intracellular storage and transport • Rough ER- secretory protein synthesis • Smooth ER- lipid and carbohydrate synthesis • Golgi apparatus-storage, alteration and package of secretory product and lysosomes • Lysosomes- intercellular removal of damaged organelles or of pathogens • Peroxisomes- neutralization of toxic compounds ENERGY WITHIN CELLS MITOCHONDRIA Mitochondria Mitochondria is the power house of the cell, it makes and stores the “power” so the cell can function properly How it prefor ms that… 1. The organelle has a double membrane; the first surrounds the entire cell, the second surrounds the inner which has many folds called cristae 2. Cristae increases the surface area exposed to the fluid contents, matrix * Metabolic enzymes - Protein-based substances that promote change in bodily cells… 3. Matrix contains metabolic enzymes that perform the reactions that provide energy for cellular function NUCLEUS AS CONTROL CENTER NUCLEUS • The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear envelope which separates it from the cytosol • Within the nuclear envelope are perinuclear space • These allow the nucleus to receive information about conditions and activities in the cytosol NUCLEOPLASM The nucleoplasm contains ions, enzymes, RNA and DNA nucleotides, proteins, small amounts of RNA and DNA I. These DNA strands form a chromosome II. These are then “read” by the nucleus controls by the process of “regulation of protein synthesis” III. What is read from the chromosome, the nucleus then tells the cell what needs done and what to do LIFE CYCLE LIFE CYCLE Life cycle- Go Phase, G1 Phase, S Phase, G2 Phase, Gm Phase, Mitosis INTERPHASE • Go Phase- the cell has normal functions (indefinite time) • G1 Phase- the cell grows, duplicates its organelles, and preforms protein synthesis (8 or more hours) • S Phase- the cell’s DNA is replicated and synthesis’s its histones (6-8 hours) • G2 Phase- the cell undergoes protein synthesis’s (2-5 hours) • Gm Phase- where the cell undergoes mitosis MITOSIS • Prophase (stage 1)- the nuclear envelope disappears • Metaphase (stage 2)- chromatids move through metaphase plate; microtubules of the spindle apparatuses attaches to each centromere • Anaphase (stage 3)- the chromatid pairs separate and the daughter chromosomes move toward the opposite ends to the cell • Teleophase (stage 4)- the nuclear membranes form, the nuclei enlarge, chromosomes gradually uncoil; once the chromosomes disappear, nucleoli reappear and the nuclei resemble those of the interphase cell IMPORTANCE TRANS -MEMBRANE POTENTIAL TRANS-MEMBRANE POTENTIAL It measures the millivolts across the cell membrane for potential difference that could result from uneven distribution of the positive and negative ions across a cell membrane A membrane enzyme called the sodium-potassium pump actively transports ions to compensate for the sodium and potassium leaks This pump uses the energy of ATP to move sodium and potassium against their electrochemical gradients The pump compensates for the sodium and potassium leaks, keeping the resting membrane potential at -70 millivolts HOW CELLS ATTACH METHODS OF ATTACHMENT Gap Junction- two cells are held together by an interlocking of membrane proteins, the result is a narrow passage way that lets small molecules and ions pass from cell to cell Tight Junction- partial fusion of the lipid portions of the two cell membranes, providing mechanical strength, but blocking the water or solutes between cells Intermediate Junction- the opposing cell membrane, while maintaining distinct, are held together by a thick layer of proteoglycans Desmosomes- the opposing cell membranes reinforced by a network of intermediate filaments that lock the two together , a dense concentration of filament beneath the cell membrane at a desmosomes anchor it to the cytoskeleton Junction Complex- when all types of junctions including desmosomes are together in one location VOCABULARY VOCAB. Cytology- the study of the structure and function of cells Transmission electron microscopy- show fine structures of cell membranes and intracellular structures Scanning electron microscopy- where electrons bounce off exposed surfaces, creates 3D perspective Extracellular fluid- a watery medium that is on the outside of cells Cell membrane- outer boundary of the cell Plasma membrane- another term for cell membrane Phospholipid bilayer- a cell membrane Peripheral proteins- attached to the inner membrane surface Integral proteins- embedded in the membrane Channels- formed by integral proteins the let water molecules, and other objects pass through it Cytoplasm- A general term for the material inside of the cell VOCAB. Intermediate filaments- provides strength, support, and transports materials within the cytoplasm Neurofilaments- found in nerve cells and provide structure and support Thick Filaments- massive strand composed of myosin protein subunits Microtubules- hollow tubes built from the globular proteins Tubulin- globular protein Microvilli- small finger-shaped projections of the cell membrane Centrioles- is a cylindrical structure composed of short microtubules Centrosome- cytoplasm surrounding Cilia- contain nine pairs of microtubules surround a central pair VOCAB. Cytoplasm- A general term for the material inside of the cell Cytosol- or intracellular fluid- dissolved nutrients, ions, soluble, and insoluble proteins and waste products. Organelles- structures that perform specific functions within the cell Inclusions- masses of insoluble materials Non-membranous organelles- in contact with cytosol Membranous Organelles- surrounded by lipid membranes that isolates them from the cytosol Cytoskeleton- an internal protein framework the gives the cytoplasm strength and flexibility Microfilaments- slender proteins strands composed of the protein actin Actin- a protein found in microfilaments Myosin- a protein VOCAB. Basal Body- an anchored compact for cilia Flagella- moves cells through the surrounding fluids Ribosomes- small, dense structure that cannot be seen; they manufacture proteins Free ribosome- one type of ribosome where its proteins scatter throughout the cytoplasm Fixed ribosome- attached to the endoplasmic reticulum, its proteins enter here Mitochondria- small organelle that have a double membrane; makes energy for the cell Cristae- second inner membrane that contains numerous folds Matrix- fluid contents of mitochondrion Respiratory enzyme- produces most of the ATP generated from the mitochondrion Nucleus- the control center for the cell Nuclear envelope- surrounds the nucleus and separates it from the cytosol Perinuclear space- a narrow passage within the nuclear envelope VOCAB. Nuclear pores- large pores that permit the movement of ions and small molecules,but too small for DNA Nucleoplasm- fluid contents of the nucleus Chromosomes- contain DNA strands Histones- proteins that bind to DNA strands Nucleosome- a structure that forms when DNA strands wind around histones Chromatin- made when chromosomes tangle fine filaments Endoplasmic reticulum- a network of intracellular membranes Cisternae- formed by the endoplasmic reticulum; reservoir for water Rough reticulum- where newly made synthetic proteins undergo chemical modification Smooth reticulum- synthesis of lipids and carbohydrates VOCAB. Golgi apparatus- synthesis and packing, renewal or modification of the cell membrane Transfer vesicles- how material moves from saccule to saccule Secretory vesicles- vesicles that contain secretion that will be discharged Lysosomes- vesicles filled with digestive enzymes; defense against disease Endocytosis- the process of lysosomes in greater detail Peroxisomes- smaller then lysosomes; absorb and neutralize toxins Gated- regulate the passage of materials that travel through channels Glycocalyx- protects cell membrane; function as receptors; keeps immune system from attacking body Permeability- objects can pass through it Impermeability- objects cannot pass through it Freely permeable- object can pass through without any trouble is said to be Selectively permeable- permits the passage of some materials VOCAB. Diffusion- net movement of material from an area where it’s concentrated from high to low Concentration gradient- the difference between low and high concentration Osmosis- the response to the difference in diffusion Osmotic pressure- force of water movement Hydrostatic pressure- when pressure is can prevent the entry of molecules Osmotic concentration/osmolality- total solute concentration in a solution Tonicity- used when describing osmotic concentration Isotonic- same solute concentration low and high Hypotonic- solution has a lower then the cytoplasm Hemolysis- when a cell burst or explodes Hypertonic-when concentration is higher than the cytoplasm