Enzyme Lab
advertisement

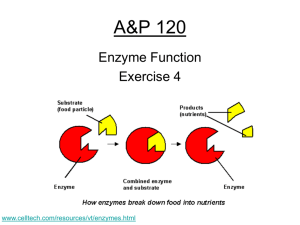
Biology 120 Enzyme Function Exercise 4 www.celltech.com/resources/vt/enzymes.html What you need to Know • Understand the experiment being preformed today • What is: Enzyme / Catalyst / Active Site / Substrate • Answer all questions in the lab handout • Understand the effect of pH, temp, and concentration has on an enzyme • Understand the scientific processes that took place Terminology • Metabolism – Definition: The sum total of all biochemical activity that takes place in a living organism • Catabolic Metabolism – break down – AB = A & B • Anabolic Metabolism – build up – A + B = AB • In vitro – out of the body (or in a tube) • Substrate - The material being acted upon Introduction • Catalyst – speeds up the rate of a reaction • Enzyme – a protein that is a organic catalyst – Hint: Most of the time ends in –ase • Active Site – a pocket at the outside of the enzyme specific to a substrate (here is where it is taken apart or put together) Bubbles H2O2 Catalase 2H2O2 Catalase H2O2 Catalase (organic) 2H2O +O2 (Hydrogen peroxide) (Water & Oxygen) Substrate **Oxygen will bubble in vitro** How Enzymes Work • Biological Catalysis (usually proteins) – Make a reaction faster • Enzymes are Proteins – built to work “active site” • Proteins are Happy’ist in their natural Temp and pH – – – – Usually ~370C or 980F & Usually a neutral pH (Function) What would happen if you boil it? Guesses -___________ What would happen if you put it in acid? ________________ What would happen in the cold?________________ • Enzymes can only work so fast…….. – If you keep adding substrate will the speed of the Rxn a) H2O2 •Poison What does cyanide do? Arsenic? O2 & H2O b) or Catalase Catalase How Enzymes Work • Biological Catalysis (usually proteins) – Make a reaction faster • Enzymes are Proteins – built to work “active site” • Proteins are Happy’ist in their natural Temp and pH – – – – Usually ~370C or 980F & Usually a neutral pH (Function) What would happen if you boil it? Guesses -____denature________ What would happen if you put it in acid? _______denature_________ What would happen in the cold?________inhibit________ • Enzymes can only work so fast…….. – If you keep adding substrate will the speed of the Rxn a) H2O2 •Poison What does cyanide do? Arsenic? O2 & H2O b) or Catalase Catalase p. 35? Temperature -cold temperatures inhibit (prevent) enzyme activity -hot temperatures denature enzymes High activity Denature: enzyme unravels/unfolds and loses structure and function Extreme heat Low activity COLD HOT Best temperature Normal enzyme Denature d enzyme p. 35? pH = 0 Acidic –less than 7 pH Neutral = 7 Basic (alkaline) – greater than 7 pH = 14 Enzymes have a certain pH at which they work best -above or below optimum pH inhibits activity Your Experiment The reaction: 2 H2 O 2 Catalase 2 H2O + O2 Hydrogen peroxide water + oxygen What’s the substrate? Product? Catalase: enzyme (organic catalyst) that converts hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen H2O2 H2O + O2 catalase (gas) The Experiment • Close the buret valve & fill with water (bucket also) • Invert the buret and clamp (make sure the water level is blow the 50 ml mark) • Add 3 Grams of plant tissue and stopper the flask ***Put the tubing into the buret*** • Put the rubber stopper on the flask an put the hose into the buret (careful not to lose the water) • Add 3 ml 2H2O2 to the flask (do NOT remove pipette) Record water level and Time!! • Swirl the flask for 30 sec. Record the Level (Table 1) • To Remove – take out the hose and then uncork • Add Tap Water to the plant tissue (Clean Flask) Water Level at: T0 = Time Start • Repeat with Blood (animal) Tf = Time Finish • Test the Effects of Temperature (Hot and Cold) – Do Not Leave The Flask Unattended when on the hot plate.*** – Follow the instructions – pg 43 & Record on Table 2 • The Effects of pH (3 different flasks) Pre-incubate – Follow instructions on pg 47&48 – Record on Table 3 – You MUST ware safety equipment when near the HCL & NaOH • The Effects of [Concentration] – Read the instructions Carefully – Be as accurate as possible – No exact time limit (until oxygen is no longer produced) • When ever you remove the Stopper…… – Where should the tube be? What would happen? • Calculate the amount of oxygen produced – Oxygen will displace the water (water level will go ) – Simple subtraction (bigger # from the smaller #) • Put answers on the board • • • • • THE CLEAN UP!!! Clean all Flasks and other glass stuff completely (Tap water) Points can (and will be) Empty all water deducted for messes left Wipe up the counter and any spills Check the center counter – Wipe up Put equipment all on the side counter Experimental Setup p. 36-37? 2 H 2 O2 2 H2 O + O2 Buret tube Tubing Water trough -Set up apparatus as described on p. 36. -Place tissue in flask -Record exact water level in buret tube -Add hydrogen peroxide -Swirl flask 30 seconds -Record exact water level after 30 seconds -Test under other conditions Rubber stopper Flask Ring Stand Why does the water level change? What specific molecule caused it to change? Is this a substrate or product? What was in the tissue that caused the reaction to occur? -To keep the swirling consistent, designate one group member to swirl gently for all activities! Activities: Plant tissue Animal tissue 1) Activity #1: Presence of catalase For #2, #3, #4 use plant tissue only!!! 2) Activity #2: Effect of Temperature -Keep on ice entire time! Ice At ~4:20, we’ll stop to discuss your observations & take roll -Remove once it bubbles or it will burn! Hot plate 3) Activity #3: Effect of pH -Let sit 10 min with HCl or NaOH before running the experiment HCl Buffer NaOH 4) Activity #4: Effect of Enzyme concentration and Substrate concentration Once you’ve completed the tables, answer questions on p. 42 and understand the objectives in the lab on p. 35 Critical Thinking Hummm What to do …. But think • Take a look at the board Brain in a jar – Do all the results match or show a trend? – Are there a few results that don’t make sense (why do you think this happened?) – What do the results lead you to conclude? – Why is it good to replicate experiments?