Finances
advertisement

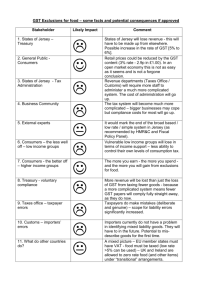
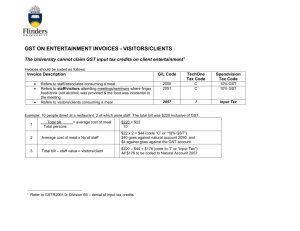
Planning 10 – EOP Page 1 of 3 Finances – Taxes Read Story 14-1 Reporting Income on the BCSC website for Planning 10. Canadians pay a lot of money in taxes. Some of this money is collected from us when we buy items at the store. Other money is taken directly off our pay cheques. As a citizen, it is important that you know where your money is going. Complete the Learning About Taxes course on the Canadian Revenue Agency’s website. There are four modules that you need to do: Module 1: Basics of Taxation Module 2: Tax Filing Process Module 3: Roles and Responsibilities Module 4: Complete a Basic Tax Return The course will take about 2 hours for you to complete. You do not have to do it at one sitting. You can come back to where you left off, as long as you make a note of where you were. As you work through the course, answer the following questions: 1. What are taxes? 2. Identify 3 “things” that are paid for by Canadian taxes. 3. What percentage of the federal budget was spent on national defence in 2007-2008? 4. Identify and explain 3 guidelines the federal government apply when implementing tax legislation? 5. When did Canada first being collecting personal income tax? Why did the government feel it was necessary to do this? 6. When did the federal government begin to collect GST?? 7. What form did the first taxation in Canada take before Confederation? Where did the taxes from the Canadians go? Hint: you will need to click on the link to Learn More About the History of Taxes in Canada at the bottom of the A Brief History of Taxation page in the lessons. 8. Who administers tax laws for the federal government and most of the provinces and territories? 9. Identify the five most common Canadian taxes. 10. Who is required to contribute to CPP? Planning 10 – EOP Page 2 of 3 11. Who must pay into Employment Insurance? Why is it a good thing to contribute to EI? 12. What taxes are collected when you purchase a video game in BC? 13. List 5 categories of items which are exempt from GST. 14. In some provinces the PST and GST are combined into a single tax. This looks convenient, but it can cause some concerns for taxpayers. There are items in BC that you do not pay PST on, but you do pay GST. For example, in BC if you eat at a restaurant the price of the meal is subject to GST only. If the tax is combined, suddenly BC taxpayers will be paying the combined tax on everything that had GST on it. That means that restaurant prices will increase by 7%. What is the combined tax called? 15. According to the CRA web site, where is the nearest community offering the Volunteer Tax Preparation Clinic? 16. What is the phone number for you to find out the status of your income tax refund? 17. What are the benefits of filing your tax return electronically? 18. What are the different ways you can file your taxes electronically? 19. What happens if you owe money on you income tax, but you don’t pay it when you file your statement? 20. Do you have to file a tax return to be eligible for the GST credit and the Chile Tax Benefit? 21. When must you file your income tax? 22. Under what circumstances are people under the age of 19 eligible to receive the GST credit? 23. What is the purpose of the Taxpayer Bill of Rights? 24. What program allows you to register your dissatisfaction with the way your concerns have been handled by the CRA? 25. What program will provide a final impartial review of a complaint against the CRA? 26. What is meant by tax avoidance? 27. What is meant by the underground economy? 28. What are the penalties if you are found guilty of a tax-related crime? 29. How long do you need to keep your supporting documents for your tax return? Planning 10 – EOP Page 3 of 3 30. What statement is used to inform you and the CRA how much money you earned in the year? 31. What was Paul’s net income, total federal non-refundable tax credits, net federal tax, and the amount of his refund?