The Atlantic Slave Trade
advertisement

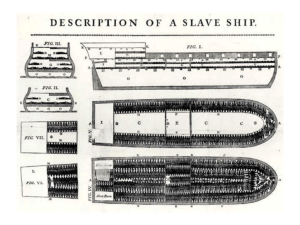
• 5/1 Focus: – To meet their growing labor needs, Europeans enslaved millions of Africans in forced labor in the Americas. • Do Now: – What made the kingdoms of West Africa wealthy? Origins of the Slave Trade • Slavery historically existed in many parts of the world • Spread of Islam into Africa increased slavery there – Slaves often had legal rights and some social mobility – Slavery in Africa was not hereditary; children were considered free Origins of the Atlantic Slave Trade • European landowners needed a large supply of workers on American plantations Origins of the Atlantic Slave Trade • Spanish attempts to use Native Americans as laborers were not successful • Large death rate due to disease and overwork • Bartolome de la Casas convinces Spanish to stop using Native Americans • English use of Indentured Servants was expensive • People who worked for a set period in exchange for passage to the Americas Origins of the Atlantic Slave Trade • Europeans began buying large numbers of Africans to fill labor shortages in Americas • Most slaves came from coast of West Africa – Were supplied by African rulers in exchange for guns or trade goods – Kidnapped by Europeans on slave raids By the 1600s Portugal, Spain, France, Holland, and England were involved in the trans-Atlantic slave trade. Most captured Africans were taken to colonies in the Caribbean and South America, then to North America. Only a small percentage came directly to the North American colonies Triangular Trade • Trade routes that linked the Americas, Europe, Africa, and the West Indies • Sea routes formed a triangle The Middle Passage • The voyage from Africa to the Americas on slave ships • Hundreds of captive Africans were crammed into tight quarters below deck in terrible conditions • Millions died from disease, brutal mistreatment, and suicide on the trip The slave ship Brookes with 482 people packed onto the decks. Interior of a Slave Ship, a woodcut illustration from the publication, A History of the Amistad Captives, reveals how hundreds of slaves could be held within a slave ship. Tightly packed and confined in an area with just barely enough room to sit up, slaves were known to die from a lack of breathable air. • Africans were crowded and chained cruelly aboard slave ships. Effects of the Slave Trade • Millions of Africans were sent to the Americas – Importation of slaves into the U.S. ended in 1807 Effects of the Slave Trade • Disrupted traditional West African political structure and society – Outbreak of local wars – Loss of population – Disappearance of small countries and societies – Formation of African states dependent on the slave trade Effects of the Slave Trade • Labor of African slaves helped build the economies of American colonies • People of African descent spread through the Americas and Western Europe – Led to the diffusion of African culture Closure • Where did most slaves involved in the Atlantic slave trade come from? • What was the Middle Passage? • What was triangular trade? • 4/19 Focus: – European Expansion into the Americas had an enormous impact, resulting in many exchanges that altered the lives of people around the world. • Do Now: – What was triangular trade? Columbian Exchange • The exchange of plants, animals, and diseases between Europe, Africa, and the Americas Effects of the Columbian Exchange • Introduction of new crops from the Americas to Europe, Africa, and Asia leads to population growth • Increased cultural diffusion – Europeans were influenced by Native American foods as well as African farming methods, cooking styles, and music Columbian Exchange