Introduction to Marketing
advertisement

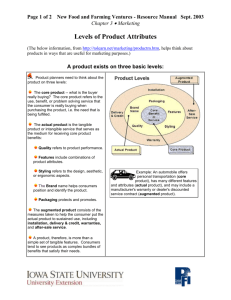
Product Strategy What is a Product? Anything that can be offered to a market for attention, acquisition, use or consumption that might satisfy a want or need Any activity or benefit that one party can offer to another that is essentially intangible and does not result in the ownership of anything - Kotler Levels of Product & Services The CORE product is NOT the tangible physical product. This cannot be touched. Its the BENEFIT of the product that makes it valuable to you. E.g when purchasing a vehicle, the benefit is convenience i.e. the ease at which you can go where you like, when you want, etc. Another core benefit is speed since you can travel around relatively quickly. The ACTUAL product is the tangible, physical product. This can be touched. And you can get some use out of it. (It is the vehicle that you test drive and buy.. The AUGMENTED product is the non-physical part of the product. It usually consists of lots of added value, for which you may or may not pay a premium. (When purchasing a car, part of the augmented product would be the warranty, the customer service support offered by the car's manufacturer and any after-sales service). The augmented product is an important way to tailor the core or actual product to the needs of an individual customer. The features of augmented products can be converted in to benefits for individuals. Product & Service classifications Consumer Products Consumer products- bought by final consumer for personal consumption Convenience products- products bought frequently, immediately and with minimum comparison and effort Shopping products- customer will compare based on suitability, quality, price & style Specialty products- products with unique characteristics & brand identification for which buyer will make a significant purchase effort Unsought products- product the consumer does not know about or knows but doesn’t normally think of buying Industrial Products Products bought by individuals and organizations for further processing of for use in conducting a business Organizations, Persons, Places and Ideas Organization marketing consists of activities to create, maintain or change the behaviour and attitude of target consumers towards the organization People marketing consists of activities to create, maintain or change the behaviour and attitude towards people. Used by Doctors, lawyers, architects, etc… (Oprah winfrey) Social marketing programs include public health campaigns to reduce smoking, drug abuse, alcoholism, etc Individual Product & Service decisions Product/Servi ce attribute Branding Packaging Labeling Product support services Product Line decision A group of products that are closely related because they function in a similar manner, are sold to the same customer groups, are marketed through the same types of outlets or fall within given price ranges. Product Mix decision The set of all product lines and items that a particular seller offers for sale. Services Marketing Nature and characteristics of Service Service inseparability- a major characteristic of services. They are produced and consumed at the same time and cannot be separated from their providers Service variability- their quality may vary greatly depending on who provides them and when, where and how Service perishability- cannot be stored for later sale or use. Marketing Strategies for Service firms The service profit chain Managing service differentiation Managing service quality Managing service productivity New Product Development strategy Idea Generation The systematic search for new product ideas Internal sources: executives, manufacturing staff, sales people External sources: customer feedback, distributors, suppliers, competitors (the use of reverse engineering) Idea Screening Screening new product ideas to spot good ideas and drop poor ones as soon as possible. Due to product development costs companies will only go ahead with product ideas that will be profitable. Concept development & testing A detailed version of the new product idea stated in meaningful terms E.g: Daimlerchrysler developing their fuel-cell powered F-cell car. Concept testing involves testing the new product with a group of target customers to see if the concept has appeal Marketing strategy development The planned product positioning including sales, market share and profit goals for the year An outline of the products' planned price, distribution and marketing budget Describes the planned long-run sales, profit goals and marketing mix strategy Business analysis A review of the sales, costs, and profit projections for a new product to find out whether these factors satisfy the company’s objectives To estimate sales the company might look at sales history of similar products and conduct surveys of market opinions Product development Developing the product concept into a physical product E.g Gillette- the entire staff get involved in product testing. A new product must have the required functional features and also convey the psychological characteristics Test marketing The product and marketing program are tested in more realistic market settings The amount of test marketing varies depending on the product A new product that requires a big investment may involve a lot of test marketing Test marketing doest guarantee success Commercialization The launch of the product into the market Company must decide where to launch; a single location, region, national market or international market The company must decide on introduction timing Product life-cycle strategies Introduction stage Growth stage Maturity stage Decline stage