132 kV Sahupuri
advertisement

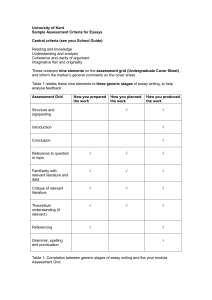
Sikkim Allahabad 132 kV Rihand - Sonenagar 132 kv Rihand-Garwah JHARKHAND W.BENGAL Raipur 220 KV Korba (MP) – Budhipadar (Orissa) Rourkella Talcher ORISSA 220 kV Balimela (Orissa) -Upper Sileru Kolar Vizag B’nggon 220 kV Birpara-Salakti D/C line 1999 BIHAR 132 kV Sahupuri-Karmanasa S/C 220 kV Dehri -Sahupuri Tala Savings of ER Constituents Due to Export YEAR ISGS Thermal GEN (MU) EXPORT (MU) TOTAL SAVING (RS. CR) 1995-96 9584 854 69 1996-97 10628 652 75 1997-98 13585 2389 309 1998-99 14063 3438 461 1999-00 16381 5931 735 2000-01 18228 6773 755 2001-02 18279 8721 943 2002-03 20460 9382 961 National Grid CTU_NORTH RLDC CTU_NE CTU – INTER REGION RLDC CTU_EAST CTU_WEST RLDC RLDC STU STU RLDC STU NLDC CTU_SOUTH ERLDC:POWERGRID BULK POWER TRANSACTION W.R C.S.GENERATORS N.R SR STATE SECTOR GENERATORS NER STATE SYSTEMS Operating Frequency 49 to 50.5 Hz Frequency band for safe operation of Steam Turbine as recommended in IEGC Pre ABT Settlement system • The payment to Central Generating Station by a constituent - proportion to total energy – Recommendation of K.P.Rao drawal Committee Report. • Both Fixed and Variable charge was payable as per energy drawal • Based on Monthly Regional Energy Account- REA • Conventional Meter Readings • Fixed cost recoverable with deemed generation ( generation not made available) •Incentive payable after accounting for deemed generation Although a two part tariff- Single part for constituent Inadequacies • Non-utilization of Utilities’ Surplus Power – No incentive for Maximization of own/ IPP/captive generation within a State as the cost of power paid is based on pooled rate of ISGS stations. – No effective commercial mechanism for pricing deviations from schedule. • Dumping of surplus power at High Freq – Forced Backing down/ Reserve Shut down – Deemed generation for backing down • Non-utilization of embedded IPP/Licensee surplus Power. – Administrative problems and no commercial arrangements for utilization of this power. Any surplus remains unutilized. • Non-utilization of Pumped Storage Scheme – No commercial mechanism to draw cheap off peak power for pumping. Bhira PSS/Kadamkadai is not being utilized in the pumping mode. Contd.. • Inability to Despatch Generation according to Grid requirement. – Generation of Licensees cannot be despatched as per Grid requirements due to commercial problems. • Curtailment of Bilateral Transactions due to Grid Indiscipline. – Overdrawing State(s) deliberately increase drawls and cause frequency to dip below 48.5 Hz so that inter-regional transactions are terminated. • Absence of Merit Order Operation – As payments are based on drawls and not on shares/schedules, fixed cost are not perceived as sunk costs. Inherent Disadvantage • No incentives for generators /utilities to respond to dispatch orders for issues like frequency control – No Incentive for helping the grid – No disincentive for hurting the grid • No signal to generators to match availability with system needs • Did not promote Grid Discipline • No signal for trading of power. Overall economy was lost. EFFECT • Backing down of cheaper CS generation – Caused high per unit cost • Dumping of energy by other utility at high frequency/off peak hours– additional fixed cost generation & transmission. • More payment Liability - Even when helped the grid liability for Ultimate Effect • Grid Indiscipline• Low Frequency during peak • High Frequency during off peak • Control Instructions • Subjective decisions • Not based on overall economy • Perpetual Operational & Commercial Dispute amongst Utilities/Central Generators • Poor Supply quality to consumers/industries • Damage to equipments • Shifting of Industries/Investments Why ABT? •Promote competition, efficiency Merit order dispatch and economy- •Competitive market based system •Possibility of trading on a non-firm basisselling of capacity entitlement •Facilitating Grid discipline- Incentive and disincentive for deviation Capacity Ch. + Energy Ch. UI A + B C TOPICS DEALT IN THE ORDER • TARGET AVAILABILITY • CRITERIA FOR INCENTIVE • PROCEDURE FOR PREVENTION OF GAMING • PROLONGED OUTAGES • UI CHARGES AND FREQUENCY VARIATION • SETTLEMENT OF UI ACCOUNT • TREATMENT OF UNALLOCATED CAPACITIES Availablity Based Tariff (ABT) • • • Links commercial mechanism & Grid Operation Promotes grid operation ABT Structure – 3 parts of tariffs A. Capacity charges – Proportionate to entitlements (not actual drawals) – Full recovery at target availability (not PLF) – Incentives linked to Availability (80%) and PLF (77%) – Incentives half of per KWh fixed charges at target availability / capped at 21 p/u B. Energy charges – Payable for schedules (not as per actual drawals) C. Unscheduled Interchange – Payable for deviations from schedules – Linked to average frequency for 15 minute time block (graph enclosed) Central Govt. CERC CTU REB RLDC CEA State Govt SEB/STU SERC SLDC ISTS & ISGS X= L- G . Control Area