FI WARE WP11 Exploitation v2711
advertisement

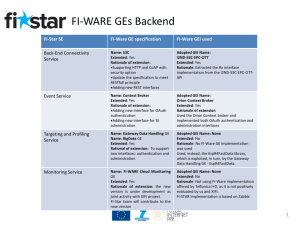
FI-WARE Exploitation Market Analysis, Exploitation Plan, IPR Management and Market and Policy Awareness http://www.fi-ware.eu http://www.fi-ppp.eu 11.1 Market and Competition Analysis Changes introduced • New overall vision has been produced › Operators are not the only objective, › We introduce the fact that most hi-tech industries have become platform battlegrounds, where convergence between IT, internet, telecommunications and media services and technologies occurs. › However, companies are planning to sell different element independently • New data and input from Platform Strategy Market Analysis included. Response to comments • Convergence HW-SW. › FI-WARE wants to be hardware agnostic • Hardware is available but we are open to new implementations. We would like to expand to the future, particularly to new protocols such as html5 11.2 Exploitation Plan including IPR Management Commercialization Involving our marketing units (Seville). It will be accelerated when they see the results of the test. Define FI WARE Platform Strategy based on the previous Platform Strategy Market analysis • The objective is validate a common Platform Strategy as a whole and not as a loose collection of GEs Marketing plan Answers to commercial questions individually by industrial partners • Identify the key segments, “ identify where FI-WARE is particularly useful - FI-WARE “Two sided market”- End Users and Developers • • Identify the main channels will be used to reach the various customer segments (Developers and End Users) and the marketing tools should be designed to be usable by the internal sales force. Identify the strategy to ecosystem management and attract as much developers as we can (Starting the Definition of the objectives for the planned Open Innovation Lab) Define Key IPR Principles • Analysis and Refinement of the existing FI-WARE Legal Notice that fulfills the needs of the three involved partners • Include the Terms and Conditions of the usage of the FI-WARE Contributions within the WIKI documentation 11.3 Market and Policy Awareness Changes introduced • Include inputs from Platform Strategy Market Analysis regarding regulation of platforms Future plans • • • • • • • • Cities are being contacted- additional contacts with European cities to wide geographic extension, Support from business associations Open innovation initial definition Events are being organized Planning Hackaton Events of different cities Support from authorities Interest in the coming call 3 the main impulse will come from the Open innovation lab and phase 3, when real users and results are expected. Exploitation Strategy scheme 1 2 Market Analysis FI-WARE Strategy Platform Market FI-WARE Strategies Strategy Analysis definition ICT Market Trends Analysis Individual Exploitation SWOT Analysis by FI WARE component Third Party Enablement FI-WARE Value Proposition FI WARE positioning FI WARE Impact Regulation concerns 3 Business plan and economical model 4 Definition of the costs structure Open Lab definition and Operational implementation Define revenue sharing business models regarding aggregation, composition, bundling, mashups. Initial Business Business Plan Model Definition elaboration GE´s Business Description Market Plan 5 Go-to-Market Distribution policy IPR, competitiveness principles 3rd FI-WARE Open Call Offers and price focused on descriptions “designing and Business SLA implementing a plan to accelerate (violations and penalties) the participation of developers Sales deployment plan IPRs Principles Test Bed and Sustainability M 12 M 24 M 36 FI-WARE Strategy settle the basis to coin an ecosystem around its technology and concept and the initial blueprint for build up a realistic business model FI-WARE Exploitation. Structure of deliverable Platform Regulation Platform Market Analysis Business model FI-WARE Strategy 3rd party enablement Individual Exploitation Plan Business Canvas Attract Sustainability Political barriers D11.1 external factors Vision SWOT D11.2 internal functions of exploitation Value Proposition Impact GE Business Description IPR Management D11.3 Regulation Regulatory attract organizations concerns Tools Policy identifies the potential barriers Dissemination Actions 11.1 Market and Competition Analysis Why Platforms? Platform Potential What is a platform? Business models FI-WARE Value Proposition Regulation FI-WARE SWOT Business ecosytem Successful Platform analysis FI-WARE value SWOT (global and per chapter) 6 Platform Market Analysis Vision of an ecosyst. A platform with potential • Eg. Smart city, IoT Build the architect ure Platform Leadership 1 Making money Coalition around the platform • Operators • Manufacturers • Developers • Customers Build and Evolve the platform 2 3 Modular/Fle xible Right Connectors Go-To-Market Value Proposition • Prizes • Subsidiza tion Two sided Platform One side Platform Choosing model FIWARE Platform Potential 1) Performs at least one essential function within the system • FI-WARE is an open, royalty-free platform -> general interoperability • IoT Communication function in FI-WARE allows unified communications 2) Easy to connect to or to build-upon • Easily aggregate services and applications, • A single set of APIs • An approach of comprehensive service description and annotation language (USDL) 3) Difficult to substitute • FI-WARE Open Specifications do not prescribe more than what is strictly required. • FI-WARE GEs can be picked and plugged together • FI-WARE Instance Provider role may decide to develop and/or integrate their own set of monitoring/mgt tools FI-WARE satisfies criteria for a successful platform At the end of the day it will be these business arguments that determine whether 3rd parties will accept the FI-WARE infrastructure. A Two Sided Business Ecosystem The classic difficulty for building a platform is the chicken-and-egg launch problem. Each side wants the other side to commit before it will spend resources to adopt the platform. This is a "critical mass" problem Implementation rules for pricing to solve the “critical mass problem” Subsidize the creators of value • For a software vendor, free access to the platform to develop and test and application, Cater to marquee users • Certain large consumer groups (Smart Cities) bring with them other large user groups, they add critical value. For end-user clients to pay for access to this application (per user, per volume-based access…). Analysis of Strategies of most successful players Technical Solution Business side Ecosystem management • Apple has demonstrated the value of integrated content/software/delivery systems • Apple’s focus on apps, rather than web browsing • End to end experience (content, developer, store, billing..) Apple store-700.000Apps on the store Walled garden Android and Apple devices dominate with 85 percent of the worldwide market • Google clearly wants to extend its dominance of search-related advertising into the mobile market and Android, no license fees, customizable and user friendly strategy • How to make money on the Internet. Google solved that essential business problem by linking focused advertising to user searches Google Play Store700.000Apps on the store Linux distribution Youtube, maps, gmail,, google, Android and Apple devices dominate with 85 percent of the worldwide market • Facebook is offering a very good product. It also has facilitated development of complementary applications by sharing with developers a special language based on HTML • Developers can sell advertisements or incorporate tools for conducting online transactions and keep all the resulting revenue. Supported by hundreds of thousands of software developers, Apple, Google and Facebook's platforms are fuelling innovation in consumer FI-WARE SWOT Analysis Strengths A complete solution for cost-effective creation of services that response to obvious market requirements Architecture that ensures the general interoperability Royalty free, open and standardization access points to essential services and technologies The possibility to easily aggregate services and applications Scalable, Flexible, seamless Supported by major IT vendors and Telco providers avoiding vendor lock-in Lower entry barriers Availability of experimentation capacities/infrastructure Opportunities Benefit form Open Innovation Feed and ecosystem where infrastructure providers can tap into novel revenue streams An open solution based on HTML5 offers the best way to access to device and network capabilities using common Web languages Broadening service offers in areas like M2M and context management Smart City potential unleash Launch concrete ecosystem around Urban Data Weaknesses Lack of ready to deploy services Lack of standards is still one of the main barriers for the deployment Limited technical integration Lack of commercial models and incentives A low base of user for potential awareness and understanding Threats Competitive platforms/solutions appear Economic barriers Protectionism: national/regional exclusionary practices Incumbent dominance: regional, layer (telecoms, IT, platform, business service) monoliths Entry or interoperation barriers Includes technology, standards, business model, contractual barriers Demand side: Lock-in, attitudes to new technology, trust Language, resistance to social/business model change Legal barriers Legal or regulatory differences, inefficiencies and ineffectiveness, due to licensing, privacy/security, standards, or financial regulation Policy fragmentation 11.2 Exploitation Plan including IPR Management IPR management strategy FI-WARE Strategy Technical Business Third Party Enablement Initial Go to Market Exploitation plan Individual & General Business Implementation Business CANVAS GEs Business Description FI-WARE Strategy Definition Technical Platform • • • Business Platform Interoperable architecture • Unified Service Description Language (USDL) • The ability to combine offerings from different FIWARE Instance Providers Open, Royalty-free and standardized access points Freedom to (re-) implement anywhere Ecosystem Management • • • Testbed and Open Innovation Lab Sustainable business models around FI-WARE Instances Usability and discovery towards end users (FI PPP Use Cases) For being successful, all sides must be tackled simultaneously. Third party enablement Open platform Long tail of customers: cities, business, manufacturing Benefits for developers - Solve fragmentation - Possibility to easily aggregate services and applications, - System support and well-tested platform (Open Innovation Lab) - 3rd parties become part of the FI-WARE ecosystem following FIWARE standards but without being forced to use all defined FIWARE GEs. - FI-WARE Instance providers get the chance to choose different market approaches developing sustainable business models around FI-WARE Instances Benefits for customers - Foster Sectorial Innovation - Useful tool to get knowledge on requirements of the market - Reduced complexity of ICT provisioning, scaling, global availability and meeting security requirements from customers and legal authorities FI-WARE directly addresses a number of the fundamental strategic concerns in the application and service provider domain Target Groups and Channels FI-WARE as a Business Innovation Platform: Focus on open ecosystem FI-WARE project as a useful tool to get knowledge on requirements of the market Developers Freely Available, tools and SDKs Service Providers Testbed Open Innovation Lab Community Internet-ofservices.com Linkedusdl.org Ecosystem Product Enablement USDL enabling Concepts & technology FI-WARE Partner´s existing customer relationships FI-PPP Use Cases Usability and discovery IPR analysis of all Enablers performed Analysis and Refinement of the existing FI-WARE Legal Notice and include the Terms and Conditions of the usage of the FI-WARE Contributions within the WIKI documentation Exploitation possibilities Platform provider Application provider service operator Telefonica/ FT /Telecom Italy •Smart city • Home services through platform • Included into FI-WARE offering Technicolor NSN, Ericsson, Intel •Home services •Service to operators • Cloud services into platform • Security services into platform • Tailored end to end IT solutions • Through use cases • Application provider • Network services IBM, Thales, DT, Atos, Siemnes< engineering Intel , NEC •Enterprise customers SAP • PPP-Partner • 3rd Parties • Partner Ecosystem • Permissive Open Source • SAP product enhancement FI WARE BUSINESS CANVAS Key partners Value proposition Key activities Application development • • • • • • • Telco Operators Software providers Software vendors IT Solution Providers System Integrators Network equipment providers Mobile terminal manufacturers • • Customer relationship Customer segments •Plus attracting end users •A two sided market • Usability and discovery Developers that towards end users (FI PPP build apps on top use cases) of FI WARE • Price/revenue share to access • SMEs the platform (Smart Cities) Traditional customers •Management of developer community Users • Attracting developers (revenue • share, Time to market, support • Enterprises systems...) • Smart Cities • Diversity of available APIs and access to network capabilities •Available documentation and support Channels •Managing different devices and OSs In collaboration with Use Cases A an innovative, open and Benefit from Open Innovation Identify the marquee developers interoperable platform that offers a complete solution for Identify influential consumers cost-effective creation and •Developers Key resources delivery of versatile digital services• Offered Catalogue of Generic Enablers • Dedicated workshops (f2f and virtual) • Cloud hosting services • Successfully attracting both • Open Source communities (Eclipse and OW2). • The IoT Communication function developers and end users • • • • • • • • • A single set of APIs, Open specifications comprehensive service description and annotation, optionally externalized through languages like the Unified Service Description Language (USDL) Provides a concept and concrete implementations of a generic and extendible ICT platform for Future Internet services addresses the requirements of Future Internet networked applications by an evolutionary Architecture Competitive pricing and billing schemes Providing developers incentives to publish on the platform (e.g. an attractive revenue sharing scheme and a tested platform Open Lab) • Support channels An appropriate Interface to the Network and to community-enabling the Devices linked-usdl.org, internet-of-services.com. Access information in a safe • National funding bodies way, preserving confidentiality • Other business service ecosystem activities from of data and privacy of the user partners (Bluevia, Movilforum, , SAP Net Weaver ) • National Platforms which have their own SMEs A integrated solution validated ecosystems And tested in different • • Building and maintaining an IT environments and sectors infrastructure to support Standardization activities Platform regulation Platform Leadership Cost Structure Infrastructure to be determined in Test-lab Customer Care or system support Marketing expenses • • • • • • •End Users • • Use partner´s existing customer relationships, plus new channels gained through the usage of the FI-WARE Platform by potential customers Inclusion in the portfolio, in the M2M market, mostly to the Smart City market Revenue Streams Licensing: (Pay per use): IaaS and SaaS , and as software component provider to build Generic Enables (GE, through licensing Selling Apps: M2M data market / Big Data and dedicated solution business Hosting service, Data storage , increase data traffic, Revenues for development tools, and professional services for customization and solution consulting As integrator of FI WARE Instances, Smart Cities as a service and revenue sharing (taxes, fees, fines…) 11.3 Market and Policy Awareness Marketing Strategy Business msg. Mkt. Msg. Mkt channels Regulatory Environment Roadmap List of Market and Policy actions Main Regulatory Concerns Online Identity, •including anonymity, digital presence, rights to delete information, etc. Traditional regulatory analysis is not equipped to deal with platforms Cloud computing, •including the risks and benefits of virtual access to information, etc. pricing and crosssubsidization strategies Content regulation, •including copyright, licenses, open access, etc bundling strategies Internet of things, •and the connections between people and devices collaboration Net Neutrality Relationships between consumers and suppliers online Cybercrime and Cyberlaw, • including phishing, cracking, cyberterrorism, etc A thorough investigation of potential risks can be recommended as a consequence of multisidedness of markets, Market Awareness Actions Action 1 Action 2 Action 3 Action 4 • Involve Relevant Actors, including Smart Cities and Large companies •get support from business associations •Assess IPR • Promote the Open innovation Lab Action 5 Action 6, 7and 8 Action 9 Action 10 •Elaborate marketing material for business impact •Organize National Events •Organize (Pan)-European Event/s •Get involved in sectorial Events (and understand specificities of the domains) •Obtain and analyse feedback from questionnaires • Hold Open Calls events (to create market awareness) Action 11 to 14 Action 15 •Validate FI-WARE messages •Assess the FI-PPP programme • Jointly participate in workshops •Submit contributions to public consultations • Organize a hackathon Potential Regulatory Actions Action 18 Action 16 To Participate in Digital Agenda events Action 17 To participate in the CFA on ICT in Regional Programmes Action 19 • Participate in the WG activities (FI PPP level) - Identify High and nontemporary barriers to entry in a market; - The dynamic state of competition behind these barriers to entry - The question of whether existing competition law is sufficient or not. Action 20 • Define roadmap of joint activities: FIWARE-ICT Labs Thanks !! http://www.fi-ppp.eu 23 Sales process : example smart city case The benefits of the FI-WARE platform that partners wishes to highlight will be sold via relevant use-cases and proof-points that demonstrate the successful adoption of FI-WARE technology. FI-WARE Open Innovation Lab From the Research and Technology Center to FI-WARE partners´ business units Production environment FI-WARE IDAS standard data format As FI-WARE usage-model Test beds in cities and other environments (FIPPP use cases ) examples and proof-points become available, highlights will be included in presentations, technical papers and demonstrations to partners and customers Smart Santander With a long term vision Results transfer in the respective business units and will strength the developer community …leveraging on global ecosystems that may boost local initiatives and entrepreneurs Provide an innovative interaction platform for industry, research and user domains Leveraging the Internet infrastructure as the basis of user-centered open innovation schemes, An open model to involve all city stakeholders and improve the local economy… Regional Authorities Public Companies National Authorities City Council MNC Companies Mayor Citizens UE Authorities City Business Tourists In the case of Smart Cities, city halls will be addressed via the conventional procedure followed within the FI-WARE partners, following the existing commercial structures. 26 Proposal on how to publish terms and conditions of use of FI-WARE GE RIs A new tab named as “Use Terms and Conditions” will be added to each entry in the FIWARE Catalogue which will be structured in three major sections: • • Use Terms and Conditions for experimentation within the FI-PPP program › Open Innovation Lab › • Standard text derived from the Collaboration Agreement Standard text that refers to “Open Innovation Lab: Use Terms and Conditions” agreement/contract that will be subscribed by third parties who will develop experimental applications to test/experiment under the umbrella of FI-WARE Open Innovation Lab activities External availability › › Text to be provided by each FI-WARE GE owner (some example texts provided in complementary .docx file) Distinguishes between use terms and conditions applying to downloadable software (binaries or open source) and to “as a Service” models, may also consider other commercial models Distinction between “Experimental Instances” and “External Instances” will be made within the “Instances” tab The "downloads" Tab should provide the means by which copies of the software (binaries or open source) can be obtained, provided that the Use Terms and conditions established for downloadable software are met.