Beaches: Rivers of sand
advertisement

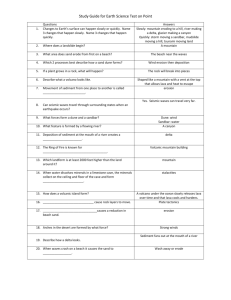
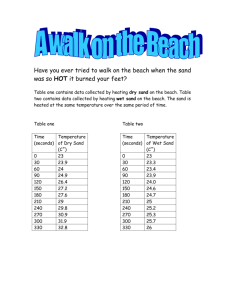
The Beach, A River of Sand River of Sand Video Swash zone: area onto the beach that waves splash Where does sand come from? From where do beaches come? • Sand, along with gravel, silt and clay are types of sediment – produced by the mechanical and chemical breakdown of rocks. • this material is then eroded by either wind, water, or ice – ultimately end as sediment in the sea. What about when there are no mountains? • sand can be entirely composed of organic material i.e. shell fragments, coral, and the tests (skeletons) of small planktonic organisms. The sand is said to be “biogenic.” Sand deposition If the sediments are… very fine sand sand cobbles boulders then they were deposited by wind small waves big waves glaciers La Jolla, California Summer Beach Gentle waves pile sand on the beach La Jolla, California Winter Beach Strong waves carry sand off the beach depositing it temporarily on off-shore sand bars • The shape of the beach is determined by how it formed… – Why is it better to surf in the winter? it is all about sand movement Longshore Drift vid consists of the transportation of sediment along a coast at an angle to the shoreline. It is dependent on: 1. direction of the wind 2. swash (turbulent water that washes up on the beach) 3. backwash (offshore flow of water) Natural Sand Deposition Features What’s happening to Block Island? a local tombolo a local spit Local barrier beaches on south shore Some features are directly created by man…why? Rip Currents • Bands of fast moving water moving off shore • Look for a channel of choppy water with a noticeable color difference DRAMATIC SEDIMENT FEATURES Sea Arch Sea Stack Blow Hole blow hole Hawaii What can you tell? Beaches are important habitats Headlands – Point Reyes, California Look! Elephant Seals “Haul Out” to molt beachmaster battle FUN with sand!! Sand detective investigation Sand gives you clues to it’s beach’s location Common constituents of sand: • Minerals: – Quartz : clear (doesn’t break down easily) – Feldspar : pinkish-tan – Mica: black and flaky – Olivine : olive – Hornblende : black/grey, dull – Garnet: reddish • Biogenic: – Coral – Shells – Foraminifera – Coralline algae • Rock: – Volcanic basalt (black islandic rock) – Granite Characteristics of sand oceanographers use to tell its origin: • Color composition • Shape (angular vs. round) distance traveled or age • Size strength of waves, wind, glacier • Pits directly from volcano • Sorting distance traveled, # of sources of material … so scientists also know about the beach’s location by… • it’s steepness, and thus power of the beach’s waves (from size of sand) • what the parent material is (color) • distance the sand traveled to get there (sorting, shape) • biogenic material…continental or island; tropical, temperate or polar • The influence of man (?) Wentworth sediment size scale, and resultant beach shape, for example Boulder Cobble Pebble Granule Very coarse sand Coarse sand Medium sand Fine sand Silt Clay Sediment size (mm) >265 65-265 4-64 2-4 1-2 0.5-1 0.25-0.5 0.07-0.25 0.25-1/256 <1/256 Average beach slope irregular 19°-25° 13°-19° 11° 9° 7° 5° 5° <5° <5° THE END