3. TASK PED and Total Revenues
advertisement

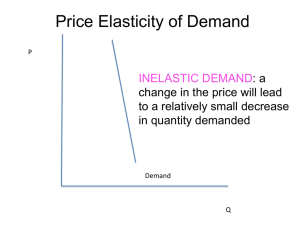
Yr 11 IB Econ WK 8 T1 Price elasticity is an important concept in economics, with numerous applications. One of these involves its relationship with the firm Total Revenue Total revenue (TR) refers to the amount of money received by firms when they sell goods and services. Total Revenue = Price of the good x Quantity of the good sold OR TR = P x Q Price Elasticity of demand helps firm to decide if by increasing the price of the good it produces will impact on the levels of its Total Revenue. HOW??? The law of demand states that Price is inversely related to Quantity. Hence when prices increase, quantity demanded decrease and vice versa. So by changing the price, would the firm’s TR increase or decrease??? This actually depends on the Price Elasticity of demand for the good. That is if PED is elastic or inelastic WHY??? INELASTIC DEMAND - EXAMPLE Assume the price of chocolate milk increases from $1 to $1.20 and the quantity demanded falls from 12 000 to 10 800 cartons. What will happen to the firm’s TR?? At P0 TR = P X Q = _______________ TR = _________ At P1 TR = P X Q = ________________ TR = _________ At the same time we need to calculate PED for chocolate milk to make a more accurate conclusion. PED = Q1 – Qo Qo x 100 P1 – Po x 100 = P0 Conclusion PED is ___________________ Therefore the firm should ___________________________ 1 Yr 11 IB Econ WK 8 T1 DIAGRAMTICALLY At Po ($1) TR = area b + c Price $ At P1 ($1.20) TR = area a + b $1.20 a $1.00 b 0 c 10 800 Before the Price increase at $1 After the Price increase at $1.20 D 12 000 Quantity in cartons TR = b + C TR = a + b The firm loses area C but gains A because the cartoons are now sold at the higher price of $1.20 Revenues at (a) = __________________________________________________ Revenues at (c) = __________________________________________________ The firm’s Total Revenue has increased by $960 ($2160 - $1200 = $960) Conclusion: if the firm has an _______________demand for its product and it wishes to INCREASE its TOTAL REVENUE then it should do that by ____________________________. ELASTIC DEMAND – EXAMPLE Assume that when a hotdog price is raised from $ 2 to $2.10 a hot dog seller finds that quantity demanded per week falls from 200 hot dogs to 180 hot dogs. What will happen to the TR of the seller? - Again it depends on PED of hot dogs!!!. Q1 – Qo PED = x 100 = Qo P1 – Po x 100 P0 2 Yr 11 IB Econ WK 8 T1 Price $ At Po ($2) TR = area b + c At P1 ($2.10) TR = area a + b $2.10 a $2.00 b c D 0 Before the Price increase at $2 After the Price increase at $2.10 180 200 Quantity of hot dogs TR = b + C TR = a + b Before the Price increase at ($2) After the Price increase at ($2.10 ) TR = _________________________ TR = _________________________ The RISE in the PRICE has clearly caused a FALL in the Total Revenues for the hotdog seller. Revenues at (a) =_______________________________________________________ Revenues at (c) = _______________________________________________________ The firm’s Total Revenue has decreased by $22 ($40 – 18 = $22) Conclusion: if the firm has an ___________________ demand for its product and it wishes to INCREASE its TOTAL REVENUE then it should ________________________________________ Thinking Point: Can you predict and explain what would be the likely outcome for Total Revenues if the PED for a product is Unitary ie PED = 1 Draw a diagram to illustrate. Student Tasks: 1. Complete questions 1 and 2 page 58 3