Food Chain Notes
advertisement

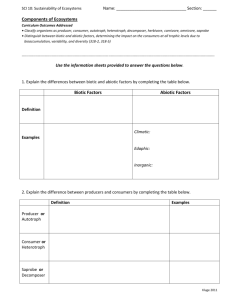
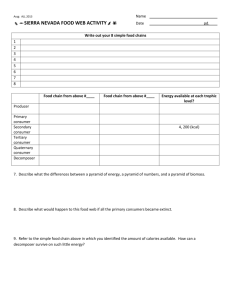
What is the difference between habitat and niche? Agenda for Tuesday Jan 5th 1. Finish/present posters 2. Food chains • If an ecosystem is to be self-sustaining it must contain a flow of energy. • The pathways of energy through the living components of an ecosystem are represented by food chains and food webs. Food Webs and Food Chains • All energy starts with the SUN • Producers – use sun’s energy – Autotrophs – Make their own food • Consumers – eat other organisms (heterotrophs) – Primary – eat plants – Secondary – eat primary consumers – Tertiary – eat secondary consumers Types of heterotrophs • Herbivores – plant eaters • Carnivores – meat eaters • Omnivore – both meat and plants • Detritivores – eat decomposing matter (detritus) Decomposers • Decomposers – eat dead organisms (detritivores) Food Chain • Feeding relationships among organisms in an ecosystem – Results in energy transfer (shown by arrows) Food Web • Interrelated food chains – Shows energy transfer – More complex = more stable Energy Pyramid • Shows trophic (feeding) levels and energy available to each level – 10% energy gets passed to each level – Lose 90% to living/respiration Fill in the levels of the food chain with the energy passed on. 1 J of energy 10 J of energy 100 J of energy 1,000 J of energy 10,000 J of energy Fill in the levels of the food chain with the energy passed on. 750,000 J of energy • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TE6wqG4 nb3M Label the trophic levels (producer, primary consumer, etc.) of each organism in the food chain. Agenda for Thursday Jan 7th 1. Go over homework/Food chain practice 2. Finish notes 3. Biomagnification Classify each member of the food web as autotroph or heterotroph. Identify the heterotrophs as herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores. Label as primary/secondary/tertiary consumer or producer Organism Autotroph/heterotroph Primary/secondary/ tertiary/producer Herbivore, carnivore, omnivore More biomass at the bottom -Less mass at upper trophic levels WHY?? Biomass Pyramid Human Impact on food chains/food webs • Introduced toxins – DDT and eagles • Extermination of a species – Wolves Biomagnification and bioaccumulation • Biomagnification = the increase in concentration of toxin as it passes through a food web – Higher level affected more • Bioaccumulation = accumulation of toxins in an organism – accumulate faster than they are broken down or excreted – Lower level affected more Biomagnification of a Toxin in Aquatic Environment Amount of Toxin in Tissue Level Tertiary Consumer 3-76 µg/g ww (fish eating birds) Secondary Consumers 1-2 µg/g ww (large fish) Primary Consumers (small fish) Primary Producers (algae and aquatic plants) 0.2-1.2 µg/g ww 0.04 µg/g ww The coyote would be which of the following: omnivore, carnivore, or herbivore Agenda for Thursday Jan 8th 1. Go over HW/review food chains 2. Biomagnification/Bioaccumulation