Ankle Rehabilitation
advertisement

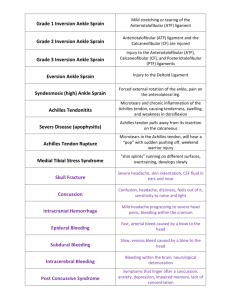
Ankle Rehabilitation ANDY DAVIS MSPT, LAT SPORT AND SPINE CLINIC OF MOSINEE Ankle Injuries Ankle Injuries Ankle Sprains The ankle is the second most commonly injured body part in sports. Ankle Sprains are the most common (85% are lateral ankle sprains) Result in alterations in postural control, ankle proprioception and neuromuscular functions. Chronic ankle instability (CAI) has been documented to develop in about 30% of ankle sprains Sports Med (2013) 43:385-393 Ankle Sprains Tissue healing timeframes for ligaments range into 6-12 weeks for scar tissue to mature to full tensile strength Reported timeframes for return to play have been around 50% of ankle sprains in high school sports return in less than one week. Athl Train 2007;42(3);381-387 J Mechanical vs Functional Instability Mechanical Ankle Instability (MAI): movement that goes beyond its normal range. This can be caused by pathological laxity, decreased joint mobility, synovial inflammation, and degenerative changes. Functional Ankle Instability (FAI): “giving way” episodes that are caused by proprioceptive deficits, neuromuscular deficits, postural control deficits, and muscle weakness. Chronic Ankle Instability Chronic Ankle Instability (CAI) can affect 10-20% of people who have an acute ankle sprain. CAI is made up of both FAI and MAI, with the patient experiencing these symptoms for greater than one year after the injury. CAI show decreases in joint position sense, reaction time, muscle activation (specifically peroneus longus), postural control, muscle strength, dorsiflexion range of motion. • FOOT AND ANKLE SPECIALIST AUG 2014 : (7) 298-326 FAI FAI group vs ankle sprain copers vs controls FAI group showed increased amount of talar tilt laxity vs the copers. J Athl Train. 2013 Sept-Oct; 48(5):581-589 Talar tilt range can be 0-23 degrees , but normal ankles have 0-5 degrees. When Anterior Talofibular ligament is involved, less laxity is noted than when Calcaneo-fibular ligament is also involved Wheeless’ Textbook of Orthopaedics Patient Self Reports Foot and Ankle Disability Index (FADI) Lower Extremity Function Test (LEFS) Foot and Ankle Ability Measure (FAAM) Sports Ankle Rating System Cumberland Ankle Instability Tool (CAIT) Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2006;87:1235-1241 Which is the best to use?? Patient Self Reports Utilize the tool that best fits the patient scenario CAIT is a tool to use to assess functional ankle instability independent of reference to the other leg. It is also able to measure the severity of the FAI. Ankle Sprains Focus today on 1st and 2nd degree lateral (inversion) ankle sprains Diagnosis - History, Palpation, Special Tests, Assessment - Ottawa Rules to help determine need of x rays Ottawa Rules Ankle Sprains Use of Temporary Immobilization Approximation of tissues Decreases capsular distention WBAT R.I.C.E. Cryotherapy Decreases metabolism to limit the secondary hypoxic injury Decrease effusion Compression Vasopneumatic compression Horseshoe/Lateral J pad Muscle Strengthening Strength work can help alter the muscle mechanorecptors, aiding in controlling joint motion. J OF ATH TRAINING 1998; VOL 33 (4), 310-314 Muscle Strengthening Decreased eversion strength for CAI Clinical Biomechanics 29(2014)439-443 Decreased muscle activation patterns *Decrease in peroneal nerve motor conduction velocity. *This decrease in reaction time can be up to 12 weeks even with 5/5 MMT AJSM 1996; 24: 362-9 AJSM 1998; 26: 72-8 Decreases also seen in hip joint abduction, adduction, and extension. *Gluteus Medius weakness is linked to ankle inversion sprains Physical Therapy in Sport 15(2014) 15-19 Muscle Strengthening Ankle Strengthening Muscle Strengthening The peroneal muscles can be affected by hemarthrosis, similar to the VM inhibition with knee pain AJSM 1998; 26 (1) 72-77 Eccentric Muscle Actions: Can enhance joint stability by providing an antagonsitic force that resists joint translation. J Athl. 2013 Jul-Aug; 48(4): 528-545 Drop Leg Test *Pt in sidelying, and examiner passively abducts the leg to the end range of hip abduction, then extends the hip 20 degrees. Patient is asked to hold this position as the examiner lets go. A drop of 2-12 inches shows weakness to the posterior fibers of the gluteus medius Physical Therapy in Sport 15 (2014) 15-19 Ankle ROM Manual joint mobilization has been shown to help decrease pain and increase DF ROM for the acute and chronic ankle sprains. Br J Sports Med 2014;48:365-370 JOSPT 2013(43)456 Reduction in ankle DF during terminal stance of gait can alter knee joint kinematics and kinetics in the sagittal and frontal planes. The Knee 21(2014)669-675 Proprioception Theory of proprioception is to shorten response times of muscles affecting joint position sense. AJSM 1997; 25(4):538-43 Postural control deficit first reported by Freeman et al (J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1965;47:678-695), and since then numerous studies have shown the importance of proprioception and balance. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2009;41:1510-30 J Strength Cond Res 2012;26:568-74 Gait and Posture 39(2014) 404-409 Ankle sprains affect single leg stance and sudden angular displacement. Proprioception Assessing and rehabbing with dynamic control may provide a better functional picture than solely testing proprioception. Foot Ankle Spec (2013) 346-351 Proprioception Proprioception BOSU muscle activation for single leg stance (Tibialis Anterior, Peroneus Longus, Medial Gastrocnemius), was different on blue vs black side J Strength Cond Res 2010; 24(1):218-22 not Functional Testing When is the athlete ready for return to play? Star Excursion Balance Test (SEBT): looks at 3 directions: anterior, posteromedial and posterlateral, with the posteromedial being the best predictor. Single leg hop, timed hop, triple hop and crossover hop (by Noyes and colleagues) Lower extremity functional test (LEFT) J Sport Rehabil. 2002;11:190-201 Functional Lower Extremity Evaluation (FLEE) JOSPT 2014(44)12:947-954 Functional Testing Functional Testing FLEE Control Sequence: timed lateral step down and timed leap and catch Hop Sequence: Single leg hop for distance, single leg timed hop, single leg triple hop for distance, and crossover hop for distance. Endurance Sequence: Square hop test, LEFT Taping vs Bracing Both have had evidence of success, especially with the individuals with a history of ankle sprains, in reduction of injuries. Ankle bracing has been shown to be a more cost effective in the long term. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(9):1840-1848 Achilles Tendon Achilles Tendon Rupture Acute Achilles tendon rupture annual incidence of 18 per 100,000 people per year. Immobilization vs. early active rehabilitation and weight bearing Fear of movement and physical activity (kinesiophobia) plays a role in rehab outcome Scand J Med Sci Sports 2014; 24:152-158 Early WB is widely accepted but no consensus on the preferable protocol Injury, Int. J Care Injured 45 (2014)1782-1790 Achilles Tendon Rupture Immediate FWB leads to higher patient satisfaction, earlier ambulation and earlier return to work and pre-injury activity level. Early ankle mobilization (free plantar flexion with DF restriction of 0 degrees) is superior to immobilization, after 3 weeks Combined functional treatment, immediate WB & early ankle mobilization, starting at week 3, is most beneficial. Injury, Int. J Care Injured 45 (2014)1782-1790 Achilles Tendon Rupture Early weight bearing can prevent muscle atrophy, stiffness, adhesions, and DVT’s and has been associated with stronger tendons due to improved vascularization and an improved immunologic response. Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery 52 (2013) 622-628 Low rerupture rates can be achieved with conservative management of acute AT ruptures and no difference in rerupture rates in WB and NWB groups. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2014;96:1073-9 Achilles Tendon Rupture Achilles Tendon Total Rupture Score and heel rise work had no difference in the early WB vs NWB of the nonoperative achilles tendon groups. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2014;96:1497-503 Ability to perform a single leg heel-rise is significantly related to patient reported outcome after Achilles tendon rupture. Scand J Med Sci Sports 2014; 24:152-158 Achilles Tendonosis Cause can be multifactorial: impaired flexibility, overuse, overload, poor running technique, cavus and planus foot types. Mistakenly interchanged with Achilles tendinitis, as tendonosis has calcifying degeneration/fibrocartilaginous near the Achilles insertion on calcaneus or 3-5 cm above. Achilles Tendonosis Eccentric exercise has been show to improve symptoms and may reduce degenerative changes. Increasing flexibility and strength are primary goals. Avoidance of hills and impact activity. Foot Ankle Clin N Am 19(2014)73-86 Thank You!