Unit 2 - Biomechanics
advertisement

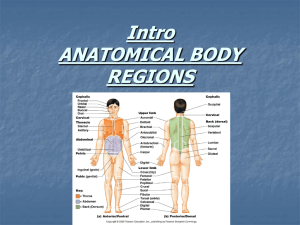
Unit 2 - Biomechanics “Perfection is a Road, NOT a Destination” What is Biomechanics? • is the sport science field that applies the laws of mechanics and physics to human performance • Cause and effect • In relation to sport, biomechanics contributes to the description, explanation, and prediction of the mechanical aspects of human exercise, sport and play. What types of Science are involved? • Biology – muscles, bones, joints • Physics – laws of motion, center of gravity, friction, projectile motion • Mathematics – angle of release, range of motion • …..alot more Background Information In order to be effective at maximizing human performance for skills, you will need to know • What the anatomical position is • What muscles perform what motion, and what bones each major muscle group moves • What each joints R.O.M. is (Range of Motion) • What certain angles of release may be • Phases of skill analysis Anatomical Position – Where we would describe the body positions Basic Body Directions • Anterior vs. Posterior – front or back of the neutral anatomical position • Superior vs. Inferior – up or down in relation to another part • Medial vs. Lateral – inside vs. outside of a body part or object • Left or Right – ummmm, it’s the same. But it’s always from the person’s view, not the observer. Question #4 Try These 1. Where is the arms in relation to the midline of the body? 2. Where is the right foot in relation to the midline of the body? 3. The hands are where in relation to the shoulder joint? Basic Body Movements • • • • • • • Flexion – decrease the angle of a joint Extension – increase the angle of a joint Abduction – bring away from the midline Adduction – bring close the midline Circumduction – circular movement of a joint. Ex. Drawing a circle with your wrist Rotation – rotating a joint medially or laterally Question #6 - Tee it up! • What movement is the left elbow joint performing? • What movement is the right shoulder performing? • What movement is the right hip performing? Throwing a Dodgeball • What body parts move to what directions? Foot moves Anterior for balance Hand and Forearm move to the Posterior in my backswing Hand is slightly MEDIAL, to the Elbow which is LATERAL to the Hand Arm quickly moves Anterior with Elbow leading the way May finish with your arm in an INFERIOR position. Throwing a Dodgeball • What body joints are involved in what movements throwing a dodgeball? Back Swing Elbow Joint Flexion Shoulder Joint Abduction Shoulder Joint Extension Acceleration Circumduction of the Shoulder Medial Rotation of the Shoulder Extension of the Elbow Flexion of the Wrist Balance and Stability • Balance and Stability Lab – review questions. • Balance is effected by the following 3 concepts: • Base of Support • Center of Mass • Line of Gravity Boys vs. Girls • Males have more muscle mass in their upper body and more density therefore they have a higher Center of Mass. • Females have a Lower Center of Mass for the opposite reason. (less mass in the upper body). Experiment • Task #1 – Try to stand up • Task #2 – Pick up the Chair • Task #3 – Pick up the Cash!! • Summary? How does this stuff apply to Sport? • Article “Making Strides Athlete Development” • • • • What are the examples they reviewed? Taylor Hall? Swimmers? Wrestlers? Balance/Stability Video Analysis • Discuss the Importance of Video Analysis in Sport and Coaching • Advantages? Biomechanical Drawings • Stick figure representations of movement. SKELETON REFERENCE! • Help to simplify movement of the body’s mechanics and the placement of proper position and errors. Phases for stick figures should be at least in the following phases: Prepartory/Preliminary, Backswing, Acceleration and Contact Points, Follow Through See Examples • Sample Video • Zygote Body • Here’s what they look like. Example #1 Example #2 • Phases of Running Handstand See video Remember the Phases of Skills • Preliminary Phase – lead up, starting postion • Backswing/Recovery Phase – getting the body into initial motion, backswings, getting ready to produce force • Force Producing Movements – the movements involved to produce the force needed for impact or propulsion. • Critical Instant – The moment of release or contact. • Follow Through – the movements that occur after contact or release Cartwheel or Handstand See tutorial Cartwheel Tutorial With your partners, go back again and execute a cartwheel…….using video from the side, front and back. Human Levers • In biomechanics, the bones function to facilitate movement, and are to help with the human levers. • All levers have three things • Fulcrum – point at the which the lever rotates • Load – Force added to the system • Effort – Force applied by the user to the system. • Eg Basic Bicep Curl with 20 lbs.