DNA
advertisement

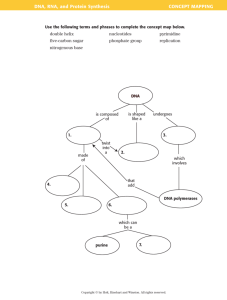
DNA The molecule of heredity. • The molecules of DNA is the information for life (determine an organism’s traits) • DNA achieves its control by determining the structure of proteins. DNA • Deoxyribonucleic Acid • nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acid The Structure of Nucleotide • DNA is made of repeating subunits called nucleotides. . Phosphate group Nitrogenous base • Nucleotide – – Simple sugar – Phosphate group – Nitrogenous base Sugar • The simple sugar in DNA is called deoxyribose which gives DNA its name • In DNA, there are four possible nitrogenous bases: – adenine (A) – guanine (G) – cytosine (C) – thymine (T). • Nucleotides join together to form long chains –the phosphate group of one nucleotide bonds to the sugar of an adjacent nucleotide(they form the backbone of the chain) • the nitrogenous bases stick out like the teeth of a zipper. • The DNA molecule is a double helix. It contains two strands of nucleotides, in a spiral shape – Sugar- phosphate chains on the outside with the nucleotides in the inside. – The nucleotides held together by H bonds between A and T, and also between G and C. (Base Pairs) • The sequence of nucleotides on one strand is matched perfectly to a complementary sequence on the other strand. • In DNA, the amount of A = amount of T, and the amount of G = amount of C. The importance of nucleotide sequences • The sequence of nucleotides forms the unique genetic information of an organism. • The closer the relationship is between organisms, the more similar their DNA nucleotide sequences will be. DNA Replication Process where DNA copies itself • Separation of strands – bonds are broken between complementary base pairs • base pairing – The bases of free nucleotides pair with the bases of the original DNA strands – Each strand builds a complementary strand • Results of DNA replication – 2 DNA molecules – Each consists of an original strand of nucleotides and a new strand • Errors sometime do occur • The wrong nucleotide is added to the new strand • A protein (enzyme) that proofreads the new DNA strand and corrects the mistake • http://www.lewport.wnyric.org/JWANAMAKER/animations/DNA%20Replication%20%20long%20.html • http://science.nhmccd.edu/biol/bio1int.htm