uro lecture
advertisement

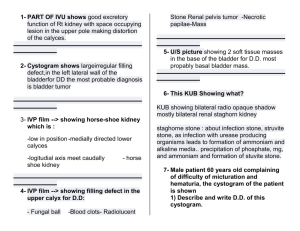
• IONIZING RADIATION Conventional (plain) radiography. Contrast studies (X-Ray + Contrast)• Computed Tomography. Isotopic scan Angiography • NONIONIZING RADIATION US. MRI. • • • • Intravenous urography Cysto-urethography Antegrade pyelography Retrograde pyelography Hysterosalpingography Conventional plain film of the abdomen is called a KUB (Kidneys, Ureters, Bladder) KIDNEYS URETERS URINARY BLADDER URETHRA Good evaluation of radio-opaque stones This is KUB taken post intravenous contrast injection KUB IVU This is KUB taken post intravenous contrast injection Also called IVP (intravenous pyelogram) Demonstrates both function and structure of the renal system •Function --- Filtration •Structure --- Contrast filled collecting system Indications: Contra-Indications: (relative) •Urolithiasis / calculus •Pyelonephritis •Hydronephrosis •Trauma •Tumour •Renal hypertension •Congenital abnormality •History of Allergy •Asthma •Cardiovascular disease •Sickle cell disease •Diabetes mellitus This is KUB taken post intravenous contrast injection Renal Pelvis • After IV injection, sequential images are taken in time order. • Immediate post IV • 5 min post IV • 10 min post IV Left Ureter Urinary Bladder This is KUB taken post intravenous contrast injection • Right Kidney Immediate post IV is nephrogram Left Kidney This is KUB taken post intravenous contrast injection • 5 min post IV is nephrogram This is KUB taken post intravenous contrast injection • 10 min post IV is nephrogram Renal Pelvis Left Ureter Full Bladder 20 min Urinary Bladder Kidney • • • • Renal fascia Hilum Renal sinus Renal cortex – Renal columns • Renal medulla – Renal pyramids • Calyces – Minor calyces – Major calyces – Renal pelvis Non-contrast Venous = Parenchymal Arterial = Cortical Excretion Case one A 29 year old female patient presented to the emergency department complaining of acute sudden severe right flank pain radiated to the groin for 1 hour associated with hematuria. • What is the likely diagnosis? • What investigation you will request? • What are the findings you expect to see? Renal tract stone Renal tract stone: Renal tract stone Renal tract stone: Urinary tract stone Case Two A 36 year old male patient involved in road traffic accident. On examination patient is conscious oriented and in pain. Abdominal examination revealed diffuse guarding and tenderness. What is the likely diagnosis? What investigation you will request? What are the findings you expect to see? Case Three A 54 years old female patient known case of diabetes and hypertension found to have high creatinine level. What is the likely diagnosis? What investigation you will request? What are the findings you expect to see? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis Case Four A 49 years old male patient smoker for 30 years. Presented to primary health case with complaint of hematuria and weight loss. Patient denied history of flank or pelvic pain. What is the likely diagnosis? What investigation you will request? What are the findings you expect to see? Renal cell tumor Renal cell tumor Transitional cell tumor Renal cysts polycystic kidney disease Horseshoe kidney Cross Ectopic Kidney