Ziegler-Natta Polymerization
advertisement

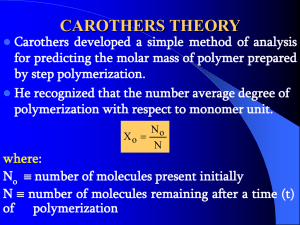
Ziegler-Natta Polymerization: Synthesis of tacticity specific polypropylene S.C.S. Lai (s.lai@chem.LeidenUniv.nl) Leiden University April 8th, 2004 Table of contents Overview Mechanism (general) Structure of catalyst Stereospecifity\ Role of ß-TiCl3 Conclusion S.C.S. Lai, April 8th 2003 Ziegler-Natta Polymerization 2 Overview, polymerization (1) Three possible polymer syntheses mechanisms: Free radicals ions metalorganic complexes Polymers of specific tacticity wanted in industries: Isotactic S.C.S. Lai, April 8th 2003 Syndiotactic Ziegler-Natta Polymerization Atactic 3 Overview, polymerization (2) Linear vs. branched polymers Ziegler-Natta catalyst generally used to produce linear, isotactic polypropylene! S.C.S. Lai, April 8th 2003 Ziegler-Natta Polymerization 4 Overview, history (1) First report in September 1955 using “purple phases” of TiCl3 (α-TiCl3 and γ-TiCl3) and AlEt3 (higher activity) or AlEt2Cl (higher stereoselectivity). Solvay 1973: Added TiCl4, which acted as a catalyst to convert β-TiCl3 into an active phase of TiCl3 (higher activity due to smaller particles). S.C.S. Lai, April 8th 2003 Ziegler-Natta Polymerization 5 Overview, history (2) Shell 1980: TiCl4 supported on MgCl2 in presence of AlEt3 or AlEt2Cl. Active species still TiCl3 . Other remarks: Awarded Nobel price in 1963. 1980’s: Process attributed to Robert Banks and J. Paul Hogan Cerutti, L; International Journal for Philosophy of Chemistry, 1999 (5), 3-41 S.C.S. Lai, April 8th 2003 Ziegler-Natta Polymerization 6 Mechanism Two complications Why Cl-vacancy? Why stereospecific? Cossee-Arlman postulate (1964) S.C.S. Lai, April 8th 2003 Ziegler-Natta Polymerization 7 Structure of the catalyst, overview Three phases of TiCl3 Color Stucture Activity α-TiCl3 Purple Hexagonal layered structure Isotactic β-TiCl3 Brown Needle structure Little stereospecifity γ-TiCl3 Purple Cubic layered structure Like α-TiCl3 S.C.S. Lai, April 8th 2003 Ziegler-Natta Polymerization 8 Structure of the catalyst, overview Schematic view of the structures of α-TiCl2, α-TiCl3 and ß-TiCl3 S.C.S. Lai, April 8th 2003 Ziegler-Natta Polymerization 9 Structure of the catalyst, Clvacancies (1) Ion count: (2m2 – 2) Cl - (m - 1)2 Ti2+ ----------------------------- Surplus of 4(m - 1) negative charges Sheet of α-TiCl2, consisting of 2 layers of Cl with Ti in the octahedral holes. S.C.S. Lai, April 8th 2003 - Offsetting by Cl vacancies Ziegler-Natta Polymerization 10 Structure of the catalyst, Clvacancies (2) - 2 2+ Thus: Surplus of 4 (m – 1) Cl on (m – 1) Ti Number of vacancies: 4(m 1) 4 4 equivalents h 2 (m 1) m 1 m mole.TiCl2 Typical crystal of ~1μm has about than 1-2 vacancies per 2+ 1000 Ti -ions. Analogous calculation for α-TiCl3 yields the same result. S.C.S. Lai, April 8th 2003 Ziegler-Natta Polymerization 11 Structure of the catalyst, active site (1) Cl-vacancies on the edges of the crystal. Electron Microscopy: active sites are on the edges Ti at the active sites in a square of Cl S.C.S. Lai, April 8th 2003 Ziegler-Natta Polymerization 12 Structure of the catalyst, active site (2) Square makes an angle of 55° with the base plane. Cl ’s not equivalent: - S.C.S. Lai, April 8th 2003 3 stuck in crystal 1 bound by 2 Ti3+ 1 loosely bound (to 1 Ti3+) Vacancy and L not equivalent sites Ziegler-Natta Polymerization 13 Stereospecifity, bonding of propylene V L V V F = Ti B B B F Ti B L = Ti Et AlEt 3 L F Ti V F B B H3C CH3 Et CH2 Ti F Two possibilities: H3C V HC CH2 Ti CH Et CH 2 F 1. Alkalyne moves back to vacancy 2. Alkalyne doesn’t move back S.C.S. Lai, April 8th 2003 Ziegler-Natta Polymerization 14 Stereospecifity, Polymerization (1) H3C CH H3C V Ti CH Et Et Ti F CH H3C H2C CH 2 H3C V H2C CH2 Ti F H3C CH H3C V Ti CH 2 CH 2 F Et H3C R Et CH3 HC CH2 H3C R CH 2 F Polymer moves back to vacancy isotactic polypropylene S.C.S. Lai, April 8th 2003 Ziegler-Natta Polymerization 15 Stereospecifity, Polymerization (2) CH3 CH3 H3C Et V CH Ti CH 2 H2C H3C CH | H3C Et HC CH H2C CH2 Ti F CH 2 F H3C R Ti CH 2 CH3 HC Et V F H3C R Polymer doesn’t back to vacancy syndiotactic polypropylene Experimental: Some syndiotactic PP at -70° S.C.S. Lai, April 8th 2003 Ziegler-Natta Polymerization 16 ß-TiCl3, Structure (1) β-TiCl3 has a needle structure: Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl Ti3+ Cl Ti3+ Cl Ti3+ Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl m Charges: 3(m+2) + 3(m+9) 3 vacancies per chain Actual structure Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl Ti3+ Cl Ti3+ Cl Ti3+ • • Cl Cl • ß1 S.C.S. Lai, April 8th 2003 m ß2 Ziegler-Natta Polymerization 17 ß-TiCl3, Structure (2) ß1 site: TiCl3FCl2L• TiCl3FClLR• Charge - 1/2 ß2 site: TiCl3FClL• 2 Charge +1/2 S.C.S. Lai, April 8th 2003 TiCl3FR• 2 Ziegler-Natta Polymerization 18 ß-TiCl3, Reactivity Reactive sites for diene-polymerization: ß1 site: 1 vacancy, limited space 1,4 trans-polymers ß2 site: 2 vacancies, both forming pi-bonds with diene 1,4 cis-polymers Experimental: butadiene: mixture of trans and cis isoprene: only cis S.C.S. Lai, April 8th 2003 Ziegler-Natta Polymerization 19 Conclusion Three phases of TiCl3 Only α-TiCl3 and γ-TiCl3 active in stereospecific ZieglerNatta polymerization - Active sites are the Cl -vacancies, located at the edges of the catalyst. Stereospecifity are due stereometric interactions, forcing the same orientation for each propagation step ß-TiCl3 has 2 different active sites, one forcing dienes to polymerize 1,4-cis, one 1,4-trans, if molecule is flexible. S.C.S. Lai, April 8th 2003 Ziegler-Natta Polymerization 20 Final remarks Slides: http://home.wanadoo.nl/scslai Questions? S.C.S. Lai, April 8th 2003 Ziegler-Natta Polymerization 21