Slide sex pada tumbuhan
advertisement

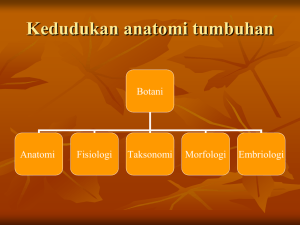
SEX DETERMINATION Many groups use sex chromosomes to determine sex. Mammals have the X and Y chromosomes XX = female, XY = male Sex of mammals is determined by the Y chromosome. In the absence of Y, gonads become ovaries. All other chromosomes are called “autosomes” Thus, humans have 46 chromosomes, 44 autosomes plus 2 sex chromosomes. X and Y Chromosomes The X has many genes on it, just like the autosomes. Most of the genes on the X have nothing to do with sex. The Y has very few genes on it. It consists of mostly inactive DNA. One gene on the Y is very important: SRY. The SRY gene is the primary determinant of sex. If SRY is present, testes develop in the early embryo. The testes secrete the hormone testosterone, which causes development as a male. If SRY is absent (no Y chromosome), ovaries develop instead of testes, and the embryo develops into a female. The X and Y chromosomes share a common region at their tips, the pseudoautosomal region. Crossing over in meiosis occurs in this region. Sex Chromosomes in Other Organisms 1. Sex chromosome composition in birds, butterflies, moths and some fish is opposite that of mammals, with the male the homogametic sex (ZZ) and the female heterogametic (ZW). Z-linked genes behave like X-linked genes in mammals, but the sexes are reversed. 2. In plants, the arrangement of sex organs varies: a.Dioecious species (e.g., ginkgo) have plants of separate sexes, one with male parts, the other with female. b.Monoecious species have male and female parts on the same plant. i. Perfect flowers have both types of parts in the same flower. ii. Imperfect flowers (e.g., corn) have male and female parts in different flowers on the same plant. 3. Some dioecious plants have sex chromosomes and use an Xchromosome-autosome balance system, but many other sex determination systems also occur in dioecious plants. Chapter 11 slide 4 KONTROL PENAMPILAN SEX Penyerbukan pada tumbuhan penyerbukan silang (alogami) penyerbukan sendiri (autogami). Tipe sex pada tumbuhan Pada individu bunga: 1. Staminat atau Androecious: bunga hanya mempunyai stamen atau benang sari saja, dan disebut bunga jantan 2. Pistilat atau Ginoecious: bunga hanya mempunyai karpel atau putik saja dan disebut bunga betina 3. Hermaprodit atau Sempurna: bunga mempunyai stamen dan karpel 4. Neuter or Agamous: bunga tanpa stamen dan karpel atau organ sex abortive Pada individu tumbuhan 1. Androecious: pada satu tanaman hanya ada bunga jantan 2. Ginoecious: pada satu tanaman hanya ada bunga betina 3. Monoecious: pada satu tanaman terdapat bunga jantan dan bunga betina pada bunga yang berbeda 4. Hermaprodit: pada satu tanaman hanya ada bunga hermaprodit 5. Andromonoecious: Pada satu tanaman terdapat bunga jantan dan bunga hermaprodit 6. Ginomonoecious: pada satu tanaman terdapat bunga betina dan bunga hermaprodit 7. Trimonoecious: pada satu tanaman selain terdapat bunga jantan dan bunga betina juga terdapat bunga sempurna Pada populasi tumbuhan 1. Monoecious: suatu populasi tumbuhan yang terdiri dari hanya tumbuhan monoecious 2. Dioecious: suatu populasi tumbuhan yang terdiri dari hanya tumbuhan androecious dan ginoecious 3. Hermaprodit: Suatu populasi tumbuhan yang terdiri dari hanya tumbuhan hermaprodit Kromosom sex pada tumbuhan Silene latifolia - tumbuhan jantan memiliki kromosom sex heteromorfik XY (22 kromosom, kromosom sex XY) - tanaman betina terdapat 22 kromosom dan kromosom sex XX. Rumex sub genus acetosa - rasio (banyaknya kromosom X/banyaknya set autosom) sama dengan 1.0 maka terjadi tumbuhan ginoecious. - jika rasionya 0.5 atau lebih kecil maka terjadi tumbuhan androecious - jika antara 0.5 dan 1.0 maka akan dijumpai tumbuhan andromonoecious, hermaprodit, atau ginomonoecious. Tanaman dioecious asparagus (Asparagus officinalis). - Yang jantan memiliki kromosom sex heteromorfik. - YY dijumpai hidup dan fertil. Cannabis sativa - tipe sex heterogametik XY monoecious - homogametik XX menampilkan ginoecious. Alel resesif pada kromosom X mengurangi kemampuan menjadi betina -tanaman XXm menampilkan tipe sex dari ginoecious sampai ke monoecious -tanaman XmXm menjadi tanaman jantan dengan morfologi bunga seperti bunga betina Gen Mendelian Yang Mengontrol Tipe Seks Penampilan seks pada ketimun Genotipe M_F_ M_ff mmF_ mmff Fenotipe Ginoesious Monoesious Hermaprodit Andromonoesious Penampilan seks pada melon Genotipe A_G_ A_gg aaG_ aagg Fenotipe Monoesious Ginomonoesious Andromonoesious Hermaprodit Penentuan sex secara molekuler Dengan menggunakan teknik PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) dimana fragment DNA dapat diamplifikasi secara in vitro, identifikasi sex pada tanaman dapat dilakukan PCR tanaman Salix viminalis PCR Silene latifolia. (no 5-8 = tanaman jantan) The search for sex-specific markers in Leucadendron : Applications of ISSR and suppression subtractive hybridisation All species Leucadendron are dioecious Karyotyping RAPD ISSR could not identify sex chromosomes 25 RAPD primers could not identify sex-specific markers for 12 Leucadendron species 37 primers and 8 combined primers failed to find sex-specific fragment Plants with heteromorphic sex chromosomes Silene latifolia, 64 RAPD primers identified 4 male-specific markers Canabis sativa, 15 RAPD primers found 2 male-specific markers Silene latifolia SCAR marker No heteromorphic sex chromosomes Ginko biloba, 1200 RAPD primers detected 1 male-linked band Pistacia vera, 1000 primers, 1 sex marker found P. atlantica, 472 primers, 1 sex marker identified Leucadendron? ♂ 45 ISSR primers could not identify sexspecific fragments 1000bp 750bp 500bp ♀ Male substracted library B 194 217 1500bp 1000bp 700bp 500bp Differential screening of male substraction (A) Probed with ♂ (B) Probed with ♀ Insert no Approx size (bp)a Clear readable sequence Accession no 2 3 600 710 220 725 AJ627251 AY586361 11 500 272 AJ428413 17 30 101 470 450 1000 463 252 321 Z00044554304 AY582139 U63020 197 620 617 AJ428413 204 510 321 BAA22288 220 680 680 AJ428413 240 510 503 AJ970307 354 620 639 AJ428413 356 620 639 AJ428413 362 650 662 AJ428413 Gene(s) cpDNA 23S rRNA cpDNA NADH dehydrogenase subunit F cpDNA rpoC2 cpDNA rrn23 cpDNA psaB cpDNA D1 protein (psbA) cpDNA petB and petD polyprotein (mat_peptides) cpDNA ycf6-psbM intergenic spacer cpDNA16S rRNA and tRNA Ile cpDNA 23S rRNA and tRNA Ala cpDNA 23S rRNA and tRNA Ala cpDNA tRNA Ile and tRNA Ala Organism Sequence identity E-value Nymphaea alba Fagus grandifolia 182/188 (96%) 466/477 (97%) 1e-88 0.0 Calycanthus fertilis var. ferax Nicotiana tabacum Panax ginseng Magnolia pyramidata Calycanthus fertilis var. ferax Oryza australiensis 213/229 (93%) 4e-86 429/438 (97% 228/239 (95%) 284/309 (91%) 0.0 7e-103 1e-108 543/593 (91%) 0.0 88/106 (83%) 2e-37 Calycanthus fertilis var. ferax 104/121 (85%) 62/70 (88%) 55/66 (83%) 466/477 (97%) 2e-19 2e-10 600/609 (98%) 0.0 601/612 (98%) 0.0 336/347(96%) 5e-168 Cucumis sativus Calycanthus fertilis var. ferax Calycanthus fertilis var. ferax Calycanthus fertilis var. ferax 0.0 the male and female genome might be rather homologous the non-recombining region in Leucadendron is very small chloroplast copy number may differentiate male and female L. discolor