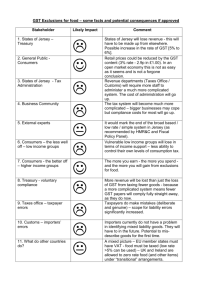
Goods and Services Tax Seamless Integration with
Existing Processes
23 Nov 2005
Cheah Chee Keong – Solution Manager, SAP South Asia
chee.keong.cheah@sap.com
Introduction
Our Prime Minister 2005 Budget Speech extract :
“… The Government proposes to replace both these
taxes (Sales Tax and Service Tax) with a single
consumption tax, based on the value-added
concept. The new tax, known as the Goods and
Services Tax (GST), will be more comprehensive,
efficient, transparent and effective, thereby
enhancing tax compliance ....”
The 2005 Budget
- 10 September 2004
SAP AG 2002, Title of Presentation, Speaker Name 2
An Overview of GST
GST is charged on the taxable supply of goods and
services made by a taxable person in the course or
furtherance of business in Malaysia
It is a multi stage tax on domestic consumption, similar
to Value Added Tax, levied on taxable supply of goods
and services in Malaysia
Imposed on majority of goods and services with minimum
exemptions and zero rating
Based on net value at each stage of business transaction
up to retail stage
Covers all sectors of the economy
Relies on invoiced-based tax
It is a tax on consumption and not on investment
SAP AG 2002, Title of Presentation, Speaker Name 3
Scope of GST
The GST is based on destination principle
Levied at all levels of production and distribution of
goods and services supplied and consumed in Malaysia
Made by the taxable person
In the course of furtherance of any business made by the
taxable person; and
On the importation of goods or services in Malaysia
SAP AG 2002, Title of Presentation, Speaker Name 4
How GST Works
The taxable person pays GST or input tax on his
business purchases.
He then adds value to those goods and services. When
the goods are sold or services are provided, GST or
output tax is collected based on the selling price.
At the end of his taxable period, he submits his return
declaring the output tax and claiming a credit on the
input tax he paid. (Output tax - Input tax)
If tax on input exceeds the tax on output (normally zero
rated goods), the difference is refunded
SAP AG 2002, Title of Presentation, Speaker Name 5
How GST Works
Collection of Multi-Stage Tax assuming at 5%
Clay Merchant
Sales Price = RM10.00
GST
= RM 0.50
Total
= RM10.50
Payment to Government
GST collected
= RM 0.50
Less GST paid
= RM -GST payable
= RM 0.50
Crockery Manufacturer
Sales Price = RM50.00
GST
= RM 2.50
Total
= RM52.50
GST collected
Less GST paid
GST payable
= RM 2.50
= RM 0.50
= RM 2.00
5% X (50 – 10)
= RM 2.00
Wholesaler
Sales Price = RM70.00
GST
= RM 3.50
Total
= RM73.50
GST collected
Less GST paid
GST payable
= RM 3.50
= RM 2.50
= RM 1.00
5% X (70 - 50)
= RM 1.00
Retailer
Sales Price = RM100.00
GST
= RM 5.00
Total
= RM105.00
GST collected
Less GST paid
GST payable
= RM 5.00
= RM 3.50
= RM 1.50
5% X (100-70)
= RM 1.50
Total GST paid
= RM 5.00
Consumer
Payment to Retailer
= RM105.00
SAP AG 2002, Title of Presentation, Speaker Name 6
Value Addedness
5% X (10 -0)
= RM 0.50
Important Notice
This GST Model is an initial proposal from the Tax
Review Panel
Any view expressed in the discussion paper is the
view of the Panel and does not represent the official
view of the Government
The Government reserves the right to change and/or
modify any part of this proposal
SAP AG 2002, Title of Presentation, Speaker Name 7
Where will GST impact?
Do you know what are the business processes areas
that GST will impact?
Do you know if your System is GST Compliant?
Do you know what it takes to implement GST in your
system?
How seamless is the integration with the existing
processes?
SAP AG 2002, Title of Presentation, Speaker Name 8
Business Process Areas where GST will Impact
Vendor invoicing and customer billing system in your system
The purchase of goods and services will give rise to GST input tax.
The sale of goods and services will give rise to GST output tax.
Payments and refunds of GST with the Kastam Diraja Malaysia
The supplier of the taxable goods or services is either eligible to
refund or liable for payment of GST tax
Reports and forms for routine filing and reporting
Subject to the requirements of the Kastam Diraja, your system will
need to provide the relevant reports and forms to support payments
and refunds, audits and regular submissions.
Changes in configuration arising from future changes in legislation
Future budget changes may likely to affect is likely to affect vendors,
customers, goods (material) and GST rates.
SAP AG 2002, Title of Presentation, Speaker Name 9
Business Process Areas where GST will Impact
Seeking refunds from Kastam DiRaja
Tax reports must be able to match eligible input tax credits
against taxable output tax
Bad Debts
GST paid for goods and services sold, but bills cannot be
collected.
Tax reports and invoices must support tax paid for customer
Business conducted in FTZs, ICDs, outside country, etc.
SAP AG 2002, Title of Presentation, Speaker Name 10
Where in your system will GST impact?
It will impact all major system areas:
Inventory
Purchase orders, Debit Notes
Sales Orders, Credit Notes
Accounts Receivable, Accounts Payable
General Ledger
Configure the relevant tax procedures, tax codes and
tax rates
Configured the relevant account determination for
GST postings
GST impact on existing forms
GST impact on existing reports
SAP AG 2002, Title of Presentation, Speaker Name 11
Transitional Issues Actions required NOW
All existing contracts extending beyond 1 January
2007 should be reviewed
The GST implications on all existing contracts should
be checked
The GST implications of new contracts entered into
from now until 1 January 2007 should be considered
Consider what further actions may be needed as a
result of the above, for example, contact a solicitor
SAP AG 2002, Title of Presentation, Speaker Name 12
Impact of not having a GST compliant system
All GST tax input and outputs forms and reports will
have to be manually generated
Risk of miscalculation, prone to errors
Strenuous and laborious task if the volume is high
Confidence of your customers and suppliers
More scrutiny from the relevant authorities e.g. IRD,
auditors
SAP AG 2002, Title of Presentation, Speaker Name 13
Some thots ….
…. Businesses that had the least problems with the GST
were those that used a computer package .…
…. Businesses that fared the worst relied on the show box
method or a system of their own design ….
…. The most common error relating to input tax credits
arose from not having a system in place to correctly record
the GST charged by suppliers …..
Excerpts from the article ‘Adjustment to GST keeps accountants on their
toes’
Max Newnham
July 15, 2002
The Age, Australia
SAP AG 2002, Title of Presentation, Speaker Name 15
Thank you
Copyright 2005 SAP AG. All Rights Reserved
No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or for any purpose without the express
permission of SAP AG. The information contained herein may be changed without prior notice.
Some software products marketed by SAP AG and its distributors contain proprietary software components of other
software vendors.
Microsoft, Windows, Outlook, and PowerPoint are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
IBM, DB2, DB2 Universal Database, OS/2, Parallel Sysplex, MVS/ESA, AIX, S/390, AS/400, OS/390, OS/400, iSeries,
pSeries, xSeries, zSeries, z/OS, AFP, Intelligent Miner, WebSphere, Netfinity, Tivoli, and Informix are trademarks or
registered trademarks of IBM Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation.
UNIX, X/Open, OSF/1, and Motif are registered trademarks of the Open Group.
Citrix, ICA, Program Neighborhood, MetaFrame, WinFrame, VideoFrame, and MultiWin are trademarks or registered
trademarks of Citrix Systems, Inc.
HTML, XML, XHTML and W3C are trademarks or registered trademarks of W3C®, World Wide Web Consortium,
Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Java is a registered trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc.
JavaScript is a registered trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc., used under license for technology invented and
implemented by Netscape.
MaxDB is a trademark of MySQL AB, Sweden.
SAP, R/3, mySAP, mySAP.com, xApps, xApp, SAP NetWeaver and other SAP products and services mentioned herein as
well as their respective logos are trademarks or registered trademarks of SAP AG in Germany and in several other
countries all over the world. All other product and service names mentioned are the trademarks of their respective
companies. Data contained in this document serves informational purposes only. National product specifications may vary.
These materials are subject to change without notice. These materials are provided by SAP AG and its affiliated
companies ("SAP Group") for informational purposes only, without representation or warranty of any kind, and SAP Group
shall not be liable for errors or omissions with respect to the materials. The only warranties for SAP Group products and
services are those that are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services, if any.
Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty.
SAP AG 2002, Title of Presentation, Speaker Name 17