Plan business requirements engineering activities
advertisement

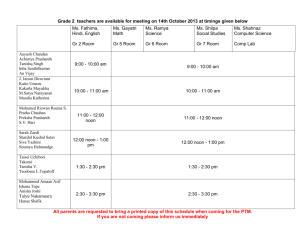
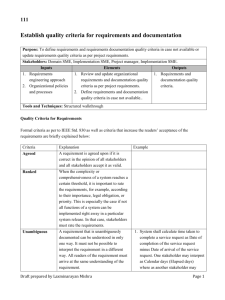
0401 1 Plan business requirements engineering activities Purpose: Determine business requirements engineering activities to be performed, deliverables to be produced, estimate effort, identify tools required to measure progress of those activities, and deliverables. Stakeholders: Sponsor, Customer, Domain SME, End users. Inputs Elements 1. Identified Stakeholders 1. Determine business requirements engineering 2. Business and system activities and deliverables. context 2. Develop estimates for business requirements 3. Past effort data on engineering work. business requirements activities Tools and Techniques: Functional decomposition. Outputs 1. Requirements engineering plan Consider location and time distribution of stakeholders, type of project or initiative while planning business requirements engineering activities. Prepare for eliciting business requirements Purpose: To ensure all needed resources are organized, and scheduled for conducting elicitation activities. Stakeholders: None. Inputs Elements Outputs 1. Identified key 1. Plan for key stakeholder interviews. 1. Resources needed for stakeholders. 2. Plan for business requirements interviews / workshops. workshop. 2. Updated Requirements 3. Send meeting invites. engineering activity plan. 4. Organize logistics for the meetings and workshop(s). 5. Establish ground rules for event-based elicitations. Tools and Techniques: Requirements engineering activity plan. Draft prepared by Laxminarayan Mishra Page 1 0401 2.3.2 Description Determine activities required for a given initiative, how those activities will be carried out, effort involved, and an estimate of how long the activities will take. 2.3.3 Inputs Business analysis performance assessment – Use prior experiences on this initiative or on others, to determine the effort involved in performing business analysis work. Elements Geographically distributed projects need more business requirements engineering effort compared to co-located projects. For geographically distributed projects, develop more detailed business requirements, detailed acceptance criteria, and more frequent review sessions. Work breakdown structure (WBS) is an important tool in defining the scope of work, and in developing estimates. WBS decomposes project scope into smaller, and smaller pieces, creating a hierarchy of deliverables. A WBS breaks down project into iterations, releases, or phases; breaks deliverables into work packages; or breaks activities into smaller tasks. Elements identified for each activity, and task include: Unique number Activity description Assumptions Dependencies Milestones To uniquely identify each task. Labelled with a verb, and a noun, and describing detailed tasks that comprise each activity. For example, an activity might be labelled as “Update business requirements document”. For each task, there may be factors or conditions which are considered to be true. Document these factors, and where present estimates will be developed using these assumptions. Identify logical relationships, such as which activities have to be completed before subsequent tasks can begin. Represent significant events in progress of a project, and are used to measure progress to earlier estimates. Milestones can be used as a time to celebrate completion, or delivery of a major deliverable or section of project work. An example of major milestone is stakeholders’, and sponsor’s formal approval of business requirements document. Draft prepared by Laxminarayan Mishra Page 2 0401 Stakeholders Domain SMEs are a major source of business requirements. Their availability is critical when planning business requirements engineering activities. Domain SMEs understandings of business requirements engineering techniques affect selection of business requirements engineering techniques. Assist Domain SMEs in understanding how business requirements are defined. Customers, and suppliers are difficult to schedule effectively. Business requirements engineering plan is integrated with, and is a component of the overall project plan. So the Project Manager should participate in business requirements engineering planning, Project Manager is responsible for ensuring that those plans are integrated with the work performed by other project personnel. Scope of business requirements engineering work within a project is managed as part of the overall project scope, and changes to the business requirements engineering scope of work, for example, as new stakeholders are identified or business requirements change, may require approval of a project scope change. Project Manager plays key role in identifying resources to perform tasks, scheduling activities, and developing cost estimates. Sponsor must participate in the approval of business requirements engineering deliverables. Real life example: Iteration 1 Stakeholder Name Designation Key Topics for Discussion Dave Richards CEO 1. KPIs and Dashboards. Mike Dent CDO Dinesh Pandey Head-PMO Lee Fung Head-IT Adi Gururaj Head-HR Iqbal Mohammed HeadAdministration 1. Non-functional business requirements 2. Project monitoring business requirements 3. Operational Dashboards. 1. Process compliance business requirements. 1. IT standards 2. Expectations from GRC system 1. Expectations from GRC system 1. Expectations from GRC system Pieter Bisemans Head-Sales 2. Expectations from GRC system John Munyan CFO and HeadLegal 3. Expectations from GRC system Draft prepared by Laxminarayan Mishra Target Date Status Page 3 0401 2 Peter Lily Shalini Paul Gajendra Battalla Nori Masa Rebecca Randad Delivery Managers 4. Project management business requirements Audit manager 5. Audit and compliance business requirements Susan Thomas Training manager 6. Training management business requirements Sara Lee Risk manager Jane Macrae Resourcing manager Surya T IT Manager 7. Enterprise risk management business requirements 8. Resource management group business requirements 9. IT resource management business requirements Description Build a detailed schedule for business requirements elicitation activity, defining specific activities, and planned dates. Understands what information should be elicited from stakeholders, and used when eliciting business requirements keeping business needs in mind. Establish ground rules for event-based elicitations (brainstorming, focus group, interview, observation, prototyping, requirements workshop). Real life example: Type of meeting Workshop Workshop Focus of workshop Stakeholder commitment Delivery Management Participants Dave Richards Mike Dent Dinesh Pandey Lee Fung Adi Gururaj Iqbal Mohammed Pieter Bisemans John Munyan Rebecca Randad Peter Lily Shalini Paul Gajendra Battalla Draft prepared by Laxminarayan Mishra Date Time 17-Mar 10:00 AM to 12:00 Noon 19-Mar 10:00 AM to 12:00 Noon Status Page 4 0401 Nori Masa Interview Audit management Rebecca Randad 21-Mar 10:00 AM to 12:00 Noon Interview Training manager Susan Thomas 22-Mar 10:00 AM to 12:00 Noon Interview Risk manager Sara Lee 23-Mar 10:00 AM to 12:00 Noon Interview Resourcing manager Jane Macrae 26-Mar 10:00 AM to 12:00 Noon Interview IT Manager Surya T 27-Mar 10:00 AM to 12:00 Noon Draft prepared by Laxminarayan Mishra Page 5