Rejuvenation Program - United States Power Squadrons
advertisement

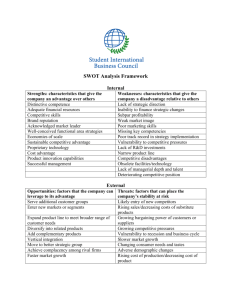
The Squadron Rejuvenation Program A Self-Directed Energizer STF/C Margaret Barber, SN How Do You Rejuvenate a Squadron? • The need must be real and recognized • The leadership has to be motivated and willing to address it • A strategic plan that fits your squadron must be developed • The leadership MUST stay focused on the plan • Everything you do should relate to the plan This is the path we want to take FUTURE STATE VISION This is where we are today STRATEGIC PLAN CURRENT STATE HERE THERE This is where we want to be tomorrow Strategic Planning • • • • • Mission Vision Analysis Goals / Outcomes Objectives Mission Statement A brief expression of the organization’s purpose It should answer the questions: – Why do we exist? – What, at the most basic level, do we do? Mission Statement To educate our members and the public to make our waterways safe, provide civic services to enhance our community and engage in fellowship opportunities to strengthen and enhance our relationships Vision Statement A description of the organization’s desired future state • It answers the question: – Where do we want to be? Vision Statement Be the Go-To-Boating Organization in our community to enhance safe boating in our area Goals Goals are expected or desired outcomes of a planning process Goals/Outcomes Focus on and increase our membership involvement and retention Objectives Precise targets are necessary to achieve the goals 2015 Goals and Objectives How do you get there from here? • There are tools and models that will guide you through the process • You can conduct the process in-house • That’s what we will look at today Before You Begin • Go back to your squadron and assess the viability of conducting a SWOT • Ask yourself and other leaders: – Can you find a champion (someone who will be in a position to support and follow through for several years?) – This is a long term project. It takes time to accomplish Before You Begin • Do you have people who will stick with the process? • Do you have the time and resources? If you answer yes to these questions, you are ready Now You Can Begin • Immediately start socializing the process • Get excited and be enthusiastic • Sell it to the people you want to be involved and recruit them for the effort • Tell them you attended the Annual USPS Meeting and learned a process that can help revitalize the squadron Facilitating an Effective SWOT Analysis Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats What is a SWOT Analysis? A tool that identifies the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of an organization Specifically, SWOT is a basic, straight-forward model that assesses what an organization can and cannot do as well as its potential opportunities and threats The Benefits of Conducting a SWOT • • • • • Simple to do Low cost Can be done quickly Collaborative Very productive Why Collaboration? • Allows all members of a group to participate • Shows the members that there are many points of view • Forces the group to verbalize the brutal realities • Promotes “Buy In” • Lays the foundation for future actions The Mindset for a Successful SWOT • Requires creative (right brain) thinking • Requires participants to think big and outside the box • Collects many ideas in a short time • There are NO bad ideas • Every idea and comment are valid and should be captured Role of the Facilitator • Should be a person with no vested interest in the outcomes • Should capture the ideas as offered by the participants on a flip chart that is in clear sight of everyone • Should keep the ground focused – right brain thinking only Role of the Facilitator • Remind Group that History is not important in this process • Solutions will be developed later, not now • A strength can also be a weakness • A threat can also be an opportunity The Participants The best groups are: • Demographically diverse • Have a wide range of experience, longevity, opinions and responsibilities within the organization • Newer members can introduce new thinking and ideas Grouping of Participants • Typically a small group (6-10) • If more than 10, split into smaller groups, each with their own table and flip chart • Two groups of 6 will develop twice as many ideas as a group of 12 • Make each small group diverse The Setting • Avoid a traditional setting • An off-site location works best in stimulating creative thinking • Avoid traditional seating arrangements for the safe reason The Materials • • • • Ensure that there are ample supplies Different color markers Chart stands Chart paper with adhesive backing (Post-itNote variety) • Or a roll of Painters Masking Tape (the blue, low adhesive type) The Process • Brainstorm a list for each area – strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats • Clarify the responses • Identify the top 3-5 responses for each area • Summarize the final results • Use the outcomes to develop an action plan Brainstorming Guidelines • • • • • Everyone participates 5 minutes to write down your thoughts Generate lots of responses No evaluation – that comes later Go around the group for one response at a time • Continue until ALL responses are captured Examples of Strenghts • • • • • • Leadership abilities Decision-making abilities Course materials Advertising Member participation Commitment Let’s Try Out the Process • Instead of using a fictitious squadron, let’s use the United States Power Squadrons • Everyone jot down all the strengths of USPS as quickly as you can • You have 5 minutes Examples of Weakness • • • • • • Leadership abilities Decision-making abilities Innovation Quality courses Quality instructors Lack of advertising Examples of Opportunities • • • • • • Additional partnerships Increased member involvement New courses Additional instructors On-the-water training Co-chairs for committees Examples of Threats • • • • • • Burn-out Economy Competition for time Many activity choices Declining membership Aging population Next Steps • Develop the organization’s Implementation Plan to achieve the desired goals • Objectives: – The steps that have to be accomplished to reach the goal (How?) Objectives • Expand our boating activities to reflect the variety of interests of our members • Activities include: – – – – Sailing Power Boating Kayaking Fishing • Have a new member town hall meeting each quarter • Have an open house with coffee and donuts and a program one Saturday each quarter Implementation / Action Plan • This is the organizational “user’s guide” to the strategic plan • It identifies the accountability, resources, time frames, check points and priority for each strategy and tactic • The implementation plan answers the questions: – What are our specific priorities? – How can we pursue our plan in a logical and feasible fashion? Implementation / Action Planning • The process that guides the day-to-day activities of an organization or project • It answers the questions: – What needs to be done? – When does it need to be done? – Who needs to do it? – What resources or inputs are needed to do it? • It is the process of operationalizing your strategic objective Implementation / Action Planning When you go through the action planning process, you end up with a practical plan to enable you to resource and carry forward the steps needed to achieve your objective/s and contribute to your long-term goal 4 Elements of an Implementation / Action Plan • Responsibility: – A clarification of who will be responsible for making sure that each step is successfully completed • Who / Department / Committee Chair • Time Frame: – Some kind of time schedule for when each step must take place and how long it is likely to take • When 4 Elements of an Implementation / Action Plan • Checkpoints: – Reporting points to keep on track or make adjustments • Accountability • Resources: – A clarification of the resources that are needed • Inputs Questions? Thank You for Participating