Symbiosis Lab: Examples & Relationships in Biology
advertisement

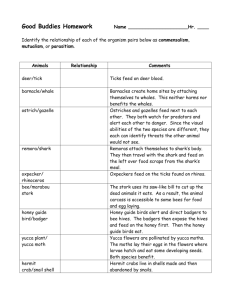
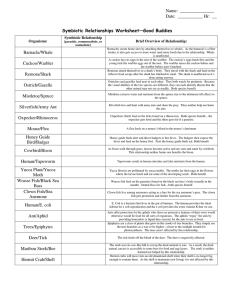
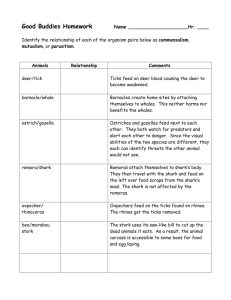
Symbiosis lab Station 1 Station 1 Athlete’s foot is a skin disease, usually starting between the toes or on the bottom of the feet, which can spread to other parts of the body. It is caused by a fungus that commonly attacks the feet, because the wearing of shoes and hosiery fosters fungus growth. The signs of athlete’s foot are dry scaly skin, itching, inflammation, and blister Station 2 Termite Termite intestinal track Protozan Station 2 Termites are nature's recyclers, breaking down and returning to the soil the cellulose containing materials of fallen trees and decaying wood. Termites derive nutrition from wood and other cellulose materials. They cannot digest the cellulose themselves. Instead they are dependent on one-celled protozoa in their stomachs that break down the cellulose into simpler compounds that the termites can use as food STATION 3 STATION 3 Once considered a parasite of southern climates, the heartworm (Dirofilaria immitis) is now recognized as a major, global pest affecting dogs, wolves, coyotes, and foxes. A mosquito serves as the intermediate host for the larval stage of the worm. Adult heartworms can reach 12 inches in length and can remain in the dog’s heart for several years. Female heartworms bear live young – thousands of them in a day. The worms grow and multiply, infesting the chambers on the right side of the heart and the arteries in the lungs. They can also lodge in the veins of the liver and the veins entering the heart. STATION 4 STATION 4 Epiphytes, or air plants, grow everywhere but can be found mainly on the branches, trunks, and even the leaves of trees. The name 'epiphyte' comes from the Greek word 'epi' meaning 'upon' and 'phyton' meaning 'plant'. Epiphytes grow on sides of tall trees in an attempt to be closer to the sunlight. They have no roots, and collect water and nutrients from the air. They begin their life in the canopy from seeds or spores transported there by birds or winds. STATION 5 Cerambycid beetle STATION 5 Pseudoscorpions are small, predaceous arthropods, mostly less than 1 centimeter is length. These scorpion like animals have pincers (chelicera) like scorpions, but lack a sting. Pseudoscorpions are common, but usually overlooked because of their small size and because they are concealed in the soil or under the bark of trees. A few species of pseudoscorpions disperse by concealing themselves under the wing covers (elyatra) of large beetles such as the cerambycid beetle. The pseudoscorpions gain the advantage of being dispersed over wide areas while simultaneously being protected from predators. The beetle is, presumably, unaffected by the presence of the hitchhikers. STATION 6 STATION 6 In many bee-pollinated flowers, there is a region of low ultraviolet reflectance near the center of each petal. This pattern is invisible to humans because our visual spectrum does not extend into the ultraviolet. Bees, however, can detect ultraviolet light. The contrasting ultraviolet pattern (called a nectar guide) helps a bee quickly locate the flower's center. This adaptation benefits both the flower (more efficient pollination) and the bee (rapid collection of nectar). Station 7 _____ barnacle/whale Barnacles create a home site by attaching themselves to whales. This neither harms nor benefits the whales. _____ mistletoe/spruce tree Mistletoe extracts water and nutrients from spruce tree to the tree’s detriment. _____ yucca plant/ yucca moth Yucca flowers are pollinated by yucca moths. The moths lay their eggs in the flowers where the larvae hatch and eat some of the developing seeds. Both species benefit. _____ hermit crab/ snail shell Hermit crabs live in shells made and then abandoned by snails. This neither harms nor benefits the snails. _____ cowbird/ buffalo As buffalos walk through grass, insect become active And are seen and eaten by cowbirds. This neither harms nor benefits the snails. Station 8 _____ mouse/ flea A flea feeds on a mouse’s blood to the mouse’s detriment. _____ wrasse fish/ black sea bass Wrasse fish feed on the parasites found on the black sea bass’s body. Bothe species benefit. _____ deer/ tick ticks feed on deer blood to the deer’s detriment. _____ cuckoo/warbler A cuckoo may lay eggs in a warbler’s nest. The cuckoo’s Young will displace the warbler’s young and will be raised by the wa Station 9 _____ honey guide bird/ badger Honey guide birds alert and direct badgers to be bee hives. The badgers then expose the hives and feed on the honey first. Then the honey guide birds eat. Both species benefit. _____ hookworms/ humans Hookworms enter the human body by burrowing into the skin of feet. Once in the skin they enter the bloodstream and travel to the small intestine where they attach to the walls and begin to drink the person’s blood and weaken the victim. _____ kapoc trees/ orchids Types of orchids grow high on branches of tall Kapok trees of the jungle. This adaptation allows the orchid to receive enough sunlight to perform its photosynthesis but the kapok tree is unaffected. _____lichen algae/lichen fungus Lichens are close associations of fungi and algae. The fungi hold the water supply and the algae perform photosynthesis and manufacture the carbohydrates for both. Station 10 _____ acacia tree/ants In the jungle of South America live a thorn tree called an acacia. A species of ant eat secretions of the acacia, drink its sap, and raise its young in the hollow thorns. The ants also keep competing vines from growing near the acacia tree and they help repel any insects that would damage the acacia tree. _____ moose / tapeworm In the flesh of the moose are cysts (dormant stage) of a worm that makes the muscles of the moose stiff and sore. If the moose is killed and eaten raw, the predator species will develop a form of tapeworm. _____ lactobacilli/ humans Lactobacilli are a type of bacteria that live in our lungs and destroy many microorganisms that enter our respiratory system. They are highly adapted to living in our lungs and can’t survive in many other habitats. _____ soybeans/ bacteria Soybeans require nitrogen from their environment. This nitrogen is provided by bacteria that live in special root nodules. In return, the bacteria receive some of the sugar (carbohydrate) manufactured by the soybeans. Station 11 Choose the correct answer 1. 2. Station 12 In the graph above the predator line is _____________ (color) and the prey line is __________(color).