The Geosphere
advertisement

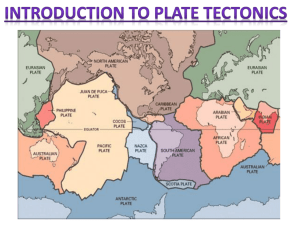
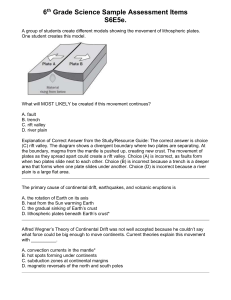
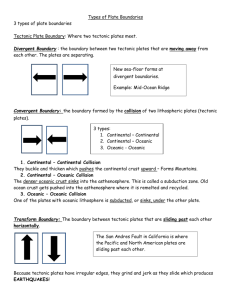
What is the GEOSPHERE? All solid parts of Earth Rocks, soils, minerals, sediments, magma The Grand Canyon, AZ What are the layers of the Earth? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v =WwiiOjyfvAU Layers of the Earth • Geologists classify Earth’s layers two ways: chemically and physically • Chemical – by composition • Physical- by structure Chemical Layers of the Earth 1. Crust- O, Si, Al 2. Mantle- O, Si, Mg, Fe 3. Core- Fe, Ni Physical Layers of the Earth • Lithosphere – Crust and upper mantle combined – Broken in chunks called tectonic plates – Oceanic plates are thinner and denser than continental plates • Asthenosphere - Layer of Jello-like magma in the mantle - Tectonic plates move due to convection currents in the asthenosphere Physical Layers, cont. Mesosphere The rest of the mantle; molten rock Outer Core Liquid metal Surrounds inner core Inner Core Densest layer Solid metal Theory of Plate Tectonics Lithosphere (upper mantle and crust) is divided into pieces called tectonic plates. These plates glide across the underlying asthenosphere like ice drifts across a pond. Continents are located on tectonic plates and move around with them Seafloor Spreading 1. Magma rises from asthenosphere 2. Creates new oceanic lithosphere 3. Pushes tectonic plates apart Seafloor-Spreading If new crust is being created by the process of seafloor spreading, is the Earth growing!? Subduction Subduction zones: A region where old crust is destroyed as it is pulled back down into the mantle Plate Boundaries The area where two plates meet is called a plate boundary. Most earthquakes and volcanoes occur at or near plate boundaries Three main types of plate boundaries: 1. Divergent- separating 2. Convergent- colliding 3. Transform- scraping past Transform Boundaries • 2 plates slide past each other • Not smooth. Plates lock, and build up tension. After too much tension builds, the plates “snap” causing earthquakes Divergent Boundaries • When two plates separate • Most common on ocean floor • Creates Mid-Ocean Ridge Divergence Forms New Ocean Floor Convergent Boundaries Three Main Types: 1. Continental & Oceanic- causes deep ocean trench and land volcanoes Ex: Andes Mountains 2. Continental & Continental- causes large land mountain ranges Ex: Himalayan Mountains 3. Oceanic & Oceanic- causes deep ocean trench and island arc (chain of volcanic mountains) Ex: Mariana trench and islands Subduction Zone Continental + Oceanic Crust Continental + Continental Crust Subduction Zone Oceanic + Oceanic Crust (another view) Subduction Zone Oceanic + Oceanic Crust Some videos for your viewing pleasure… Plate Movement: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kwfNGatxUJI http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ryrXAGY1dmE&feature=e ndscreen&NR=1 San Andreas Fault: http://www.youtube.com/watch?NR=1&v=ZxPTLmg0ZCw&feature=endscr een Exit Ticket 1. Arrows in the block diagram below show the relative movement along a tectonic plate boundary. What is this type of plate boundary called? a. b. c. d. transform plate boundary convergent plate boundary divergent plate boundary subduction plate boundary Exit Ticket 2. When two tectonic plates collide, oceanic crust usually subducts beneath continental crust because oceanic crust is primarily composed of igneous rock that is: a. b. c. d. thin and less dense thick and less dense thin and more dense thick and more dense Exit Ticket 3. The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. Which type of plate boundary is shown? a. divergent b. transform c. convergent d. complex Exit Ticket 4. The Himalaya Mountains were formed in a collision at a: a. divergent boundary b. convergent boundary c. transform boundary d. fracture zone Exit Ticket 5. In which Earth layer are most convection currents that cause seafloor spreading thought to be located? a. b. c. d. crust outer core asthenosphere inner core Tectonic Plates Active Volcanoes Earthquakes Worldwide